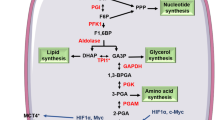
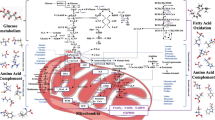
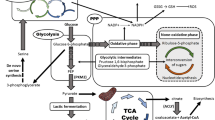
Abstract
Pyruvate kinase (PK) catalyzes the last irreversible reaction of glycolysis pathway, generating pyruvate and ATP, from Phosphoenol Pyruvate (PEP) and ADP precursors. In mammals, four different tissue-specific isoforms (M1, M2, L and R) of PK exist, which are translated from two genes (PKL and PKR). PKM2 is the highly expressed isoform of PK in cancers, which regulates the aerobic glycolysis via reprogramming cancer cell’s metabolic pathways to provide an anabolic advantage to the tumor cells. In addition to the established role of PKM2 in aerobic glycolysis of multiple cancer types, various recent findings have highlighted the non-metabolic functions of PKM2 in brain tumor development. Nuclear PKM2 acts as a co-activator and directly regulates gene transcription. PKM2 dependent transactivation of various oncogenic genes is instrumental in the progression and aggressiveness of Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM). Also, PKM2 acts as a protein kinase in histone modification which regulates gene expression and tumorigenesis. Ongoing research has explored novel regulatory mechanisms of PKM2 and its association in GBM progression. This review enlists and summarizes the metabolic and non-metabolic roles of PKM2 at the cellular level, and its regulatory function highlights the importance of the nuclear functions of PKM2 in GBM progression, and an emerging role of PKM2 as novel cancer therapeutics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnihotri S, Zadeh G (2016) Metabolic reprogramming in glioblastoma: the influence of cancer metabolism on epigenetics and unanswered questions. Neuro-Oncology 18:160–172. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nov125
Allen AE, Locasale JW (2018) Glucose metabolism in Cancer: the Saga of pyruvate kinase continues. Cancer Cell 33:337–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.02.008
Altenberg B, Greulich KO (2004) Genes of glycolysis are ubiquitously overexpressed in 24 cancer classes. Genomics. 84:1014–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2004.08.010
Amin S, Yang P, Li Z (2019) Pyruvate kinase M2: a multifarious enzyme in non-canonical localization to promote cancer progression. BBA - Rev Cancer 1871:331–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.02.003
Anastasiou D, Poulogiannis G, Asara JM, Boxer MB, Jiang JK, Shen M, Bellinger G, Sasaki AT, Locasale JW, Auld DS, Thomas CJ, Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC (2011) Inhibition of pyruvate kinase M2 by reactive oxygen species contributes to cellular antioxidant responses. Science 334:1278–1283. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1211485
Ashizawa K, Willingham MC, Liang CM, Cheng SY (1991) In vivo regulation of monomer-tetramer conversion of pyruvate kinase subtype M2 by glucose is mediated via fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem 266:16842–16846
Azoitei N, Becher A, Steinestel K, Rouhi A, Diepold K, Genze F, Simmet T, Seufferlein T (2016) PKM2 promotes tumor angiogenesis by regulating HIF-1α through NF-κB activation. Mol Cancer 15:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0490-2
Bailleul J, Yazal T, Sung D, Dao A, Palomera D, Sehgal A, Vlashi E (2019) Irradiation reprograms GBM metabolism towards an antioxidant profile that drives radiation resistance. Int J Radiat Oncol 105:165–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.06.189
Barbarulo A, Iansante V, Chaidos A, Naresh K, Rahemtulla A, Franzoso G, Karadimitris A, Haskard DO, Papa S, Bubici C (2013) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase family member 14 (PARP14) is a novel effector of the JNK2-dependent pro-survival signal in multiple myeloma. Oncogene. 32:4231–4242. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.448
