Abstract
Purpose
The impact of metabolic syndrome (MetS) on recurrence of atrial fibrillation (AF) after catheter ablation remains uncertain. We conducted a meta-analysis to summarize the relative risks (RR) of AF recurrence after catheter ablation in patients with vs. without MetS and its components.
Methods
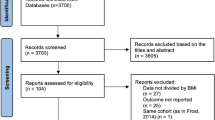
Among 839 articles identified from PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, we included 23 studies with a total of 12,924 patients (7,594 with paroxysmal AF and 5,330 with nonparoxysmal AF) for analysis. Five of these had complete information on MetS components. Variables assessed comprised study design and population characteristics, AF ablation methods, use of anti-arrhythmic drugs, AF recurrence ascertainment methods, adjustment variables, and other quality indicators.
Results
Our meta-analysis found an elevated risk of AF recurrence after ablation in patients with vs. without MetS (pooled RR, 1.63; 95 % confidence interval (CI), 1.25–2.12). Among components of MetS, hypertension was a predictor of AF post-ablation recurrence in studies without adjustment for other MetS components (RR, 1.62; 95 % CI, 1.23–2.13) but not in those adjusting for two or more additional MetS components (RR, 1.03; 95 % CI, 0.88–1.20). There was a borderline association between overweight/obesity and AF recurrence after ablation (RR, 1.27; 95 % CI, 0.99–1.64).
Conclusions
MetS is associated with an increased risk of AF recurrence after catheter ablation. Further study of the MetS and its components as determinants of AF risk could help refine patient selection and improve procedural outcomes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Go, A. S., Hylek, E. M., Phillips, K. A., Chang, Y., Henault, L. E., Selby, J. V., et al. (2001). Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the Anticoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA : the Journal of the American Medical Association, 285, 2370–2375.
Fuster, V., Ryden, L. E., Cannom, D. S., Crijns, H. J., Curtis, A. B., Ellenbogen, K. A., et al. (2011). ACCF/AHA/HRS focused updates incorporated into the ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation, 123, e269–e367.
Cappato, R., Calkins, H., Chen, S. A., Davies, W., Iesaka, Y., Kalman, J., et al. (2005). Worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 111, 1100–1105.
Patel, D., Mohanty, P., Di Biase, L., Shaheen, M., Lewis, W. R., Quan, K., et al. (2010). Safety and efficacy of pulmonary vein antral isolation in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: the impact of continuous positive airway pressure. Circulation Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology, 3, 445–451.
Arya, A., Hindricks, G., Sommer, P., Huo, Y., Bollmann, A., Gaspar, T., et al. (2010). Long-term results and the predictors of outcome of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation using steerable sheath catheter navigation after single procedure in 674 patients. Europace, 12, 173–180.
Mohanty, S., Mohanty, P., Di Biase, L., Bai, R., Pump, A., Santangeli, P., et al. (2012). Impact of metabolic syndrome on procedural outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing catheter ablation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 59, 1295–1301.
Alberti, K. G., Eckel, R. H., Grundy, S. M., Zimmet, P. Z., Cleeman, J. I., Donato, K. A., et al. (2009). Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation, 120, 1640–1645.
Chang, S. L., Tuan, T. C., Tai, C. T., Lin, Y. J., Lo, L. W., Hu, Y. F., et al. (2009). Comparison of outcome in catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with versus without the metabolic syndrome. American Journal of Cardiology, 103, 67–72.
Chao, T. F., Suenari, K., Chang, S. L., Lin, Y. J., Lo, L. W., Hu, Y. F., et al. (2010). Atrial substrate properties and outcome of catheter ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation associated with diabetes mellitus or impaired fasting glucose. American Journal of Cardiology, 106, 1615–1620.
Shah, A. N., Mittal, S., Sichrovsky, T. C., Cotiga, D., Arshad, A., Maleki, K., et al. (2008). Long-term outcome following successful pulmonary vein isolation: pattern and prediction of very late recurrence. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 19, 661–667.
