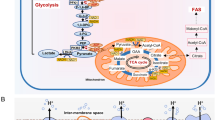
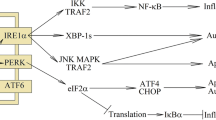
Abstract
Chronic low-grade inflammation is now widely accepted as one of the most important contributors to metabolic disorders. Glycoprotein 130 (gp130) cytokines are involved in the regulation of metabolic activity. Studies have shown that several gp130 cytokines, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), oncostatin M (OSM), ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), and cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1), have divergent effects on adipogenesis, lipolysis, and insulin sensitivity as well as food intake. In this review, we will summarize the present knowledge about gp130 cytokines, including IL-6, LIF, CNTF, CT-1, and OSM, in adipocyte biology and metabolic activities in conditions such as obesity, cachexia, and type 2 diabetes. It is valuable to explore the diverse actions of these gp130 cytokines on the regulation of the biological functions of adipocytes, which will provide potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of obesity and cachexia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
White, U.A., and J.M. Stephens. 2011. The gp130 receptor cytokine family: Regulators of adipocyte development and function. Current Pharmaceutical Design 17 (4): 340–346.
Fujio, Y., M. Maeda, T. Mohri, M. Obana, T. Iwakura, A. Hayama, T. Yamashita, H. Nakayama, and J. Azuma. 2011. Glycoprotein 130 cytokine signal as a therapeutic target against cardiovascular diseases. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 117 (4): 213–222.
Ernst, M., and B.J. Jenkins. 2004. Acquiring signalling specificity from the cytokine receptor gp130. Trends in Genetics 20 (1): 23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2003.11.003.
Kajimura, S. 2017. Adipose tissue in 2016: advances in the understanding of adipose tissue biology. Nature Reviews. Endocrinology 13 (2): 69–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2016.211.
Murakami, S. 2017. The physiological and pathophysiological roles of taurine in adipose tissue in relation to obesity. Life Sciences 186: 80–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.08.008.
White, U.A., W.C. Stewart, and J.M. Stephens. 2011. Gp130 cytokines exert differential patterns of crosstalk in adipocytes both in vitro and in vivo. Obesity (Silver Spring) 19 (5): 903–910. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2010.293.
Fruhbeck, G., J. Gomez-Ambrosi, F.J. Muruzabal, and M.A. Burrell. 2001. The adipocyte: a model for integration of endocrine and metabolic signaling in energy metabolism regulation. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism 280 (6): E827–E847. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.2001.280.6.E827.
Mohamed-Ali, V., S. Goodrick, A. Rawesh, D.R. Katz, J.M. Miles, J.S. Yudkin, S. Klein, and S.W. Coppack. 1997. Subcutaneous adipose tissue releases interleukin-6, but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in vivo. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 82 (12): 4196–4200. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.82.12.4450.
Lazar, M.A. 2005. How obesity causes diabetes: not a tall tale. Science 307 (5708): 373–375. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1104342.
Sabio, G., M. Das, A. Mora, Z. Zhang, J.Y. Jun, H.J. Ko, T. Barrett, J.K. Kim, and R.J. Davis. 2008. A stress signaling pathway in adipose tissue regulates hepatic insulin resistance. Science 322 (5907): 1539–1543. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1160794.
Klover, P.J., T.A. Zimmers, L.G. Koniaris, and R.A. Mooney. 2003. Chronic exposure to interleukin-6 causes hepatic insulin resistance in mice. Diabetes 52 (11): 2784–2789.
Khaodhiar, L., P.R. Ling, G.L. Blackburn, and B.R. Bistrian. 2004. Serum levels of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein correlate with body mass index across the broad range of obesity. JPEN Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 28 (6): 410–415. https://doi.org/10.1177/0148607104028006410.
Bastard, J.P., C. Jardel, E. Bruckert, P. Blondy, J. Capeau, M. Laville, H. Vidal, and B. Hainque. 2000. Elevated levels of interleukin 6 are reduced in serum and subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese women after weight loss. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 85 (9): 3338–3342. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.85.9.6839.
Matthews, V.B., T.L. Allen, S. Risis, M.H. Chan, D.C. Henstridge, N. Watson, L.A. Zaffino, et al. 2010. Interleukin-6-deficient mice develop hepatic inflammation and systemic insulin resistance. Diabetologia 53 (11): 2431–2441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-010-1865-y.
Wallenius, V., K. Wallenius, B. Ahren, M. Rudling, H. Carlsten, S.L. Dickson, C. Ohlsson, and J.O. Jansson. 2002. Interleukin-6-deficient mice develop mature-onset obesity. Nature Medicine 8 (1): 75–79. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0102-75.