Beinat C, Patel CB, Xie Y, Gambhir SS (2019) Evaluation of glycolytic response to multiple classes of anti-glioblastoma drugs by noninvasive measurement of pyruvate kinase M2 using [18F]DASA-23. Mol Imaging Biol 22:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-019-01353-2
Bhardwaj A, Das S (2016) Sirt6, sirtuin family member deacetylase PKM2 at the lysine 433 residue and results in PKM2 nuclear export via specific exportin 4. As a result of this PKM2 nuclear export, PKM2 nuclear functions are abolished such as protein kinase and transactivation function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:E538–E547. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1520045113
Chaneton B, Gottlieb E (2012) Rocking cell metabolism: revised functions of the key glycolytic regulator PKM2 in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci 37:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2012.04.003
Cholia RP, Dhiman M, Kumar R, Mantha AK (2018) Oxidative stress stimulates invasive potential in rat C6 and human U-87 MG glioblastoma cells via activation and cross-talk between PKM2, ENPP2 and APE1 enzymes. Metab Brain Dis 33:1307–1326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0233-3
Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Wu N, Asara JM, CantleyLC (2008a) Pyruvate kinase M2 is a phosphotyrosine-binding protein. Nature 452:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06667
Christofk HR, Heiden MGV, Harris MH, Ramanathan A, Gerszten RE, Wei R, Fleming MD, Schreiber SL, Cantley LC (2008b) The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature. 452:230–233. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06734
DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G, Thompson CB (2008a) The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab 7:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2007.10.002
Deberardinis RJ, Sayed N, Ditsworth D, Thompson CB (2008b) Brick by brick: metabolism and tumor cell growth. Curr Opin genet Dev 18:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2008.02.003
Dombrauckas JD, Santarsiero BD, Mesecar AD (2005) Structural basis for tumor pyruvate kinase M2 allosteric regulation and catalysis. Biochemistry 44:9417–9429. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0474923
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, Chin L, DePinho RA, Cavenee WK (2007) Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev 21:2683–2710. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1596707
Gao X, Wang H, Jenny JY, Liu X, Liu XR (2012) Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates gene transcription by acting as a protein kinase. Mol Cell 45:598–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.01.001
Gao X, Wang H, Yang JJ, Chen J, Jie J, Li L, Zhang Y, Liu ZR (2013) Reciprocal regulation of protein kinase and pyruvate kinase activities of pyruvate kinase M2 by growth signals. J Biol Chem 288:15971–15979. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.448753
Gladitz J, Klink B, Seifert M (2018) Network-based analysis of oligodendrogliomas predicts novel cancer gene candidates within the region of the 1p/19q co-deletion. Acta Neuropathol Commun 6:49. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-018-0544-y
Gladson CL, Prayson RA, Liu W (2010) The pathobiology of Glioma tumors. Annu Rev Pathol 5:33–50 5:33–50. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-121808-102109
Goldberg MS, Sharp PA (2012) Pyruvate kinase M2-specific siRNA induces apoptosis and tumor regression. J Exp Med 209:217–224. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20111487
Gruning NM, Rinnerthaler M, Bluemlein K, Mulleder M, Wamelink MMC, Lehrach H, Jakobs C, Breitenbach M, Ralser M (2011) Pyruvate kinase triggers a metabolic feedback loop that controls redox metabolism in respiring cells. Cell Metab 14:415–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.06.017
