Abstract
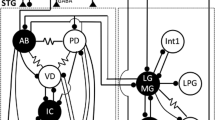
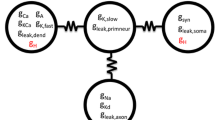
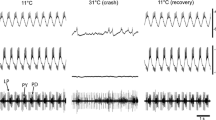
Neuronal networks produce reliable functional output throughout the lifespan of an animal despite ceaseless molecular turnover and a constantly changing environment. Central pattern generators, such as those of the crustacean stomatogastric ganglion (STG), are able to robustly maintain their functionality over a wide range of burst periods. Previous experimental work involving extracellular recordings of the pyloric pattern of the STG has demonstrated that as the burst period varies, the inter-neuronal delays are altered proportionally, resulting in burst phases that are roughly invariant. The question whether spike delays within bursts are also proportional to pyloric period has not been explored in detail. The mechanism by which the pyloric neurons accomplish phase maintenance is currently not obvious. Previous studies suggest that the co-regulation of certain ion channel properties may play a role in governing neuronal activity. Here, we observed in long-term recordings of the pyloric rhythm that spike delays can vary proportionally with burst period, so that spike phase is maintained. We then used a conductance-based model neuron to determine whether co-varying ionic membrane conductances results in neural output that emulates the experimentally observed phenomenon of spike phase maintenance. Next, we utilized a model neuron database to determine whether conductance correlations exist in model neuron populations with highly maintained spike phases. We found that co-varying certain conductances, including the sodium and transient calcium conductance pair, causes the model neuron to maintain a specific spike phase pattern. Results indicate a possible relationship between conductance co-regulation and phase maintenance in STG neurons.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard, P., & De Schutter, E. (2006). Complex parameter landscape for a complex neuron model. PLoS Computational Biology, 2(7), e94. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.0020094.
Ball, J. M., Franklin, C. C., Tobin, A. E., Schulz, D. J., & Nair, S. S. (2010). Coregulation of ion channel conductances preserves output in a computational model of a crustacean cardiac motor neuron. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(25), 8637–8649.
Baro, D. J., Levini, R. M., Kim, M. T., Willms, A. R., Lanning, C. C., Rodriguez, H. E., et al. (1997). Quantitative single-cell-reverse transcription-PCR demonstrates that A-current magnitude varies as a linear function of shal gene expression in identified stomatogastric neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 17(17), 6597–6610.
Brochini, L., Carelli, P. V., & Pinto, R. D. (2011). Single synapse information coding in intraburst spike patterns of central pattern generator motor neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(34), 12297–12306.
Bucher, D., Prinz, A. A., & Marder, E. (2005). Animal-to-animal variability in motor pattern production in adults and during growth. Journal of Neuroscience, 25(7), 1611–1619.
Dayan, P., & Abbott, L. F. (2001). Theoretical neuroscience. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Goldman, M. S., Golowasch, J., Marder, E., & Abbott, L. F. (2001). Global structure, robustness, and modulation of neuronal models. Journal of Neuroscience, 21(14), 5229–5238.
Golowasch, J., Goldman, M. S., Abbott, L. F., & Marder, E. (2002). Failure of averaging in the construction of a conductance-based neuron model. Journal of Neurophysiology, 87(2), 1129–1131.
Graubard, K. (1978). Synaptic transmission without action potentials: input–output properties of a nonspiking presynaptic neuron. Journal of Neurophysiology, 41(4), 1014–1025.
Hooper, S. L. (1997a). Phase maintenance in the pyloric pattern of the lobster (Panulirus interruptus) stomatogastric ganglion. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 4(3), 191–205.
Hooper, S. L. (1997b). The pyloric pattern of the lobster (Panulirus interruptus) stomatogastric ganglion comprises two phase-maintaining subsets. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 4(3), 207–219.
Hooper, S. L., & Weaver, A. L. (2000). Motor neuron activity is often insufficient to predict motor response. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 10(6), 676–682.
Hudson, A. E., & Prinz, A. A. (2010). Conductance ratios and cellular identity. PLoS Computational Biology, 6(7), e1000838. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000838.
Huguenard, J. R., & McCormick, D. A. (1992). Simulation of the currents involved in rhythmic oscillations in thalamic relay neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 68(4), 1373–1383.
Khorkova, O., & Golowasch, J. (2007). Neuromodulators, not activity, control coordinated expression of ionic currents. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(32), 8709–8718.
Lago-Fernandez, L. F. (2007). Spike alignment in bursting neurons. Neurocomputing, 70, 1788–1791.
Latorre, R., Rodriguez, F. B., & Varona, P. (2006). Neural signatures: multiple coding in spiking-bursting cells. Biological Cybernetics, 95(2), 169–183.
