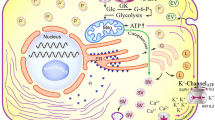
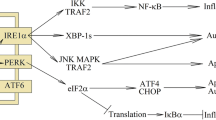
Abstract
In the context of high human consumption of fructose diets, there is an imperative need to understand how dietary fructose intake influence cellular and molecular mechanisms and thereby affect β-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. While evidence exists for a relationship between high-fat-induced insulin resistance and metabolic disorders, there is lack of studies in relation to high-fructose diet. Therefore, we attempted to study the effect of different diets viz., high-fat diet (HFD), high-fructose diet (HFS), and a combination (HFS + HFD) diet on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in male Wistar rats compared to control animals fed with normal pellet diet. Investigations include oral glucose tolerance test, insulin tolerance test, histopathology by H&E and Masson’s trichrome staining, mRNA expression by real-time PCR, protein expression by Western blot, and caspase-3 activity by colorimetry. Rats subjected to high-fat/fructose diets became glucose intolerant, insulin-resistant, and dyslipidemic. Compared to control animals, rats subjected to different combination of fat/fructose diets showed increased mRNA and protein expression of a battery of ER stress markers both in pancreas and liver. Transcription factors of β-cell function (INSIG1, SREBP1c and PDX1) as well as hepatic gluconeogenesis (FOXO1 and PEPCK) were adversely affected in diet-induced insulin-resistant rats. The convergence of chronic ER stress towards apoptosis in pancreas/liver was also indicated by increased levels of CHOP mRNA & increased activity of both JNK and Caspase-3 in rats subjected to high-fat/fructose diets. Our study exposes the experimental support in that high-fructose diet is equally detrimental in causing metabolic disorders.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GRP-78:
-
Glucose-regulated protein-78
- PERK:
-
PKR-like ER kinase
- IRE-1α :
-
Inositol-requiring enzyme-1α
- XBP1:
-
X box-binding protein1
- CHOP:
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding homologous protein
- INSIG1:
-
Insulin-induced gene1
- SREBP1c:
-
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein
- PDX1:
-
Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1
- FOXO1:
-
Forkhead box protein O1
- PEPCK:
-
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinases
References
Gross LS, Li L, Ford ES, Liu S (2004) Increased consumption of refined carbohydrates and the epidemic of type 2 diabetes in the United States: an ecologic assessment. Am J Clin Nutr 79:774–779
Malik VS, Hu FB (2015) Fructose and cardiometabolic health: what the evidence from sugar-sweetened beverages tells us. J Am Coll Cardiol 66(14):1615–1624. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2015.08.025
Gulati S, Misra A (2014) Sugar intake, obesity, and diabetes in India. Nutrients 6:5955–5974. doi:10.3390/nu6125955
Mirmiran P, Bahadoran Z, Delshad H, Azizi F (2014) Effects of energy-dense nutrient-poor snacks on the incidence of metabolic syndrome: a prospective approach in Tehran lipid and glucose study. Nutrition 30:538–543. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2013.09.014
Liese AD, Weis KE, Schulz M, Tooze JA (2009) Food intake patterns associated with incident type 2 diabetes: the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes Care 32:263–268. doi:10.2337/dc08-1325
Lorenzo C, Wagenknecht LE, D’Agostino RB, Rewers MJ, Karter AJ, Haffner SM (2010) Insulin resistance, beta-cell dysfunction, and conversion to type 2 diabetes in a multiethnic population: the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes Care 33:67–72. doi:10.2337/dc09-1115
Manco M, Calvani M, Mingrone G (2004) Effects of dietary fatty acids on insulin sensitivity and secretion. Diabetes Obes Metab 6:402–413. doi:10.1111/j.1462-8902.2004.00356
Bizeau ME, Pagliassotti MJ (2005) Hepatic adaptations to sucrose and fructose. Metab Clin Exp 54:1189–1201. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2005.04.004