Cai L, Yin Y, Ling Z, Su L, Liu Z, Wu J, Du H, Lan X, Fan J, Chen W, Xu Y, Zhou P, Zhu J, Zrenner B. (2013) Predictors of late recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. International Journal of Cardiology 164:82–87
Berkowitsch, A., Kuniss, M., Greiss, H., Wojcik, M., Zaltsberg, S., Lehinant, S., et al. (2012). Impact of impaired renal function and metabolic syndrome on the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation: a long term follow-up. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology: PACE, 35, 532–543.
Tang, R. B., Dong, J. Z., Liu, X. P., Long, D. Y., Yu, R. H., Kalifa, J., et al. (2009). Metabolic syndrome and risk of recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. Circulation Journal, 3, 438–443.
Andrade, J. G., Khairy, P., Verma, A., Guerra, P. G., Dubuc, M., Rivard, L., et al. (2012). Early recurrence of atrial tachyarrhythmias following radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology: PACE, 35, 106–116.
Higgins, J. P., & Thompson, S. G. (2002). Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine, 21, 1539–1558.
Begg, C. B., & Mazumdar, M. (1994). Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics, 50, 1088–1101.
Wokhlu, A., Hodge, D. O., Monahan, K. H., Asirvatham, S. J., Friedman, P. A., Munger, T. M., et al. (2010). Long-term outcome of atrial fibrillation ablation: impact and predictors of very late recurrence. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 21, 1071–1078.
Berruezo, A., Tamborero, D., Mont, L., Benito, B., Tolosana, J. M., Sitges, M., et al. (2007). Pre-procedural predictors of atrial fibrillation recurrence after circumferential pulmonary vein ablation. European Heart Journal, 28, 836–841.
Bhargava, M., Di Biase, L., Mohanty, P., Prasad, S., Martin, D. O., Williams-Andrews, M., et al. (2009). Impact of type of atrial fibrillation and repeat catheter ablation on long-term freedom from atrial fibrillation: results from a multicenter study. Heart Rhythm: the Official Journal of the Heart Rhythm Society, 6, 1403–1412.
Chao, T. F., Sung, S. H., Wang, K. L., Lin, Y. J., Chang, S. L., Lo, L. W., et al. (2011). Associations between the atrial electromechanical interval, atrial remodelling and outcome of catheter ablation in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Heart, 97, 225–230.
Chao, T. F., Lin, Y. J., Chang, S. L., Lo, L. W., Hu, Y. F., Tuan, T. C., et al. (2011). Associations between renal function, atrial substrate properties and outcome of catheter ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation Journal: Official Journal of the Japanese Circulation Society, 75, 2326–2332.
Chilukuri, K., Dalal, D., Marine, J. E., Scherr, D., Henrikson, C. A., Cheng, A., et al. (2009). Predictive value of obstructive sleep apnoea assessed by the Berlin Questionnaire for outcomes after the catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Europace, 11, 896–901.
Hwang, H. J., Lee, J. M., Joung, B., Lee, B. H., Kim, J. B., Lee, M. H., et al. (2010). Atrial Electroanatomical remodeling as a determinant of different outcomes between two current ablation strategies: circumferential pulmonary vein isolation vs pulmonary vein isolation. Clinical Cardiology, 33, E69–E74.
Jongnarangsin, K., Chugh, A., Good, E., Mukerji, S., Dey, S., Crawford, T., et al. (2008). Body mass index, obstructive sleep apnea, and outcomes of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 19, 668–672.
Khaykin, Y., Oosthuizen, R., Zarnett, L., Essebag, V., Parkash, R., Seabrook, C., et al. (2011). Clinical predictors of arrhythmia recurrences following pulmonary vein antrum isolation for atrial fibrillation: predicting arrhythmia recurrence post-PVAI. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22, 1206–1214.
Letsas, K. P., Weber, R., Burkle, G., Mihas, C. C., Minners, J., Kalusche, D., et al. (2009). Pre-ablative predictors of atrial fibrillation recurrence following pulmonary vein isolation: the potential role of inflammation. Europace, 11, 158–163.
Letsas KP, Siklody CH, Korantzopoulos P, Weber R, Burkle G, Mihas CC, Kalusche D, Arentz T. (2013) The impact of body mass index on the efficacy and safety of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. International Journal of Cardiology 164:94–98
Okumura, Y., Watanabe, I., Nakai, T., Ohkubo, K., Kofune, T., Kofune, M., et al. (2011). Impact of biomarkers of inflammation and extracellular matrix turnover on the outcome of atrial fibrillation ablation: importance of matrix metalloproteinase-2 as a predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22, 987–993.
