Abstract
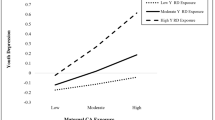
Past research links childhood exposure to intimate partner violence (IPV) to Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), with preliminary evidence that white children may be more traumatized by IPV exposure than African American children. Despite this, few studies have explored the moderating effect of race/ethnicity on children’s IPV exposure and subsequent trauma symptoms. Using a diverse sample of children in the U.S. child welfare system (n = 713) with high prevalence of IPV exposure, this study employs subpopulation analysis with multivariate regression to explore whether race/ethnicity moderates the relationship between IPV exposure and trauma symptoms, and whether differential predictors of trauma exist for white, African American, and Hispanic children exposed to IPV. Race/ethnicity moderates the relationship between childhood exposure to IPV and trauma, with Hispanic children exhibiting fewer trauma symptoms than white children as IPV exposure becomes more frequent. Differential predictors of trauma also emerged by child race/ethnicity. Caregiver’s depression predicted white and African American children’s trauma, while neighborhood quality predicted Hispanic children’s trauma. This study suggests that race/ethnicity correlates with different risk factors for child welfare-supervised children and, as such, should be considered when designing and implementing interventions for this population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard, S. (2009). Mismatches and unmet needs: Access to social services in urban and rural America. In J. P. Ziliak (Ed.), Welfare Reform and its Long-Term Consequence for America’s Poor. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Appel, A. E., & Holden, G. W. (1998). The co-occurrence of spouse and physical child abuse: A review and appraisal. Journal of Family Psychology, 12(4), 578–599. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-3200.12.4.578.
Babor, T.F., Higgins-Biddle, J.C., Saunders, J.B., & Monteiro, M.G. (2001). AUDIT - The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test: Guidelines for use in primary care (second edition). Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. Retrieved from: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/2001/WHO_MSD_MSB_01.6a.pdf
Beeman, S. K., Hagemeister, A. K., & Edleson, J. L. (2001). Case assessment and service receipt in families experiencing both child maltreatment and woman battering. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 16(5), 437–458.
Bell, B. A., Kromrey, J. D., & Ferron, J. M. (2009). Missing data and complex samples: The impact of listwise deletion vs. subpopulation analysis on statistical bias and hypothesis test results when data are MCAR and MAR. Proceedings of the Joint Statistical Meetings, Survey Research Methods Section, 26, 759–4770.
Bernal, G., & Sáez-Santiago, E. (2006). Culturally centered psychosocial interventions. Journal of Community Psychology, 34(2), 121–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcop.20096.
Biemer, P., Christ, S., Wheeless, S., & Wiesen, C. (2008). National Survey of Child and Adolescent Well-Being (NSCAW): Statistical Analysis Manual. Administration on Children and Families.
Briere, J. (1996). Trauma Symptom Checklist for Children (TSCC) Professional Manual. Odessa: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Campbell, K. A., Thomas, A. M., Cook, L. J., & Keenan, H. T. (2013). Resolution of intimate partner violence and child behavior problems after investigation for suspected child maltreatment. Journal of American Medical Association Pediatrics, 167(3), 236–242. https://doi.org/10.1001/2013.jamapediatrics.324.
Casanueva, C., Martin, S. L., Runyan, D. K., Barth, R. P., & Bradley, R. H. (2008). Quality of maternal parenting among intimate-partner violence victims involved with the child welfare system. Journal of Family Violence, 23, 413–427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-008-9167-6.
Casanueva, C., Dolan, M., Smith, K., & Ringeisen, H. (2012). NSCAW Child Well-Being Spolight: Children with Substantiated and Unsubstantiated Reports of Child Maltreatment are at Similar Risk for Poor Outcomes. OPRE Report #2012–31, Washington, DC: Office of Planning, Research and Evaluation.
Casanueva, C., Ringeisen, H., Smith, K., & Dolan, M. (2013). NSCAW Child Well-Being Spotlight: Parents Reported for Maltreatment Experience High Rates of Domestic Violence. OPRE Report #2013–04, Washington, DC: Office of Planning, Research and Evaluation, Administration for Children and Families, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Chemtob, C. M., & Carlson, J. G. (2004). Psychological effects of domestic violence on children and their mothers. International Journal of Stress Management, 11(3), 209–226. https://doi.org/10.1037/1072-5245.11.3.209.
Costello, E. J., Keeler, G. P., & Angold, A. (2001). Poverty, race/ethnicity, and psychiatric disorder: A study of rural children. American Journal of Public Health, 91, 1494–1498.