Guo J, Xue Q, Liu K, Ge W, Liu W, Wang J, Zhang M, Li Q, Cai D, Shan C, Zhang C, Liu X, Li J (2019) Dimethylaminomicheliolide (DMAMCL) suppresses the proliferation of Glioblastoma cells via targeting pyruvate kinase 2 (PKM2) and rewiring aerobic glycolysis. Front Oncol 9:993. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00993
Hacker HJ, Steinberg P, Bannasch P (1998) Pyruvate kinase isoenzyme shift from L-type to M2-type is a late event in hepatocarcinogenesis induced in rats by a cholinedeficient/DL-ethionine-supplemented diet. Carcinogenesis. 19:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/19.1.99
Han B, Meng X, Chen H, Chen L, Liu X, Wang H, Liu D, Gao F, Lin L, Ming J, Sun B, Yin S, Wang R, Wu P, Cai J, Jiang C (2017) Epigenetic silencing of miR-338 facilitates glioblastoma progression by de-repressing the pyruvate kinase M2-β-catenin axis. Aging (Albany NY) 9:1885-1897. Doi: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101271
Harada K, Saheki S, Wada K, Tanaka T (1978) Purification of four pyruvate kinase isozymes of rats by affinity elution chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta 524:327–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2744(78)90169-9
Hatchell H (2017) The relationship between docohexanoic acid (DHA) and L-serine, providing an insight into the biochemistry of meningioma. Thesis, University of Central Lancashire
Haumann R, Videira JC, Kaspers GJL, Vuurden DGV, Hulleman E (2020) Overview of current drug delivery methods across the blood–brain barrier for the treatment of primary brain tumors. CNS Drugs 34:1121–1131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-020-00766-w
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M (1997) Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 387:296–299. https://doi.org/10.1038/387296a0
Hitosugi T, Kang S, Vander Heiden MG, Chung TW, Elf S, Lythgoe K, Lonial S, Wang X, Chen GZ, Xie J, Gu TL, Polakiewicz RD, Roesel JL, Boggon TJ, Khuri FR, Gilliland DG, Cantley LC, Kaufman J, Chen J (2009) Tyrosine phosphorylation inhibits PKM2 to promote the Warburg effect and tumor growth. Sci Signal 2(97):ra73. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2000431
Hitosugi T, Zhou L, Fan J, Elf S, Zhang L, Xie J, Wang Y, Gu TL, Aleckovic M, LeRoy G, Kang Y, Kang HB, Seo JH, Shan C, Jin P, Gong W, Lonial S, Arellano ML, Khoury HJ, Chen GZ, Shin DM, Khuri FR, Boggon TJ, Kang S, He C, Chen J (2013) Tyr26 phosphorylation of PGAM1 provides a metabolic advantage to tumours by stabilizing the active conformation. Nat Commun 4:1790. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2759
Huang L, Yu Z, Zhang T, Zhao X, Huang G (2014) HSP40 interacts with pyruvate kinase M2 and regulates glycolysis and cell proliferation in tumor cells. PLoS One 9(3):e92949. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092949
Iansante V, Choy PM, Fung SW, Liu Y, Chai JG, Dyson J, Del Rio A, D'Santos C, Williams R, Chokshi S, Anders RA, Bubici C, Papa S (2015) PARP14 promotes the Warburg effect in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting JNK1-dependent PKM2 phosphorylation and activation. NatCommun 6:7882. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8882
Israelsen WJ, Heiden MGV (2015) Pyruvate kinase: function, regulation and role in cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol 43:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.08.004
Jiang X, Sun Q, Li H, Li K, Ren X (2014a) The role of phosphoglycerate mutase 1 in tumor aerobic glycolysis and its potential therapeutic implications. Int J Cancer 135:1991–1996. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28637
Jiang Y, Li X, Yang W, Hawke DH, Zheng Y, Xia Y, Aldape K, Wei C, Guo F, Chen Y, Lu Z (2014b) PKM2 regulates chromosome segregation and mitosis progression of tumor cells. Mol Cell 53:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2013.11.001
Jiang Y, Wang Y, Wang T, Hawke DH, Yanhua LX, Zhou Q, Majumder S, Bi E, Liu DX, Huang S, Lu Z (2014c) PKM2 phosphorylates MLC2 and regulates cytokinesis of tumor cells. Nat Commun 5:5566. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6566
