Abstract
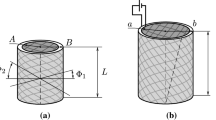
To reveal the electro-viscoelastic performance of a tubular dielectric elastomer actuator, a dissipative model for the actuator is formulated by adopting the nonlinear theory of viscoelastic dielectrics. The actuator is made by rolling a layer of dielectric elastomer membrane into a tube, which is then fixed tightly with two rigid disks at top and bottom edges respectively. Once actuated by internal pressure and voltage, the tube inflates and deforms into an out-of plane shape, undergoing large deformation. To depict the deformation, the non-equilibrium thermodynamics is employed to derive the state equations and the governing equations, and to characterize the dissipative process, a rheological spring-dashpot model is applied to obtaining the kinetic equations. Numerical simulation is conducted by a joint use of the shooting method and the improved Euler method, and the variations of the considered variables and the profiles of the deformed tube are obtained and demonstrated graphically. The effects of the internal pressure, the voltage as well as the aspect ratio of the tube on the performance of the actuator are considered. The results show that for small pressure or small voltage, the actuator can eventually evolve into a stable state, while for large pressure or large voltage, the actuator can’t reach a stable state due to the occurrence of purely mechanical instability or electromechanical instability. As for the aspect ratio, it significantly influences the performance of the actuator. It is hoped that the approach may provide a better understanding of the electro-viscoelastic performance of such actuators and some guidelines in designing such actuators.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, L., Wang, F.F., Cheng, S.B., Lu, T.Q., Wang, T.J.: Experimental investigation of the electromechanical phase transition in a dielectric elastomer tube. Smart Mater. Struct. 24, 035006 (2015)
Dorfmann, A., Ogden, R.W.: Nonlinear electroelasticity. Acta Mech. 174, 167–183 (2005)
Foo, C.C., Koh, S.J.A., Keplinger, C., Kaltseis, R., Bauer, S., Suo, Z.G.: Performance of dissipative dielectric elastomer generators. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 094107 (2012)
Goulbourne, N., Mockenstrum, E., Frecker, M.: A nonlinear model for dielectric elastomer membranes. J. Appl. Mech. 72, 899 (2005)
Gisby, T.A., Xie, S.Q., Calius, E.P., Anderson, I.A.: Leakage current as a predictor of failure in dielectric elastomer actuators. Proc. SPIE 7642, 764213 (2010)
Henann, D.L., Chester, S.A., Bertoldi, K.: Modeling of dielectric elastomers: design of actuators and energy harvesting devices. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 61, 2047–2066 (2013)
He, T.H., Cui, L.L., Chen, C., Suo, Z.G.: Nonlinear deformation analysis of a dielectric elastomer membrane–spring system. Smart Mater. Struct. 19, 085017 (2009a)
He, T.H., Zhao, X.H., Suo, Z.G.: Dielectric elastomer membranes undergoing inhomogeneous deformation. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 083522 (2009b)
He, X.Z., Yong, H.D., Zhou, Y.H.: The characteristics and stability of a dielectric elastomer spherical shell with a thick wall. Smart Mater. Struct. 20, 055016 (2011)
Huang, J.S., Li, T.F., Foo, C.C., Zhu, J., Clarke, D.R., Suo, Z.G.: Giant, voltage-actuated deformation of a dielectric elastomer under dead load. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 836 (2012)
Keplinger, C., Li, T.F., Baumgartner, R., Suo, Z.G., Bauer, S.: Harnessing snap-through instability in soft dielectrics to achieve giant voltage-triggered deformation. Soft Matter 8, 285–288 (2012)
Keplinger, C., Kaltenbrunner, M., Arnold, N., Bauer, S.: Röntgen’s electrode-free elastomer actuators without electromechanical pull-in instability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 4505 (2010)
Keplinger, C., Kaltenbrunner, M., Arnold, N., Bauer, S.: Capacitive extensometry for transient strain analysis of dielectric elastomer actuators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 192903 (2008)