Dirlewanger M, Schneiter P, Jéquier E, Tappy L (2000) Effects of fructose on hepatic glucose metabolism in humans. Am J physiol Endocr metab 279:11
Topsakal S, Ozmen O, Cankara FN, Yesilot S, Bayram D, Genç Özdamar N, Kayan S (2016) Alpha lipoic acid attenuates high-fructose-induced pancreatic toxicity. Pancreatology 3:347–352. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2016.03.001
Jonsson A, Ladenvall C, Ahluwalia TS, Kravic J, Krus U, Taneera J, Isomaa B, Tuomi T, Renström E, Groop L, Lyssenko V (2013) Effects of common genetic variants associated with type 2 diabetes and glycemic traits on α- and β-cell function and insulin action in humans. Diabetes 62:2978–2983. doi:10.2337/db12-1627
Sharma PR, Mackey AJ, Dejene EA, Ramadan JW, Langefeld CD, Palmer ND, Taylor KD, Wagenknecht LE, Watanabe RM, Rich SS, Nunemaker CS (2015) An Islet-targeted genome-wide association scan identifies novel genes implicated in cytokine-mediated islet stress in type 2 diabetes. Endocrinology 156:3147–3156. doi:10.1210/en.2015-1203
Turner N, Kowalski GM, Leslie SJ, Risis S, Yang C, Lee-Young RS, Babb JR, Meikle PJ, Lancaster GI, Henstridge DC, White PJ, Kraegen EW, Marette A, Cooney GJ, Febbraio MA, Bruce CR (2013) Distinct patterns of tissue-specific lipid accumulation during the induction of insulin resistance in mice by high-fat feeding. Diabetologia 56:1638–1648. doi:10.1007/s00125-013-2913-1
Huang C-JJ, Haataja L, Gurlo T, Butler AE, Wu X, Soeller WC, Butler PC (2007) Induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced beta-cell apoptosis and accumulation of polyubiquitinated proteins by human islet amyloid polypeptide. Am J physiol Endocr metab 293:62. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00318.2007
Balasubramanyam M, Lenin R, Monickaraj F (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes: new insights of clinical relevance. Indian J Clin Biochem 25:111–118. doi:10.1007/s12291-010-0022-1
Lenin R, Sankaramoorthy A, Mohan V, Balasubramanyam M (2015) Altered immunometabolism at the interface of increased endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Leukoc Biol 98:615–622. doi:10.1189/jlb.3A1214-609R
Dobiasova M (2004) Atherogenic index of plasma [log(triglycerides/HDL-cholesterol)]: theoretical and practical implications. Clin Chem 50(7):1113–1115
Viswanad B, Srinivasan K, Kaul CL, Ramarao P (2006) Effect of tempol on altered angiotensin II and acetylcholine-mediated vascular responses in thoracic aorta isolated from rats with insulin resistance. Pharmacol Res 53(3):209–215
Srinivasan K, Patole PS, Kaul CL, Ramarao P (2004) Reversal of glucose intolerance by by pioglitazone in high fat diet-fed rats. Method Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 26:327–333
Zhang W, Patil S, Chauhan B, Guo S, Powell DR, Le J, Klotsas A, Matika R, Xiao X, Franks R, Heidenreich KA, Sajan MP, Farese RV, Stolz DB, Tso P, Koo S-HH, Montminy M, Unterman TG (2006) FoxO1 regulates multiple metabolic pathways in the liver: effects on gluconeogenic, glycolytic, and lipogenic gene expression. J Biol Chem 281:10105–10117. doi:10.1074/jbc.M600272200
Balasubramanyam M, Aravind S, Gokulakrishnan K, Prabu P, Sathishkumar C, Ranjani H, Mohan V (2011) Impaired miR-146a expression links subclinical inflammation and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Mol Cell Biochem 351:197–205. doi:10.1007/s11010-011-0727-3
Swinburn BA, Boyce VL, Bergman RN, Howard BV, Bogardus C (1991) Deterioration in carbohydrate metabolism and lipoprotein changes induced by modern, high fat diet in Pima Indians and Caucasians. J Clin Endocr Metab 73:156–165. doi:10.1210/jcem-73-1-156
Maiztegui B, Borelli MI, Raschia MA, Del Zotto H, Gagliardino JJ (2009) Islet adaptive changes to fructose-induced insulin resistance: beta-cell mass, glucokinase, glucose metabolism, and insulin secretion. J Endocr 200:139–149. doi:10.1677/joe-08-0386
Hotamisligil GSS (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140:900–917. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.034