Jiang X, Baucom C, Elliott RL (2019) Mitochondrial toxicity of azithromycin results in aerobic glycolysis and DNA damage of human mammary epithelia and fibroblasts. Antibiot (Basel) 8(3):Pii: E110. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030110
Keller KE, Tan IS, Lee YS (2012) SAICAR stimulates pyruvate kinase isoform M2 and promotes Cancer cell survival in glucose -limited conditions. Science. 338:1069–1072. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1224409
Kumar S, Barth A (2010) Phosphoenolpyruvate and Mg2+ binding to pyruvate kinase monitored by infrared spectroscopy. Biophys J 98:1931–1940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2009.12.4335
Li N, Feng L, Liu H, Wang J, Kasembeli M, Tran MK, Tweardy DJ, Lin SH, Chen J (2016) PARP inhibition suppresses growth of EGFR-mutant cancers by targeting nuclear PKM2. Cell Rep 15:843–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.070
Li Y, He ZC, Liu Q, Zhou K, Shil Y, Yao XH, Zhang X, Kung FH, Bian XW, Ping YF (2018) Large Intergenic non-coding RNA-RoR inhibits aerobic glycolysis of Glioblastoma cells via Akt pathway. J Cancer 9:880–889. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.20869
Liang J, Cao R, Zhang Y, Xia Y, Zheng Y, Li X, Wang L, Yang W, Lu Z (2016) PKM2 dephosphorylation by Cdc25A promotes the Warburg effect and tumorigenesis. NatCommun 7:12431. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12431
Liang J, Cao R, Wang X, Zhang Y, Wang P, Gao H, Li C, Yang F, Zeng R, Wei P, Li D, Li W, Yang W (2017) Mitochondrial PKM2 regulates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis by stabilizing Bcl2. Cell Res 27:329–351. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.159
Liu VM, Vander Heiden MG (2015) The role of pyruvate kinase M2 in Cancer metabolism. Brain Pathol 25:781–783. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12311
Liu K, Li F, Han H, Chen Y, Mao Z, Luo J, Zhao Y, Zheng B, Gu W, Zhao W (2016) Parkin regulates the activity of pyruvate kinase M2. J Biol Chem 291:10307–10317. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.703066
Liu F, Ma F, Wang Y, Hao L, Zeng H, Jia C, Wang Y, Liu P, Ong IM, Li B, Chen G, Jiang J, Gong S, Li L, Xu W (2017) PKM2 methylation by CARM1 activates aerobic glycolysis to promote tumorigenesis. Nat Cell Biol 19:1358–1370. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3630
Liu T, Li S, Wu L, Yu Q, Li J, Feng J, Zhang J, Chen J, Zhou Y, Ji J, Chen K, Mao Y, Wang F, Dai W, Fan X, Wu J, Guo C (2020) Experimental study of hepatocellular carcinoma treatment by Shikonin through regulating PKM2. J Hepatocell Carcinoma 7:19–31. https://doi.org/10.2147/JHC.S237614
Lu Z (2012) Nonmetabolic functions of pyruvate kinase isoform M2 in controlling cell cycle progression and tumorigenesis. Chin J Cancer 31:5–7. https://doi.org/10.5732/cjc.011.10446
Lu Z, Hunter T (2014) Prolylisomerase pin-1 cancer. Cell Res 24:1033–1049. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2014.109
Lu Y, Liu X, Zhang E, Kopras EJ, Smith EP, Astreinidis A, Li C, Leung YK, Ho SM, Yu JJ (2020) Estrogen activates pyruvate kinase M2 and increases the growth of TSC2-deficient cells. PLoS One 15:e0228894. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228894
Lunt SY, Muralidhar V, Hosios AM, Israelsen WJ, Gui DY, Newhouse L, Ogrodzinski M, Hecht V, Xu K, Acevedo PN, Hollern DP, Bellinger G, Dayton TL, Christen S, Elia I, Dinh AT, Stephanopoulos G, Manalis SR, Yaffe MB, Andrechek ER, Fendt SM, Vander Heiden MG (2015) Pyruvate kinase isoform expression alters nucleotide synthesis to impact cell proliferation. Mol Cell 57:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.10.027
Luo W, Hu H, Chang R, Zhong J, Knabel M, O'Meally R, Cole RN, Pandey A, Semenza GL (2011) Pyruvate kinase M2 is a PHD3-stimulated coactivator for hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell 145:732–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.054