Kofod, G.: The static actuation of dielectric elastomer actuators: how does pre-stretch improve actuation? J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 41, 2801–2809 (2008)
Kollosche, M., Kofod, G., Suo, Z.G., Zhu, J.: Temporal evolution and instability in a viscoelastic dielectric elastomer. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 76, 47–64 (2015)
Koh, S.J.A., Zhao, X.H., Suo, Z.G.: Maximal energy that can be converted by a dielectric elastomer generator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 262902 (2009)
Li, T.F., Qu, S.X., Yang, W.: Energy harvesting of dielectric elastomer generators concerning inhomogeneous fields and viscoelastic deformation. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 034119 (2012)
Lu, T.Q., Cai, S.Q., Wang, H.M., Suo, Z.G.: Computational model of deformable lenses actuated by dielectric elastomers. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 104104 (2013)
Lu, T.Q., Foo, C.C., Huang, J.S., Zhu, J., Suo, Z.G.: Highly deformable actuators made of dielectric elastomers clamped by rigid rings. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 184105 (2014)
McMeeking, R.M., Landis, C.M.: Electrostatic forces and stored energy for deformable dielectric materials. J. Appl. Mech. 72, 581–590 (2005)
Plante, J., Dubowsky, S.: Large-scale failure modes of dielectric elastomer actuators. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 7727–7751 (2006)
Pelrine, R., Kornbluh, R., Pei, Q.B.: High-speed electrically actuated elastomers with strain greater than 100%. Science 287, 836–839 (2000)
Suo, Z.G., Zhao, X.H., Greene, W.H.: A nonlinear field theory of deformable dielectrics. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56, 467–486 (2008)
Suo, Z.G.: Theory of dielectric elastomers. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 23, 549–578 (2010)
Tavakol, B., Holmes, D.P.: Voltage-induced buckling of dielectric films using fluid electrodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 112901 (2016)
Wang, B., Wang, Z.G., He, T.H.: Investigation on the viscoelastic behaviors of a circular dielectric elastomer membrane undergoing large deformation. AIP Adv. 6, 125127 (2016a)
Wang, H.M., Cai, S.Q., Carpi, F., Suo, Z.G.: Computational model of hydrostatically coupled dielectric elastomer actuators. J. Appl. Mech. 79, 031008 (2012)
Wang, H.M., Lei, M., Cai, S.Q.: Viscoelastic deformation of a dielectric elastomer membrane subject to electromechanical loads. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 213508 (2013)
Wang, S., Decker, M., Henann, D.L., Chester, S.A.: Modeling of dielectric viscoelastomers with application to electromechanical instabilities. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 95, 213–229 (2016b)
Wissler, M., Mazza, E.: Mechanical behavior of an acrylic elastomer used in dielectric elastomer actuators. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 134, 494–504 (2007)
Yu, Z.B., Yuan, W., Brochu, P., Chen, B., Liu, Z.T., Pei, Q.B.: Large-strain, rigid-to-rigid deformation of bistable electroactive polymers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 30 (2009)
Zhao, X.H., Suo, Z.G.: Method to analyze electromechanical stability of dielectric elastomers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 061921 (2007)
Zhao, X.H., Koh, S.J.A., Suo, Z.G.: Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of dielectric elastomers. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 3, 203–217 (2011)
Zhang, J.S., Tang, L.L., Li, B., Wang, Y.J., Chen, H.L.: Modeling of the dynamic characteristic of viscoelastic dielectric elastomer actuators subject to different conditions of mechanical load. J. Appl. Phys. 117, 836 (2015)
Zhou, J.Y., Jiang, L.Y., Khayat, R.E.: Viscoelastic effects on frequency tuning of a dielectric elastomer membrane resonator. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 124106 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11372123).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, T., Wang, Z. Electro-viscoelastic performance of a tubular dielectric elastomer actuator. Int J Mech Mater Des 15, 199–212 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-018-9408-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-018-9408-7