Themistoclakis, S., Schweikert, R. A., Saliba, W. I., Bonso, A., Rossillo, A., Bader, G., et al. (2008). Clinical predictors and relationship between early and late atrial tachyarrhythmias after pulmonary vein antrum isolation. Heart Rhythm : the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society, 5, 679–685.
Wong, C. X., Abed, H. S., Molaee, P., Nelson, A. J., Brooks, A. G., Sharma, G., et al. (2011). Pericardial fat is associated with atrial fibrillation severity and ablation outcome. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 57, 1745–1751.
Deepa, M., Farooq, S., Datta, M., Deepa, R., & Mohan, V. (2007). Prevalence of metabolic syndrome using WHO, ATPIII and IDF definitions in Asian Indians: the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES-34). Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, 23, 127–134.
Sundstrom, J., Riserus, U., Byberg, L., Zethelius, B., Lithell, H., & Lind, L. (2006). Clinical value of the metabolic syndrome for long term prediction of total and cardiovascular mortality: prospective, population based cohort study. BMJ, 332, 878–882.
Stang, A. (2010). Critical evaluation of the Newcastle–Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. European Journal of Epidemiology, 25, 603–605.
Konings, K. T., Kirchhof, C. J., Smeets, J. R., Wellens, H. J., Penn, O. C., & Allessie, M. A. (1994). High-density mapping of electrically induced atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation, 89, 1665–1680.
Duval, S., & Tweedie, R. (2000). Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics, 56, 455–463.
Rosenberg, M. S. (2005). The file-drawer problem revisited: a general weighted method for calculating fail-safe numbers in meta-analysis. Evolution: International Journal of Organic Evolution, 59, 464–468.
Sterne, J. A., Gavaghan, D., & Egger, M. (2000). Publication and related bias in meta-analysis: power of statistical tests and prevalence in the literature. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 53, 1119–1129.
Wyse, D. G., & Gersh, B. J. (2004). Atrial fibrillation: a perspective: thinking inside and outside the box. Circulation, 109, 3089–3095.
Tanaka, K., Zlochiver, S., Vikstrom, K. L., Yamazaki, M., Moreno, J., Klos, M., et al. (2007). Spatial distribution of fibrosis governs fibrillation wave dynamics in the posterior left atrium during heart failure. Circulation Research, 101, 839–847.
Munger, T. M., Dong, Y. X., Masaki, M., Oh, J. K., Mankad, S. V., Borlaug, B. A., et al. (2012). Electrophysiological and hemodynamic characteristics associated with obesity in patients with atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 60, 851–860.
Wang, T. J., Parise, H., Levy, D., D’Agostino, R. B., Sr., Wolf, P. A., Vasan, R. S., et al. (2004). Obesity and the risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation. JAMA : the Journal of the American Medical Association, 292, 2471–2477.
Schotten, U., Neuberger, H. R., & Allessie, M. A. (2003). The role of atrial dilatation in the domestication of atrial fibrillation. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, 82, 151–162.
Dandona, P., Aljada, A., Chaudhuri, A., Mohanty, P., & Garg, R. (2005). Metabolic syndrome: a comprehensive perspective based on interactions between obesity, diabetes, and inflammation. Circulation, 111, 1448–1454.
Korantzopoulos, P., Kolettis, T. M., Galaris, D., & Goudevenos, J. A. (2007). The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis and perpetuation of atrial fibrillation. International Journal of Cardiology, 115, 135–143.
Ng, C. Y., Liu, T., Shehata, M., Stevens, S., Chugh, S. S., & Wang, X. (2011). Meta-analysis of obstructive sleep apnea as predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation. The American Journal of Cardiology, 108, 47–51.
Dewire, J., & Calkins, H. (2010). State-of-the-art and emerging technologies for atrial fibrillation ablation. Nature Reviews Cardiology, 7, 129–138.
Financial support
Dr. Kizer is supported by R01 HL094555 from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, K.J., Cho, S.I., Tiwari, N. et al. Impact of metabolic syndrome on the risk of atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 39, 211–223 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-013-9863-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-013-9863-x