Lv L, Xu YP, Zhao D, Li FL, Wang W, Sasaki N, Jiang Y, Zhou X, Li TT, Guan KL, Lei QY, Xiong Y (2013) Mitogenic and oncogenic stimulation of K433 acetylation promotes PKM2 protein kinase activity and nuclear localization. Mol Cell 52:340–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2013.09.004
Mack SC, Agnihotri S, Bertrand KC, Wang X, Shih DJ, Witt H, Hill N, Zayne K, Barszczyk M, Ramaswamy V, Remke M, Thompson Y, Ryzhova M, Massimi L, Grajkowska W, Lach B, Gupta N, Weiss WA, Guha A, Hawkins C, Croul S, Rutka JT, Pfister SM, Korshunov A, Pekmezci M, Tihan T, Philips JJ, Jabado N, Zadeh G, Taylor MD (2015) Spinal MyxopapillaryEpendymomas demonstrate a Warburg phenotype. Clin Cancer Res 21:3750–3758. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2650
Magno LD, Manzi D, D’Amico D, Coni S, Macone A, Infante P, Marcotullio LD, Smaele ED, Ferretti E, Screpanti I, Agostinelli E, Gulino A, Canettieri G (2014) Druggable glycolytic requirement for hedgehog-dependent neuronal and medulloblastoma growth. Cell Cycle 13(21):3404–3413. https://doi.org/10.4161/15384101.2014.952973
Majumder PK, Febbo PG, Bikoff R, Berger R, Xue Q, McMahon LM, Manola J, Brugarolas J, McDonnel TJ, Golub TR, Loda M, Lane HA, Seller WR (2004) mTOR inhibition reverses Aktdependent prostate intraepithelial neoplasia through regulation of apoptotic and HIF-1-dependent pathways. Nat Med 10:594–601. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1052
Marie SKN, Shinjo SMO (2011) Metabolism and brain Cancer. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 66:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1807-59322011001300005
Mazurek S (2011) Pyruvate kinase type M2: a key regulator of the metabolic budget system in tumor cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:969–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2010.02.005
Morfouace M, Lalier L, Oliver L, Cheray M, Pecqueur C, Cartron PF, Vallette FM (2014) Control of glioma cell death and differentiation by PKM2-Oct4 interaction. Cell Death Dis 5(1):e1036. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.561
Morita M, Sato T, Nomura M, Sakamoto Y, InoueY TR, Ito S, Kurosawa K, Yamaguchi K, Sugiura Y, Takizaki H, Yamashita Y, Katakura R, Sato I, Kawai M, Okada Y, Watanabe H, Kondoh G, Matsumoto S, Kishimoto A, Obata M, Matsumoto M, Fukuhara T, Motohashi H, Suematsu M, Komatsu M, Nakayama KI, Watanabe T, Soga T, Shima H, Maemondo M, Tanuma N (2018) PKM1 confers metabolic advantages and promotes cell-autonomous tumor cell growth. Cancer Cell 33:355–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.02.004
Mukherjee J, Phillips JJ, Zheng S, Wiencke J, Ronen SM, Pieper RO (2013) Pyruvate kinase M2 expression, but not pyruvate kinase activity, is up-regulated in a grade-specific manner in human glioma. PLoS One 8(2):e57610. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057610
Mukherjee J, Ohba S, See WL, Phillips JJ, Molinaro AM, Pieper RO (2016) PKM2 uses control of HuR localization to regulate p27 and cell cycle progression in human glioblastoma cells. Int J Cancer 139:99–111. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30041
Ni W, Xia Y, Luo L, Wen F, Hu D, Bi Y, Qi J (2019) High expression of ALDH1A3 might independently influence poor progression free and overall survival in patients with glioma via maintaining glucose uptake and lactate production. Cell Biol Int 44:569–582. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11257
Nie S, Qian X, Shi M, Li H, Peng C, Ding X, Zhang S, Zhang B, Xu G, Lv Y, Wang L, Friess H, Kong B, Zou X, Shen S (2020) ALDH1A3 accelerates pancreatic Cancer metastasis by promoting glucose metabolism. Front Oncol 10:915. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00915
Noguchi T, Yamada K, Inoue H, Matsuda T, Tanaka T (1987) The L- and R-type isozymes of rat pyruvate kinase are produced from a single gene by use of different promoters. J Biol Chem 262:14366–14371
