Abstract
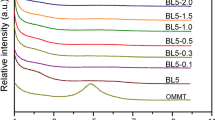
In this work, a reinforcing organoclay montmorillonite (OMMT) (i.e., 0, 2.5, 5, 7.5 and 10 phr) and novel alloys were prepared, which significantly improved the thermal, mechanical and rheological properties of immiscible XNBR/EPDM alloys. Results revealed that optimum cure time (t90) and scorch time (t5), decrease with increasing OMMT (Cloisite 15A) content; while the cure time was prolonged with increasing EPDM content. The results of X-ray diffraction show an increase in the distance between the layers of the silicate plates in the continuous XNBR/EPDM rubber phase in all of the compositions compared with the nanoclay powder. This indicates the penetration of rubber chains among the silicate layers. This phenomenon was also confirmed by direct observation of the intercalated and exfoliated microstructure of the nanocomposite by a transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Utracki LA (2002) Introduction to polymer blends, in: Utracki LA (Ed.), Polymer Blends Handbook. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 1–24
Satyanarayana MS, Bhowmick AK, Dinesh Kuma K (2016) Preferentially fixing nanoclays in the phases of incompatible carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR)-natural rubber (NR) blend using thermodynamic approach and its effect on physico mechanical properties. Polymer 99:21–43
Durandish M, Alipour A (2013) Investigation into morphology, microstructure and properties of SBR/EPDM/ORGANO montmorillonite nanocomposites. Chin J Polym Sci 31:660–669
Mansilla MA, Valentín JL, López-Manchado MA, González-Jiménez A, Marzocca AJ (2016) Effect of entanglements in the microstructure of cured NR/SBR blends prepared by solution and mixing in a two-roll mill. Eur Polym J 81:365–375
Shabafrooz V, Bandla S, Allahkarami S (2018) Graphene/polyethylene terephthalate nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties. J Polym Res 25:256–262
Salzano de Luna M, Filippone G (2016) Effects of nanoparticles on the morphology of immiscible polymer blends challenges and opportunities. Eur Polym J 79:198–218
Krause IC (2000) Polymer-polymer compatibility. In: Paul DR, Bucknall CB (eds) Polymer Blends. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New York, pp 15–30
Ibarra L, Rodrı’guez A, Mora I (2007) Ionic nanocomposites based on XNBR-OMg filled with layered nanoclays. Eur Polym J 43:753–761
Ai C, Gong G, Zhao X, Liu P (2017) Determination of carboxyl content in carboxylated nitrile butadiene rubber (XNBR) after degradation via olefin cross metathesis. Polym Testing 60:250–252
Ghosh P, Chakrabarti A (2000) Conducting carbon black filled EPDM Vulcanizates: assessment of dependence of physical and mechanical properties and conducting character on variation of fillers loading. Eur Polym J36:1043–1054
Doufnoune R, Haddaoui N (2017) Effects of surface functionalized partially reduced graphene oxide and different compatibilizers on the properties and structure of PP/EPR nanocomposites. J Polym Res 24:138–147
Jovanovic V, Samarzˇija-Jovanovic S, Simendic JB, Markovic G, Marinovic-Cincovic M (2013) Composites based on carbon black reinforced NBR/EPDM rubber blends. Compos B 45:333–340
Sarawut P, Kanokwan K, Nattapon S (2016) Physico-mechanical properties and automotive fuel resistance of EPDM/ENR blends containing hybrid fillers. J Polym Res 23:228–237
Wen Yen H, Kuo Bing C, Chang Mou W (2017) Compatibilizer effect on Organosilicate reinforced NBR nanocomposites. J Polym Res 24:205–216
Samarzˇija-Jovanovic S, Jovanovic V, Markovic G, Konstantinovic S, Marinovic-Cincovic. M (2011) Nanocomposites based on silica-reinforced ethylene propylene diene–monomer/acrylonitrile butadiene rubber blends. Compos B 42:1244–1250
Chen H, Li Y, Wang S, Li Y, Zhou Y (2018) Highly ordered structured montmorillonite/brominated butyl rubber nanocomposites: Dramatic enhancement of the gas barrier properties by an external magnetic field. J Membrane Sci 546:22–30
Singh K, Nanda T, Mehta R (2017) Addition of nanoclay and compatibilized EPDM rubber for improved impact strength of epoxy glass fiber composites. Compos A: Appl Sci Manufact 103:263–271
Zhang Z, Yu F, Yu W, Zhang H (2015) Non-isothermal crystallization behavior of dynamically vulcanized long chain branched polypropylene/ethylene-propylene-diene monomer blends. J Polym Res 22:198–206
Maroufkhani M, Katbab AA, Zhang J (2018) Manipulation of the properties of PLA nanocomposites by controlling the distribution of nanoclay via varying the acrylonitrile content in NBR rubber. Polym Testing 65:313–321
