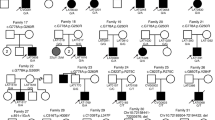
Autism is a heterogeneous neurodevelopmental disorder with a 3–4 times higher sex ratio in males than females. X chromosome genes may contribute to this higher sex ratio through unusual skewing of X chromosome inactivation. We studied X chromosome skewness in 30 females with classical autism and 35 similarly aged unaffected female siblings as controls using the polymorphic androgen receptor (AR) gene. Significantly, increased X chromosome skewness (e.g., >80:20%) was detected in our autism group (33%) compared to unaffected females (11%). X chromosome skewness was also seen in 50% of the mothers with autistic daughters. No mutation was seen in the promoter region of the XIST gene reported to be involved in X chromosome inactivation in our subjects. X chromosome skewness has been reported in female carriers of other neurological disorders such as X-linked mental retardation, adrenoleukodystrophy and Rett syndrome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen R. C., Zoghbi H. Y., Moseley A. B., Rosenblatt H. M., Belmont J. W., (1992). Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation American Journal of Human Genetics 51: 1229–1239
Azofeifa J., Voit T., Hubner C., Cremer M., (1995). X-chromosome methylation in manifesting and healthy carries of dystrophinopathies: Concordance of activation ratios among first degree female relatives and skewed inactivation as cause of the affected phenotypes Human Genetics 96: 167–176
Brown C. J., Carrel L., Willard H. F., (1997). Expression of genes from the human active and inactive X chromosomes American Journal of Human Genetics 60: 1333–1343
Brown C. J., Hendrich B. D., Rupertt J. L., Lafreniere R. G., Xing Y., Lawrence J., Willard H. F., (1992). The human XIST gene: Analysis of a 17 kb inactive X-specific RNA that contains conserved repeats and is highly localized within the nucleus Cell 71: 527–542
Brown C. J., Lafreniere R. G., Powers V. E., Sebastio G., Ballabio A., et al. (1991). Localization of the X inactivation center on the human X chromosome in Xq13 Nature 349: 82–84
Carrel L., Cottle A. A., Goglin K. C., Willard H. F., (1999). A first-generation X-inactivation profile of the human X chromosome Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 7: 14440–14444
Devriendt K., Matthijs G., Legius E., Schollen E., Blockmans D., van Geet C., Degreef H., Cassiman J. J., Fryns J. P., (1997). Skewed X-chromosome inactivation in female carriers of dyskeratosis congenita American Journal of Human Genetics 60: 581–587
Harris A., Collins J., Vetrie D., Cole C., Bobrow M., (1992). X inactivation as a mechanism of selection against lethal alleles: Further investigation of incontinentia pigmenti and X linked lymphoproliferative disease Journal of Medical Genetics 29: 608–614
Ishikawa-Brush Y., Powell J. F., Bolton P., Miller A. P., Francis F., Willard H. F., Lehrach H., Monaco A. P., (1997). Autism and multiple exostoses associated with an X;8 translocation occurring within the GRPR gene and 3′ to the SDC2 gene Human Molecular Genetics 6: 1241–1250
Jamain S., Quach H., Betancur C., Rastam M., Colineaux C., Gillberg I. C., Soderstrom H., Giros B., Leboyer M., Gillberg C., Bourgeron T., (2003). Mutations of the X-linked genes encoding neuroligins NLGN3 and NLGN4 are associated with autism. Paris Autism Research International Sibpair Study Nature Genetics 34: 27–29
Karasawa M., Tsukamoto N., Yamane A., Okamoto K., Maehara T., Yokohama A., Nojima Y., Omine M., (2001). Analysis of the distribution of CAG repeats and X-chromosome inactivation status of HUMARA gene in healthy female subjects using improved fluorescence-based assay International Journal of Hematology 74: 281–286
Lau A. W., Brown C. J., Penaherrera M., Langlois S., Kalousek D. K., Robinson W. P., (1997). Skewed X-chromosome inactivation is common in fetuses or newborns associated with confined placental mosaicism American Journal of Human Genetics 61: 1353–1361
Lord C., Rutter M., Le Couteur A., (1994). Autism diagnostic interview—revised: A revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 24: 659–685
Lyon M. F., (1961). Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.) Nature 190: 372–373