Omuro A, DeAngelis LM (2013) Glioblastoma and other malignant gliomas: a clinical review. JAMA 310:1842–1850. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.280319
Ozaki T, Nakagawara A (2011) Role of p53 in cell death and human cancers. Cancers (Basel) 3:994–1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers3010994
Pan C, Wang X, Shi K, Zheng Y, Li J, Chen Y, Jin L, Pan Z (2016) MiR-122 reverses the doxorubicin-resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through regulating the tumor metabolism. PLoS One 11:e0152090. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0152090
Pan Y, Wang W, Huang S, Ni W, Wei Z, Cao Y, Yu S, Jia Q, Wu Y, Chai C, Zheng Q, Zhang L, Wang A, Sun Z, Huang S, Wang S, Chen W, Lu W (2019) Beta-elemene inhibits breast cancer metastasis through blocking pyruvate kinase M2 dimerization and nuclear translocation. J Cell Mol Med 23:6846–6858. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14568
Panasyuk G, Espeillac C, Chauvin C, Pradelli LA, Horie Y, Suzuki A, Annicotte JS, Fajas L, Foretz M, Verdeguer F, Pontoglio M, Ferré P, Scoazec JY, Birnbaum MJ, Ricci JE, Pende M (2012) PPARγ contributes to PKM2 and HK2 expression in fatty liver. Nat Commun 3:672. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1667
Prakasam G, Iqbal MA, Bamezai RNK, Mazurek S (2018) Posttranslational modifications of pyruvate kinase M2: tweaks that benefit Cancer. FrontOncol 8:22. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00022
Presek P, Glossmann H, Eigenbrodt E, Schoner W, Rubsamen H, Friis RR, Bauer H (1980) Similarities between a phosphoprotein (pp60src) associated protein kinase of rous sarcoma virus and cyclic adenosine 3′-5′-monophosphate-independent protein kinase that phosphorylates pyruvate kinase type M2. Cancer Res 40:1733–1741
Reinacher M, Eigenbrodt E (1981) Immunohistological demonstration of the same type of pyruvate kinase isoenzyme (M2-Pk) in tumors of chicken and rat. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol 37:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02892557
Reinacher M, Eigenbrodt E, Schering B, Schoner W (1979) Immunohistochemical localization of pyruvate kinase isoenzymes in chicken tissues. Histochemistry 64:145–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00490095
Rose IA (1970) Stereochemistry of pyruvate kinase, pyruvate carboxylase, and malate enzyme reactions. J Biol Chem 245:6052–6056
Seeholzer SH, Jaworowski A, Rose IA (1991) Enolpyruvate: chemical determination as a pyruvate kinase intermediate. Biochemistry. 30:727–732. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00217a022
Singh NS, Bernier M, Wainer IW (2016) Selective GPR55 antagonism reduces chemoresistance in cancer cells. Pharmacol Res 111:757–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.07.013
Sizemore ST, Zhang M, Cho JH, Sizemore GM, Hurwitz B, Kaur B, Lehman NL, Ostrowski MC, Robe PA, Miao W, Wang Y, Chakravarti A, Xia F (2018) Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates homologous recombination-mediated DNA double-strand break repair. Cell Res 28:1090–1102. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0086-7
Steinberg P, Klingelhoffer A, Schafer A, Wust G, Weisse G, Oesch F (1999) Expression of pyruvate kinase M2 in preneoplastic hepatic foci of N-nitrosomorpholinetreated rats. Virchows Arch 434:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004280050330
Sun K, Tang S, Hou Y, Xi L, Chen Y, Yin J, Peng M, Zhao M, Cui X, Liu M (2019) Oxidized ATM-mediated glycolysis enhancement in breast cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to tumor invasion through lactate as metabolic coupling. EBioMedicine 41:370–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.02.025
Suzuki A, Puri S, Leland P, Puri A, Moudgil T, Fox BA, Puri RK, Joshi BH (2019) Subcellular compartmentalization of PKM2 identifies anti-PKM2 therapy response in vitro and in vivo mouse model of human non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One 14:e0217131. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217131