Ebrahimi-Jahromi A, Ebrahimi-Jahromi HR, Hemmati F, Saeb MR, .Formela K (2016) Morphology and mechanical properties of polyamide/clay nanocomposites toughened with NBR/NBR-g-GMA: A comparative study., Compos B: Eng 90:478–484
Bhuyan B, Srivastava SK, Pionteck J (2017) MWCNT/hectorite hybrid filled acrylonitrile butadiene rubber/ ethylene-co-vinyl acetate blend nanocomposites: preparation and properties. J Polym Res 24:150–159
Alipour A, Naderi G, Ghoreishy MH (2013) Effect of nanoclay content and matrix composition on properties andstress–strain behavior of NR/EPDM nanocomposites. J Appl Sci 127:1275–1284
Fathurrohman MI, Soegijono B, Budianto E, Rohman S, Ramadhan A (2015) The effect of Organoclay on curing characteristic, mechanical properties, swelling and morphology of natural rubber/Organoclay nanocomposites. Macromol Symp 353:62–69
Shen L, Xia L, Han T, Wu H, Guo S (2016) Improvement of hardness and compression set properties of EPDM seals with alternating multilayered structure for PEM fuel cells. Int J Hydrog Energy 41:23164–23172
Chantaratcharoen A, Sirisinha C, Amornsakchai T, Bualek-Limcharoen S, Meesiri W (1999) Improvement of interfacial adhesion of poly(m-phenyleneisophthalamide) short fiber thermoplastic elastomer (SEBS) composites by N-alkylation on fiber surface. Appl Polym Sci 74:2414–2422
Pasquini C, Figueiredo FC, Prince B (2007) Evaluation of the Mooney viscosity of natural rubber by near-infrared spectroscopy. Spectrosc Lett 38:741–748
Rooj S, Das A, Stöckelhuber KW (2012) Highly exfoliated natural rubber/clay composites by “propping-open procedure”: the influence of fatty acid chain length on exfoliation. Macromol Mater Eng 297:369–383
Jeddi J, Yousefzade O, Babaei A, Ghanbar S, Rostami A (2017) Morphology, microstructure and rheological properties of SAN/EPDM nanocomposites: investigating the role of organoclay type and order of mixing. Mater Chem Phys 187:181–202
Stöckelhuber KW, Das A, Jurk R, Heinrich G (2010) Contribution of physico-chemical properties of interfaces on dispersibility, adhesion and flocculation of filler particles in rubber. Polymer 51:1954–1963
Funt JM (1998) Dynamic testing and reinforcement of rubber. Rubber Chem Technol 6:842–865
Fu X, Huang G, Xie Z, Xing W (2015) New insights into reinforcement mechanism of nanoclay-filled isoprene rubber during uniaxial deformation by in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction. RSC Adv 5:25171–25182
Xu G, Qin S, Yu J, Huang Y, Zhang M, Ruan W (2015) Effect of migration of layered nanoparticles during melt blending on the phase morphology of poly (ethylene terephthalate)/polyamide 6/montmorillonite ternary nanocomposites. RSC Adv 5:29924–29931
Zachariah AK, Geethamma VG, Chandra AK, Mohammed PK, Thomas S (2014) Rheological behaviour of clay incorporated natural rubber and chlorobutyl rubber nanocomposites. RSC Adv 4:58047–58058
Klueppel M, Heinrich G (1994) Network structure and mechanical properties of sulfur-cured rubbers. Macromolecules 27:3596–3603
Laskowska A, Zaborski M, Boiteux G, Gain O, Marzec A, Maniukiewicz W (2014) Ionic elastomers based on carboxylated nitrile rubber (XNBR) and magnesium aluminum layered double hydroxide (hydrotalcite). e XPRESS Polym Lett 8:374–386
Hisham A, Salwa H, Sabbagh E, Magda E, Assche TGV, Barhoum A (2018) Assessment of provoked compatibility of NBR/SBR polymer blend with montmorillonite amphiphiles from the thermal degradation kinetics. 75:1417–1430
Varghese S, Karger-Kocsis J (2003) Melt-compounded natural rubber nanocomposites with pristine and organophilic layered silicates of natural and synthetic origin. J Appl Polym Sci 9:813–819
Wang Y, Zhang H, Wu Y, Yang J, Zhang L (2005) Structure and properties of strain-induced crystallization rubber-clay nanocomposites by co-coagulating the rubber latex and clay aqueous suspension. J Appl Polym Sci 96:318–323
Acknowledgements
The financial Zolal Gostar Rooz (ZGR) Company gratefully is acknowledged by the authors. The authors also thank Khazra Sazan Rad Polymer Parsian, Consulting Polymer Engineers CO for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Conflict of interest the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this research paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azizli, M.J., Khonakdar, H.A., Mokhtary, M. et al. Investigating the effect of organoclay montmorillonite and rubber ratio composition on the enhancement compatibility and properties of carboxylated acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber/ethylene-propylene-diene monomer hybrid elastomer nanocomposites. J Polym Res 26, 221 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1885-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1885-3