Mauer, J., B. Chaurasia, J. Goldau, M.C. Vogt, J. Ruud, K.D. Nguyen, S. Theurich, A.C. Hausen, J. Schmitz, H.S. Brönneke, E. Estevez, T.L. Allen, A. Mesaros, L. Partridge, M.A. Febbraio, A. Chawla, F.T. Wunderlich, and J.C. Brüning. 2014. Signaling by IL-6 promotes alternative activation of macrophages to limit endotoxemia and obesity-associated resistance to insulin. Nature Immunology 15 (5): 423–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2865.
Scheller, J., A. Chalaris, D. Schmidt-Arras, and S. Rose-John. 2011. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1813 (5): 878–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.01.034.
Kraakman, M.J., T.L. Allen, M. Whitham, P. Iliades, H.L. Kammoun, E. Estevez, G.I. Lancaster, and M.A. Febbraio. 2013. Targeting gp130 to prevent inflammation and promote insulin action. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 15 (Suppl 3): 170–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12170.
Jostock, T., J. Mullberg, S. Ozbek, R. Atreya, G. Blinn, N. Voltz, M. Fischer, M.F. Neurath, and S. Rose-John. 2001. Soluble gp130 is the natural inhibitor of soluble interleukin-6 receptor transsignaling responses. European Journal of Biochemistry 268 (1): 160–167.
Kraakman, M.J., H.L. Kammoun, T.L. Allen, V. Deswaerte, D.C. Henstridge, E. Estevez, V.B. Matthews, B. Neill, D.A. White, A.J. Murphy, L. Peijs, C. Yang, S. Risis, C.R. Bruce, X.J. du, A. Bobik, R.S. Lee-Young, B.A. Kingwell, A. Vasanthakumar, W. Shi, A. Kallies, G.I. Lancaster, S. Rose-John, and M.A. Febbraio. 2015. Blocking IL-6 trans-signaling prevents high-fat diet-induced adipose tissue macrophage recruitment but does not improve insulin resistance. Cell Metabolism 21 (3): 403–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.02.006.
Sun, K., J. Tordjman, K. Clement, and P.E. Scherer. 2013. Fibrosis and adipose tissue dysfunction. Cell Metabolism 18 (4): 470–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.06.016.
Sun, K., J. Park, O.T. Gupta, W.L. Holland, P. Auerbach, N. Zhang, R. Goncalves Marangoni, S.M. Nicoloro, M.P. Czech, J. Varga, T. Ploug, Z. An, and P.E. Scherer. 2014. Endotrophin triggers adipose tissue fibrosis and metabolic dysfunction. Nature Communications 5: 3485. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4485.
Sun, K., N. Halberg, M. Khan, U.J. Magalang, and P.E. Scherer. 2013. Selective inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha ameliorates adipose tissue dysfunction. Molecular and Cellular Biology 33 (5): 904–917. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00951-12.
Timper, K., J.L. Denson, S.M. Steculorum, C. Heilinger, L. Engstrom-Ruud, C.M. Wunderlich, S. Rose-John, F.T. Wunderlich, and J.C. Bruning. 2017. IL-6 Improves Energy and Glucose Homeostasis in Obesity via Enhanced Central IL-6 trans-Signaling. Cell Reports 19 (2): 267–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.03.043.
Moreno-Indias, I., and F.J. Tinahones. 2015. Impaired adipose tissue expandability and lipogenic capacities as ones of the main causes of metabolic disorders. Journal Diabetes Research 2015: 970375. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/970375.
Yang, Y., D. Ju, M. Zhang, and G. Yang. 2008. Interleukin-6 stimulates lipolysis in porcine adipocytes. Endocrine 33 (3): 261–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-008-9085-7.
Petersen, E.W., A.L. Carey, M. Sacchetti, G.R. Steinberg, S.L. Macaulay, M.A. Febbraio, and B.K. Pedersen. 2005. Acute IL-6 treatment increases fatty acid turnover in elderly humans in vivo and in tissue culture in vitro. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism 288 (1): E155–E162. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00257.2004.
Petruzzelli, M., M. Schweiger, R. Schreiber, R. Campos-Olivas, M. Tsoli, J. Allen, M. Swarbrick, S. Rose-John, M. Rincon, G. Robertson, R. Zechner, and E.F. Wagner. 2014. A switch from white to brown fat increases energy expenditure in cancer-associated cachexia. Cell Metabolism 20 (3): 433–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.06.011.
Morelli, M., M. Gaggini, G. Daniele, P. Marraccini, R. Sicari, and A. Gastaldelli. 2013. Ectopic fat: the true culprit linking obesity and cardiovascular disease? Thrombosis and Haemostasis 110 (4): 651–660. https://doi.org/10.1160/th13-04-0285.
Gaggini, M., C. Saponaro, and A. Gastaldelli. 2015. Not all fats are created equal: adipose vs. ectopic fat, implication in cardiometabolic diseases. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig 22 (1): 7–18. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2015-0006.
Abdullahi, A., and M.G. Jeschke. 2016. White Adipose Tissue Browning: A Double-edged Sword. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism 27 (8): 542–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2016.06.006.