Tamada M, Nagano O, Tateyama S, Ohmura M, Yae T, Ishimoto T, Sugihara E, Onishi N, Yamamoto T, Yanagawa H, Suematsu M, Saya H (2012) Modulation of glucose metabolism by CD44 contributes to antioxidant status and drug resistance in cancer cells. Cancer Res 72:1438–1448. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3024
Tennant DA, Durán RV, Gottlieb E (2010) Targeting metabolic transformation for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 10:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2817
Vander HMG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB (2009) Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1160809
Veelen CWV, Staal GE, Verbiest H, Vlug AM (1977) Alanine inhibition of pyruvate kinase in gliomas and meningiomas. A diagnostic tool in surgery for gliomas? Lancet 2:384–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90308-7
Venneti S, Thompson CB (2013) Metabolic modulation of epigenetics in gliomas. Brain Pathol 23:217–221. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12022
Wang HJ, Hsieh YJ, Cheng WC, Lin CP, Lin YS, Yang SF, Chen CC, Izumiya Y, Yu JS, Kung HJ, Wang WC (2014) JMJD5 regulates PKM2 nuclear translocation and reprograms HIF-1α–mediated glucose metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:279–284
Wang X, Zhang F, Wu X (2017a) Inhibition of pyruvate kinase M2 markedly reduces Chemoresistance of advanced bladder Cancer to Cisplatin. Sci Rep 7:45983. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45983
Wang Y, Liu J, Jin X, Zhang D, Li D, Hao F, Feng Y, Gu S, Meng F, Tian M, Zheng Y, Xin L, Zhang X, Han X, Aravind L, Wei M (2017b) O-GlcNAcylation destabilizes the active tetrameric PKM2 to promote the Warburg effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:13732–13737. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1704145115
Warburg O (1956a) On respiratory impairment in cancer cells. Science. 124:269–270
Warburg O (1956b) On the origin of cancer cells. Science 123, 309–314. Science.123:309–314. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.123.3191.309
Ward PS, Thompson CB (2012) Metabolic reprogramming: a Cancer Hallmark even Warburg did not anticipate. Cancer Cell 21:297–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.014
Wiese EK, Hitosug T (2018) Tyrosine kinase signaling in Cancer metabolism: PKM2 paradox in the Warburg effect. Front Cell Dev Biol 6:79. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2018.00079
Wong N, Melo JD, Tang D (2013) PKM2, a central point of regulation in Cancer metabolism. Int J Cell Biol 2013:242513–242511. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/242513
Wong N, Ojo D, Yan J, Tang D (2015) PKM2 contributes to cancer metabolism. Cancer Lett 356:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.01.031
Wu S, Le H (2013) Dual roles of PKM2 in cancer metabolism. ActaBiochimBiophys Sin (Shanghai) 45:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gms106
Xia L, Wang XR, Wang XL, Liu SH, Ding XW, Chen GQ, Lu Y (2016) A novel role for pyruvate kinase M2 as a Corepressor for P53 during the DNA damage response in human tumor cells. J Biol Chem 291:26138–26150. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.737056
Xu Q, Tu J, Dou C, Zhang J, Yang L, Liu X, Lei K, Liu Z, Wang Y, Li L, Bao H, Wang J, Tu K (2017) HSP90 promotes cell glycolysis, proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by regulating PKM2 abundance via Thr-328 phosphorylation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer 16:178. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0748-y
Yamada K, Noguchi T (1999) Regulation of pyruvate kinase M gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 256:257–262. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1999.0228
Yan H, Bigner DD, Velculescu V, Parsons DW (2009) Mutant metabolic enzymes are at the origin of gliomas. Cancer Res 69:9157–9159. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2650