LeMasson, G., Marder, E., & Abbott, L. F. (1993). Activity-dependent regulation of conductances in model neurons. Science, 259(5103), 1915–1917.
Levitan, I. B. (1988). Modulation of ion channels in neurons and other cells. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 11, 119–136.
Liu, Z., Golowasch, J., Marder, E., & Abbott, L. F. (1998). A model neuron with activity-dependent conductances regulated by multiple calcium sensors. Journal of Neuroscience, 18(7), 2309–2320.
MacLean, J. N., Zhang, Y., Johnson, B. R., & Harris-Warrick, R. M. (2003). Activity-independent homeostasis in rhythmically active neurons. Neuron, 37(1), 109–120.
MacLean, J. N., Zhang, Y., Goeritz, M. L., Casey, R., Oliva, R., Guckenheimer, J., et al. (2005). Activity-independent coregulation of IA and Ih in rhythmically active neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 94(5), 3601–3617.
Marder, E. (1997). Computational dynamics in rhythmic neural circuits. The Neuroscientist, 3, 295–302.
Marder, E., & Bucher, D. (2007). Understanding circuit dynamics using the stomatogastric nervous system of lobsters and crabs. Annual Review of Physiology, 69, 291–316.
Morris, L. G., & Hooper, S. L. (1997). Muscle response to changing neuronal input in the lobster (Panulirus interruptus) stomatogastric system: spike number- versus spike frequency-dependent domains. Journal of Neuroscience, 17(15), 5956–5971.
Morris, L. G., Thuma, J. B., & Hooper, S. L. (2000). Muscles express motor patterns of non-innervating neural networks by filtering broad-band input. Nature Neuroscience, 3(3), 245–250.
Prinz, A. A., Billimoria, C. P., & Marder, E. (2003a). Alternative to hand-tuning conductance-based models: construction and analysis of databases of model neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 90(6), 3998–4015.
Prinz, A. A., Thirumalai, V., & Marder, E. (2003b). The functional consequences of changes in the strength and duration of synaptic inputs to oscillatory neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 23(3), 943–954.
Prinz, A. A., Bucher, D., & Marder, E. (2004). Similar network activity from disparate circuit parameters. Nature Neuroscience, 7(12), 1345–1352.
Raper, J. A. (1979). Nonimpulse-mediated synaptic transmission during the generation of a cyclic motor program. Science, 205(4403), 304–306.
Schulz, D. J., Goaillard, J. M., & Marder, E. (2006). Variable channel expression in identified single and electrically coupled neurons in different animals. Nature Neuroscience, 9(3), 356–362.
Schulz, D. J., Goaillard, J. M., & Marder, E. E. (2007). Quantitative expression profiling of identified neurons reveals cell-specific constraints on highly variable levels of gene expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(32), 13187–13191.
Selverston, A. I. (2010). Invertebrate central pattern generator circuits. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 365(1551), 2329–2345.
Selverston, A. I., & Moulins, M. (1985). Oscillatory neural networks. Annual Review of Physiology, 47, 29–48.
Swensen, A. M., & Bean, B. P. (2003). Ionic mechanisms of burst firing in dissociated Purkinje neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 23(29), 9650–9663.
Swensen, A. M., & Bean, B. P. (2005). Robustness of burst firing in dissociated purkinje neurons with acute or long-term reductions in sodium conductance. Journal of Neuroscience, 25(14), 3509–3520.
Szucs, A., Pinto, R. D., Rabinovich, M. I., Abarbanel, H. D., & Selverston, A. I. (2003). Synaptic modulation of the interspike interval signatures of bursting pyloric neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology, 89(3), 1363–1377.
Tobin, A. E., Cruz-Bermúdez, N. D., Marder, E., & Schulz, D. J. (2009). Correlations in ion channel mRNA in rhythmically active neurons. PLoS One, 4(8), e6742. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006742.
Turrigiano, G., LeMasson, G., & Marder, E. (1995). Selective regulation of current densities underlies spontaneous changes in the activity of cultured neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 15(5 Pt 1), 3640–3652.
Acknowledgements
We thank Amber Hudson for informative discussions and valuable comments on the manuscript. We also thank the reviewers of the manuscript for their constructive criticism. This work was supported by grants from the National Institute of Health/National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (1F31NS071834-01 to SA and R01 NS054911 to AP), two National Science Foundation IGERT awards (to SA and WS), and a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship (to WS).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Action Editor: Frances K. Skinner
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 411 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soofi, W., Archila, S. & Prinz, A.A. Co-variation of ionic conductances supports phase maintenance in stomatogastric neurons. J Comput Neurosci 33, 77–95 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-011-0375-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-011-0375-3