Tsutsumi A, Motoshima H, Kondo T, Kawasaki S, Matsumura T, Hanatani S, Igata M, Ishii N, Kinoshita H, Kawashima J, Taketa K, Furukawa N, Tsuruzoe K, Nishikawa T, Araki E (2011) Caloric restriction decreases ER stress in liver and adipose tissue in ob/ob mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404:339–344. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.11.120
Leng Y-PP, Qiu N, W-jJ Fang, Zhang M, He Z-MM, Xiong Y (2014) Involvement of increased endogenous asymmetric dimethylarginine in the hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress of type 2 diabetic rats. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0097125
Hummasti S, Hotamisligil GSS (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in obesity and diabetes. Circ Res 107:579–591. doi:10.1161/circresaha.110.225698
Kakuma T, Lee Y, Higa M, Wang Z, Pan W, Shimomura I, Unger RH (2000) Leptin, troglitazone, and the expression of sterol regulatory element binding proteins in liver and pancreatic islets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8536–8541
Yang T, Espenshade PJ, Wright ME, Yabe D, Gong Y, Aebersold R, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (2002) Crucial step in cholesterol homeostasis: sterols promote binding of SCAP to INSIG-1, a membrane protein that facilitates retention of SREBPs in ER. Cell 110:489–500
Chen K, Jin P, H-hH He, Y-hH Xie, X-yY Xie, Z-hH Mo (2011) Overexpression of Insig-1 protects β cell against glucolipotoxicity via SREBP-1c. J Biomed Sci 18:57. doi:10.1186/1423-0127-18-57
Sachdeva MM, Claiborn KC, Khoo C, Yang J, Groff DN, Mirmira RG, Stoffers DA (2009) Pdx1 (MODY4) regulates pancreatic beta cell susceptibility to ER stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19090–19095. doi:10.1073/pnas.0904849106
Gao T, McKenna B, Li C, Reichert M, Nguyen J, Singh T, Yang C, Pannikar A, Doliba N, Zhang T, Stoffers DA, Edlund H, Matschinsky F, Stein R, Stanger BZ (2014) Pdx1 maintains β cell identity and function by repressing an α cell program. Cell Metab 19:259–271. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2013.12.002
Wang H, Kouri G, Wollheim CB (2005) ER stress and SREBP-1 activation are implicated in beta-cell glucolipotoxicity. J Cell Sci 118:3905–3915. doi:10.1242/jcs.02513
Nerurkar PV, Nishioka A, Eck PO, Johns LM, Volper E, Nerurkar VR (2012) Regulation of glucose metabolism via hepatic forkhead transcription factor 1 (FoxO1) by Morinda citrifolia (noni) in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Br J Nutr 108:218–228. doi:10.1017/s0007114511005563
Deng J, Lu PD, Zhang Y, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Sonenberg N, Harding HP, Ron D (2004) Translational repression mediates activation of nuclear factor kappa B by phosphorylated translation initiation factor 2. Mol Cell Biol 24:10161–10168. doi:10.1128/mcb.24.23.10161-10168.2004
Harris TR, Bettaieb A, Kodani S, Dong H, Myers R, Chiamvimonvat N, Haj FG, Hammock BD (2015) Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates hepatic fibrosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 286:102–111. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2015.03.022
Malhi H, Kaufman RJ (2011) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver disease. J Hepatol 54:795–809. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2010.11.005
Lanuza-Masdeu J, Arévalo MI, Vila C, Barberà A, Gomis R, Caelles C (2013) In vivo JNK activation in pancreatic β-cells leads to glucose intolerance caused by insulin resistance in pancreas. Diabetes 62:2308–2317. doi:10.2337/db12-1097
Kelley GL, Allan G, Azhar S (2004) High dietary fructose induces a hepatic stress response resulting in cholesterol and lipid dysregulation. Endocrinology 145:548–555. doi:10.1210/en.2003-1167
Sun RQ, Wang H, Zeng XY, Chan SM, Li SP, Jo E, Leung SL, Molero JC, Ye JM (2015) IRE1 impairs insulin signaling transduction of fructose-fed mice via JNK independent of excess lipid. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852:156–165. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.11.017