Dowd, K., Dolan, M., Wallin, J., Miller, K., Biemer, P., Aragon-Logan, E, et al. (2012). National Survey of Child and Adolescent Well-Being II, Combined Waves 1–2, Data File User’s Manual, Restricted Release Version. Administration on Children and Families.
Edleson, J. L. (1999). Children’s witnessing of adult domestic violence. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 14, 839–870.
Edleson, J. L., Gassman-Pines, J., & Hill, M. B. (2006). Defining child exposure to domestic violence as neglect: Minnesota’s Difficult Experience. Social Work, 51, 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1093/sw/51.2.167.
English, D. J., Upadhyaya, M. P., Litrownik, A. J., Marshall, J. M., Runyan, D. K., Graham, J. C., & Dubowitz, H. (2005). Maltreatment’s wake: The relationship of maltreatment dimensions to child outcomes. Child Abuse & Neglect, 29, 596–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2004.12.008.
Evans, S. E., Davies, C., & DiLillo, D. (2008). Exposure to domestic violence: A meta-analysis of child and adolescent outcomes. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 13, 131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2008.02.005.
Finkelhor, D., Turner, H., Ormrod, R., & Hamby, S. L. (2009). Violence, abuse, and crime exposure in a national sample of children and youth. Pediatrics, 124(5), 1411–1423. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-0467.
Fluke, J. D., Yuan, Y. T., Hedderson, J., & Curtis, P. A. (2003). Disproportionate representation of race and ethnicity in child maltreatment: Investigation and victimization. Child and Youth Services Review, 25, 359–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-7409(03)00026-4.
Font, S. A., & Maguire-Jack, K. (2013). Academic engagement and performance: Estimating the impact of out of home care for maltreated children. Children & Youth Services Review, 35, 856–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2013.02.010.
Fontes, L. (2002). Child discipline and physical abuse in immigrant Latino families: Reducing violence and misunderstandings. Journal of Counseling and Development, 80, 31–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1556-6678.2002.tb00163.x.
Fox, N.A., & Leavitt, L.A. (1995). The Violence Exposure Scale for Children-VEX. College Park: Department of Human Development, University of Maryland.
Furstenburg, F. (1990). Philadelphia Family Management Study-parent interview schedule. Philadelphia, PA: Population Studies Center, University of Pennsylvania and Boulder, CO; Institute of Behavioral Science, University of Colorado.
Garrido, E. F., Culhane, S. E., Petrenko, C. L., & Taussig, H. N. (2011). Psychosocial consequences of intimate partner violence (IPV) exposure in maltreated adolescents: Assessing more than IPV occurrence. Journal of Family Violence, 26, 511–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-011-9386-0.
Gerwitz, A. H., DeGarmo, D. S., & Medhanie, A. (2011). Effect of mother’s parenting practices on child internalizing trajectories following partner violence. Journal of Family Psychology, 25, 29–38. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0022195.
Gleason, W. J. (1993). Mental disorders in battered women: An empirical study. Violence and Victims, 8, 53–68.
Golding, J. M. (1999). Intimate partner violence as a risk factor for mental disorders: A meta-analysis. Journal of Family Violence, 14, 99–132. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022079418229.
Goodmark, L. (2010). Mothers, domestic violence, and child protection: An American legal perspective. Violence Against Women, 16, 524–529. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077801210366290.
Graham-Bermann, S. A., & Levendosky, A. A. (1998). Traumatic stress symptoms in children of battered women. Journal Interpersonal Violence, 13, 111–128. https://doi.org/10.1177/088626098013001007.
Graham-Bermann, S., DeVoe, E. R., Mattis, J. S., Lynch, S., & Thomas, S. A. (2006). Ecological predictors of traumatic stress symptoms in Caucaisan and Ethnic minority children exposed to intimate partner violence. Violence Against Women, 12, 662–692. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077801206290216.
Graham-Bermann, S. A., Gruber, G., Howell, K., & Girz, L. (2009). Factors discriminating among profiles of resilience and psychopathology in children exposed to intimate partner violence (IPV). Child Abuse & Neglect, 33, 648–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2009.01.002.
Grych, J. H., Jouriles, E. N., Swank, P. R., McDonald, R., & Norwood, W. D. (2000). Patterns of adjustment among children of battered women. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 68, 84–94. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.68.1.84.
Hamby, S., Finkelhor, D., Turner, H., & Ormrod, R. (2011). Children’s Exposure to Intimate Partner Violence and Other Family Violence. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention.