Maier E. M., Kammerer S., Muntau A. C., Wichers M., Braun A., Roscher A. A., (2002). Symptoms in carriers of adrenoleukodystrophy relate to skewed X inactivation Annals of Neurology 52: 683–688
Migeon B. R., (1998). Non-random X chromosome inactivation in mammalian cells Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics 80: 142–148
Naumova A. K., Plenge R. M., Bird L. M., Leppert M., Morgan K., Willard H. F., Sapienza C., (1996). Heritability of X chromosome—inactivation phenotype in a large family American Journal of Human Genetics 58: 1111–1119
Penny G. D., Kay G. F., Sheardown S. A., Rastan S., Brockdorff N., (1996). Requirement for XIST in X chromosome inactivation Nature 379: 131–137
Plenge R. M., Hendrich B. D., Schwartz C., Arena F., Naumova A., Sapienza C., Winter R. M, Willard H. F., (1997). A promoter mutation in the XIST gene in two unrelated families with skewed X-chromosome inactivation Nature Genetics 17: 353–356
Plenge R. M., Stevenson R. A., Lubs H. A., Schwartz C. E., Willard H. F., (2002). Skewed X-chromosome inactivation is a common feature of X-linked mental retardation disorders American Journal of Human Genetics 71: 168–173
Rao P. N., Klinepeter K., Stewart W., Hayworth R., Grubs R., Pettenati M. J., (1994). Molecular cytogenetic analysis of duplication Xp in a male: Further delineation of a possible sex influencing region on the X chromosome Human Genetics 94: 149–153
Russell L. B., (1963). Mammalian X-chromosome action: Inactivation limited in spread and region of origin Science 140: 976–978
Sangha K. K., Stephenson M. D., Brown C. J., Robinson W. P., (1999). Extremely skewed X-chromosome inactivation is increased in women with recurrent spontaneous abortion American Journal of Human Genetics, 65: 913–917
Sun Y. J., Baumer A., (1999). Nonrandom X inactivation and selection of fragile X full mutation in fetal fibroblasts American Journal of Medical Genetics 86: 162–164
Thomas N. S., Sharp A. J., Browne C. E., Skuse D., Hardie C., Dennis N. R., (1999). Xp deletions associated with autism in three females Human Genetics 104: 43–48
Villard L., Levy N., Xiang F., Kpebe A., Labelle V., Chevillard C., Zhang Z., Schwartz C. E., Tardieu M., Chelly J., Anvret M., Fontes M., (2001). Segregation of a totally skewed pattern of X chromosome inactivation in four familial cases of Rett syndrome without MECP2 mutation: Implications for the disease Journal of Medical Genetics 38: 435–442
Volkmar F. R., Szatmari P., Sparrow S. S., (1993). Sex differences in pervasive developmental disorder Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 23: 579–591
Willard H. F., (1995). The sex chromosome and X-chromosome inactivation. In: Scriver C. R., Beaudet A. L., Sly W. S., Valle D., (Eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, 717–737
Yonan A. L., Alarcon M., Cheng R., Magnusson P. K., Spence S. J., Palmer A. A., Grunn A., Juo S. H., Terwilliger J. D., Liu J., Cantor R. M., Geschwind D. H., Gilliam T. C.. (2003). A genomewide screen of 345 families for autism-susceptibility loci American Journal of Human Genetics 73: 886–897
Yoshioka M., Yorifuji T., Mituyoshi I., (1998). Skewed X inactivation in manifesting carriers of Duchenne muscular dystrophy Clinical Genetics 53: 102–107
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the AGRE families without whom none of this research would be possible. The AGRE Program, founded by Cure Autism Now, is supported through private donations from Cure Autism Now and by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) to UCLA and collaborating investigators. Continual scientific oversight is provided by the AGRE Scientific Steering Committee, chaired by Dan Geschwind, M.D., Ph.D., Director of the Neurogenetics Program, Department of Neurology, UCLA. Partial funding support for this study was from CMH Special Gift Funds (GL 01.2650).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talebizadeh, Z., Bittel, D., Veatch, O. et al. Brief Report: Non-Random X Chromosome Inactivation in Females with Autism. J Autism Dev Disord 35, 675–681 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-005-0011-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-005-0011-z