Yan M, Chakravarthy S, Tokuda JM, Pollack L, Bowman GD, Lee YS (2016) SAICAR activates PKM2 in its dimeric form. Biochemistry. 55:4731–4736. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00658
Yang W, Lu Z (2013) Nuclear PKM2 regulates the Warburg effect. Cell Cycle 12:3154–3158. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.26182
Yang W, Xia Y, Ji H, Zheng Y, Liang J, Huang W, Gao X, Aldape K, Lu Z (2011) Nuclear PKM2 regulates β-catenin transactivation upon EGFR activation. Nature 480:118–122. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10598
Yang W, Xia Y, Cao Y, Zheng Y, Bu W, Zhang L, You MJ, Koh MY, Cote G, Aldape K, Li Y, Verma IM, Chiao PJ, Lu Z (2012a) EGFR-induced and PKCεmonoubiquitylation-dependent NF-κB activation upregulates PKM2 expression and promotes tumorigenesis. Mol Cell 48:771–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.09.028
Yang W, Xia Y, Hawke D, Li X, Liang J, Xing D, Aldape K, Hunter T, Alfred Yung WK, Lu Z (2012b) PKM2 phosphorylates histone H3 and promotes gene transcription and tumorigenesis. Cell 150:685–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.07.018
Yang W, Zheng Y, Xia Y, Ji H, Chen X, Guo F, Lyssiotis CA, Aldape K, Cantley LC, Lu Z (2012c) ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of PKM2 promotes the Warburg effect. Journal Nat Cell Biol 14:1295–1304. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2629
Yang P, Li Z, Fu R, Wu H, Li Z (2014) Pyruvate kinase M2 facilitates colon cancer cell migration via the modulation of STAT3 signaling. Cell Signal 26:1853–1862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.03.020
Yang YC, Chien MH, Liu HY, Chang YC, Chen CK, Lee WJ, Kuo TC, Hsiao M, Hua KT, Cheng TY (2018) Nuclear translocation of PKM2/AMPK complex sustains cancer stem cell populations under glucose restriction stress. Cancer Lett 421:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.075
Zhang M, Sun H, Den Y, Su M, We S, Wang P, Yu L, Liu J, Shen L, Guo J, Wang X, Han X, He Q (2019) COPI-mediated nuclear translocation of EGFRvIII promotes STAT3 phosphorylation and PKM2 nuclear localization. Int J Biol Sci 15:114–126. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.28679
Data availability statement
Being a review article, this article does not contain any data or experimental results on the studies performed by any of the authors. Hence, authors claim none to share.
Funding
This work being supported to A.K.M. by the BSR-startup grant [F.20–39 (12)/2013 (BSR)], University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi, India, and Research Seed Money (RSM: CUPB/CC/14/OO/4507), Central University of Punjab, Bathinda, India. H.V., and S.K. thankfully acknowledges financial support in the form of junior research fellowship and senior research fellowship from the University Grants Commission (UGC-CSIR), New Delhi, India, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.V.; R.P.C.; conceived and provided major contribution in writing the manuscript; S.K. provided additional contribution while revising the manuscript. M.D. and A.K.M. conceptualized the work, interpreted, supervised and are the major contributors in writing the manuscript. Because of the limited focus of the article, many relevant and appropriate references could not be included, for which the authors apologize. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical concern
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
Authors H.V.; R.P.C.; S.K.; M.D.; and A.K.M declares that none of them have no conflict of interest exists.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, H., Cholia, R.P., Kaur, S. et al. A short review on cross-link between pyruvate kinase (PKM2) and Glioblastoma Multiforme. Metab Brain Dis 36, 751–765 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00690-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00690-y