Hazen, A. L., Connelly, C. D., Kelleher, K. J., Barth, R. P., & Landsverk, J. A. (2006). Female caregivers’ experiences with intimate partner violence and behavior problems in children investigated as victims of maltreatment. Pediatrics, 117, 99–109. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2004-2542.
Holmes, M. R. (2013). Aggressive behavior of children exposed to intimate partner violence: An examination of maternal mental health, maternal warmth and child maltreatment. Child Abuse & Neglect, 37, 520–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2012.12.006.
Holt, S., Buckley, H., & Whelan, S. (2008). The impact of exposure to domestic violence on children and young people: A review of literature. Child Abuse and Neglect, 32, 797–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2008.02.004.
Jaffe, P. G., Wolfe, D. A., & Wilson, S. K. (1990). Children of battered women. Newbury Park: Sage.
Jaffe, P. G., Crooks, C. V., & Wolfe, D. A. (2003). Legal and policy responses to children exposed to domestic violence: The need to evaluate intended and unintended consequences. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 6, 205–213. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024914517072.
Janca, A., Robins, L. N., Bucholz, K. K., Early, T. S., & Shayka, J. J. (1992). Comparison of composite international diagnostic interview and clinical DSM-III-R criteria checklist diagnoses. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 85(6), 440–443. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.1992.tb03208.x.
Jones, L. P., Gross, E., & Becker, I. (2002). The characteristics of domestic violence victims in a child protective service caseload. Families in Society, 83(4), 405–415. https://doi.org/10.1606/1044-3894.14.
Jouriles, E. N., McDonald, R., Norwood, W. D., Shinn Ware, H., Collazos Spiller, L., & Swank, P. R. (1998). Knives, guns and interparental violence: Relations with child behaviour problems. Journal of Family Psychology, 12, 178–194. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-3200.12.2.178.
Kasturirangan, A., Krishnan, S., & Riger, S. (2004). The impact of culture and minority status on women’s experience of domestic violence. Trauma, Violence, & Abuse, 5, 318–332. https://doi.org/10.1177/1524838004269487
Kessler, R. C., Andrews, G., Mroczek, D., Ustun, T. B., & Wittchen, H.-U. (1998). The World Health Organization Composite International Diagnostic Interview Short Form (CIDI-SF). International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research, 7(4), 171–185.
Kilpatrick, D. G., Ruggiero, K. J., Acierno, R., Saunders, B. E., Resnick, H. S., & Best, C. L. (2003). Violence and risk of PTSD, major depression, substance abuse/dependence, and comorbidity: results from the National Survey of Adolescents. Journal of Consultation in Clinical Psychology, 71(4), 692–700. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.71.4.692.
Kissane, R. J. (2010). “We call it the badlands”: How social-spatial geographies influence social service use. Social Service Review, 84, 3–28.
Kitzmann, K. M., Gaylord, N. K., Holt, A. R., & Kenny, E. D. (2003). Child witnesses to domestic violence: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 71(2), 339–352. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.71.2.339.
Kolko, D. J., Hurlburt, M. S., Zhang, J., Barth, R. P., Leslie, L. K., & Burns, B. J. (2010). Posttraumatic stress symptoms in children and adolescents referred for child welfare investigation: A national sample of in-home and out-of-home care. Child Maltreatment, 15, 48–63. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077559509337892.
Koverola, C., Papas, M. A., Pitts, S., Murtaugh, C., Black, M. M., & Dubowitz, H. (2005). Longitudinal investigation of the relationship among maternal victimization, depressive symptoms, social support, and children’s behavior and development. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 20, 1523–1546. https://doi.org/10.1177/0886260505280339.
Lehmann, P. (1997). The development of PTSD in a sample of child witnesses to mother assault. Journal of Family Violence, 12(3), 241–257. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022842920066.
McCloskey, L. A., & Walker, M. (2000). Posttraumatic stress in children exposed to family violence and single-event trauma. Journal of American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 39, 108–115. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004583-200,001,000-00023.
McIntosh, J. E. (2003). Children living with domestic violence: Research foundations for early intervention. Journal of Family Studies, 9(2), 219–234. https://doi.org/10.5172/jfs.9.2.219.
McRoy, R. G. (2005). Overrepresentation of children and youth of color in foster care. In G. P. Mallon & P. McCartt Hess (Eds.), Child welfare for the twenty-first Century: A handbook of practices, policies, and programs (pp. 623–634). New York City: Columbia University Press.