Baena M, Sangüesa G, Dávalos A, Latasa MJ, Sala-Vila A, Sánchez RM, Roglans N, Laguna JC, Alegret M (2016) Fructose, but not glucose, impairs insulin signaling in the three major insulin-sensitive tissues. Sci Rep 6:26149. doi:10.1038/srep26149
Marchetti P, Del Guerra S, Marselli L, Lupi R, Masini M, Pollera M, Bugliani M, Boggi U, Vistoli F, Mosca F, Del Prato S (2004) Pancreatic islets from type 2 diabetic patients have functional defects and increased apoptosis that are ameliorated by metformin. J Clin Endocr Metab 89:5535–5541. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-0150
Crescenzo R, Bianco F, Coppola P, Mazzoli A, Tussellino M, Carotenuto R, Liverini G, Iossa S (2014) Fructose supplementation worsens the deleterious effects of short-term high-fat feeding on hepatic steatosis and lipid metabolism in adult rats. Exp Physiol 99:1203–1213. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2014.079632
Dornas WC, de Lima WG, Pedrosa ML, Silva ME (2015) Health implications of high-fructose intake and current research. Adv Nutr 6(6):729–737. doi:10.3945/an.114.008144
Herman MA, Samuel VT (2016) The sweet path to metabolic demise: fructose and lipid synthesis. Trend Endocrinol Metab. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2016.06.005
Polakof S, Dardevet D, Lyan B, Mosoni L, Gatineau E, Martin JF, Pujos-Guillot E, Mazur A, Comte B (2016) time course of molecular and metabolic events in the development of insulin resistance in fructose-fed rats. J Proteom Res 15(6):1862–1874. doi:10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00043
Saad AF, Dickerson J, Kechichian TB, Yin H, Gamble P, Salazar A, Patrikeev I, Motamedi M, Saade GR, Costantine MM (2006) High-fructose diet in pregnancy leads to fetal programming of hypertension, insulin resistance, and obesity in adult offspring. Am J Obstet Gynecol 378:e1–6. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2016.03.038
Dupas J, Goanvec C, Feray A, Guernec A, Alain C, Guerrero F, Mansourati J (2016) progressive induction of type 2 diabetes: effects of a reality-like fructose enriched diet in young Wistar rats. PLoS One 11(1):e0146821. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0146821
Seyssel K, Meugnier E, Lê KA, Durand C, Disse E, Blond E, Pays L, Nataf S, Brozek J, Vidal H, Tappy L, Laville M (2016) Fructose overfeeding in first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetic patients impacts energy metabolism and mitochondrial functions in skeletal muscle. Mol Nutr Food Res. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201600407
Botezelli JD, Coope A, Ghezzi AC, Cambri LT, Moura L, Scariot P, Gaspar RS, Mekary RA, Ropelle ER, Pauli JR (2016) strength training prevents hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance, and inflammation independent of weight loss in fructose-fed animals. Sci Rep 6:31106. doi:10.1038/srep31106
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge grant support from the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) & Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi, Govt. of India. Authors also acknowledge financial assistance (Senior Research Fellowship) from the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India.
Author Contributions
M. B. conceived and designed the study, provided critical research materials, assisted with analysis of the results, composed, drafted, and edited the manuscript. V. M. reviewed and edited the manuscript. B. M., L. R., D. P., C. S., and P. P. performed the experiments, acquired and analyzed the data, interpreted the results, and contributed to discussion. Both B. M and L. R. equally contributed to the molecular investigations on ER stress markers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balakumar, M., Raji, L., Prabhu, D. et al. High-fructose diet is as detrimental as high-fat diet in the induction of insulin resistance and diabetes mediated by hepatic/pancreatic endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Mol Cell Biochem 423, 93–104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2828-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2828-5