National Data Archive on Child Abuse and Neglect. (2011). National Survey of Child and Adolescent Well-Being II, Combined Waves 1–2, Appendix Volume II, NSCAW II Constructs and Measures. Ithaca: Cornell University.
O’Keefe, M. (1994). Racial/ethnic differences among battered women and their children. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 3, 283–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02234687.
Osofsky, J. D. (2003). Prevalence of children’s exposure to domestic violence and child maltreatment: Implications for prevention and intervention. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 6(3), 161–170. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024958332093.
Pecora, P., Williams, J., Kessler, R., Hiripi, E., O’Brien, K., Emerson, J., et al. (2006). Assessing the educational achievements of adults who were formerly placed in family foster care. Child and Family Social Work, 11, 220–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2206.2006.00429.x.
Robins, L. N., Wing, J., Wittchen, H. U., Helzer, J. E., Babor, T. F., Burke, J., Farmer, A., Jablenski, A., Pickens, R., Regier, D. A., et al. (1988). The Composite International Diagnostic Interview: An epidemiologic instrument suitable for use in conjunction with different diagnostic systems and in different cultures. Archives of General Psychiatry, 12, 1069–1077. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1988.01800360017003.
Sadowski, C., & Friedrich, W. (2000). Psychometric properties of the Trauma Symptom Checklist for Children (TSCC) with psychiatrically hospitalized adolescents. Child Maltreatment, 5, 364–372. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077559500005004008.
Saltzman, K. M., Holden, G. W., & Holahan, C. J. (2005). The psychobiology of children exposed to marital violence. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 34, 129–139. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15374424jccp3401_12.
Sarkisian, N., & Gerstel, N. (2004). Kin support among blacks and whites: Race and family organization. American Sociological Review, 69, 812–837. https://doi.org/10.1177/000312240406900604.
Skinner, H. A. (1982). The drug abuse screening test. Addictive Behavior, 7(4), 363–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4603(82)90005-3.
Skopp, N. A., McDonald, R., Jouriles, E. N., & Rosenfield, D. (2007). Partner aggression and children’s externalizing problems: Maternal and partner warmth as protective factors. Journal of Family Psychology, 21, 459–467. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-3200.21.3.459.
Sorenson, S. B., Upchurch, D. M., & Shen, H. (1996). Violence and injury in martial arguments: risk patterns and gender differences. American Journal of Public Health, 86, 35–40.
StataCorp. (2018). Stata Statistical Software: Release 15. College Station: StataCorp LP.
Sternberg, K. J., Baradaran, L. P., Abbott, C. B., Lamb, M. E., & Guterman, E. (2006). Type of violence, age, and gender differences in the effects of family violence on childrens behavior problems: A mega-analysis. Developmental Review, 26, 89–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dr.2005.12.001.
Stone, S. (2007). Child maltreatment, out-of-home placement and academic vulnerability: A fifteen-year review of evidence and future directions. Children and Youth Services Review, 29(2), 139–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2006.05.001.
Straus, M. A., Sherry, L., Hamby, D., Finkelhor, D., Moore, W., & Runyan, D. (1998). Identification of child maltreatment with the Parent-Child Conflict Tactics Scales: Development and psychometric data for a national sample of American parents. Child Abuse and Neglect, 22, 249–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0145-2134(97)00174-9.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Children and Families, Administration on Children, Youth and Families, Children’s Bureau. (2012). Child Maltreatment 2011. Available from http://www.acf.hhs.gov/programs/cb/research-data-technology/statistics-research/child-maltreatment.
West, B., Berglund, P., & Heeringa, S. (2008). A closer examination of subpopulation analysis of complex-sample survey data. The Stata Journal, 8(4), 520–531.
Wittchen, H. U. (1994). Reliability and validity studies of the WHO-Composite International Diagnostic Interview (CIDI): a critical review. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 28, 57–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3956(94)90036-1.
Wolfe, D. A., Crooks, C. V., Lee, V., McIntyre-Smith, A., & Jaffe, P. G. (2003). The effects of children’s exposure to domestic violence: A meta-analysis and critique. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 6(3), 171–187. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024910416164.
Wright, E. M., & Benson, M. L. (2010). Immigration and intimate partner violence: Exploring the immigrant paradox. Social Problems, 57(3), 480–503. https://doi.org/10.1525/sp.2010.57.3.480.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costello, L.F., Klein, S. Racial/Ethnic Differences in Determinants of Trauma Symptomatology among Children in the U.S. Child Welfare System Exposed to Intimate Partner Violence. J Fam Viol 34, 33–45 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-018-9976-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-018-9976-1