Wueest, S., F. Item, F.C. Lucchini, T.D. Challa, W. Muller, M. Bluher, and D. Konrad. 2016. Mesenteric Fat Lipolysis Mediates Obesity-Associated Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 65 (1): 140–148. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-0941.
Perry, R.J., J.G. Camporez, R. Kursawe, P.M. Titchenell, D. Zhang, C.J. Perry, M.J. Jurczak, et al. 2015. Hepatic acetyl CoA links adipose tissue inflammation to hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Cell 160 (4): 745–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.012.
Wueest, S., C.I. Laesser, M. Boni-Schnetzler, F. Item, F.C. Lucchini, M. Borsigova, W. Muller, M.Y. Donath, and D. Konrad. 2018. IL-6-Type Cytokine Signaling in Adipocytes Induces Intestinal GLP-1 Secretion. Diabetes 67 (1): 36–45. https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-0637.
Wueest, S., and D. Konrad. 2018. The role of adipocyte-specific IL-6-type cytokine signaling in FFA and leptin release. Adipocyte 7 (3): 226–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/21623945.2018.1493901.
Akiyama, Y., N. Kajimura, J. Matsuzaki, Y. Kikuchi, N. Imai, M. Tanigawa, and K. Yamaguchi. 1997. In vivo effect of recombinant human leukemia inhibitory factor in primates. Japanese Journal of Cancer Research 88 (6): 578–583.
Nicola, N.A., and J.J. Babon. 2015. Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews 26 (5): 533–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.07.001.
Aubert, J., S. Dessolin, N. Belmonte, M. Li, F.R. McKenzie, L. Staccini, P. Villageois, B. Barhanin, A. Vernallis, A.G. Smith, G. Ailhaud, and C. Dani. 1999. Leukemia inhibitory factor and its receptor promote adipocyte differentiation via the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 274 (35): 24965–24972.
Gimble, J.M., F. Wanker, C.S. Wang, H. Bass, X. Wu, K. Kelly, G.D. Yancopoulos, and M.R. Hill. 1994. Regulation of bone marrow stromal cell differentiation by cytokines whose receptors share the gp130 protein. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 54 (1): 122–133. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.240540113.
Hogan, J.C., and J.M. Stephens. 2005. Effects of leukemia inhibitory factor on 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The Journal of Endocrinology 185 (3): 485–496. https://doi.org/10.1677/joe.1.05980.
White, U.A., W.C. Stewart, R.L. Mynatt, and J.M. Stephens. 2008. Neuropoietin attenuates adipogenesis and induces insulin resistance in adipocytes. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 283 (33): 22505–22512. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M710462200.
Mori, M., K. Yamaguchi, and K. Abe. 1989. Purification of a lipoprotein lipase-inhibiting protein produced by a melanoma cell line associated with cancer cachexia. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 160 (3): 1085–1092.
Metcalf, D., N.A. Nicola, and D.P. Gearing. 1990. Effects of injected leukemia inhibitory factor on hematopoietic and other tissues in mice. Blood 76 (1): 50–56.
Marshall, M.K., W. Doerrler, K.R. Feingold, and C. Grunfeld. 1994. Leukemia inhibitory factor induces changes in lipid metabolism in cultured adipocytes. Endocrinology 135 (1): 141–147. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.135.1.8013346.
Arora, G.K., A. Gupta, S. Narayanan, T. Guo, P. Iyengar, and R.E. Infante. 2018. Cachexia-associated adipose loss induced by tumor-secreted leukemia inhibitory factor is counterbalanced by decreased leptin. JCI Insight 3 (14). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.121221.
Beretta, E., H. Dhillon, P.S. Kalra, and S.P. Kalra. 2002. Central LIF gene therapy suppresses food intake, body weight, serum leptin and insulin for extended periods. Peptides 23 (5): 975–984.
Grossberg, A.J., J.M. Scarlett, X. Zhu, D.D. Bowe, A.K. Batra, T.P. Braun, and D.L. Marks. 2010. Arcuate nucleus proopiomelanocortin neurons mediate the acute anorectic actions of leukemia inhibitory factor via gp130. Endocrinology 151 (2): 606–616. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-1135.
Lee, S., J. Lee, G.M. Kang, and M.S. Kim. 2018. Leptin directly regulate intrinsic neuronal excitability in hypothalamic POMC neurons but not in AgRP neurons in food restricted mice. Neuroscience Letters 681: 105–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2018.05.041.
Miller, R.G., J.H. Petajan, W.W. Bryan, C. Armon, R.J. Barohn, J.C. Goodpasture, R.J. Hoagland, G.J. Parry, M.A. Ross, and S.C. Stromatt. 1996. A placebo-controlled trial of recombinant human ciliary neurotrophic (rhCNTF) factor in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis rhCNTF ALS Study Group. Ann Neurol 39 (2): 256–260. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410390215.
A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial of subcutaneous recombinant human ciliary neurotrophic factor (rHCNTF) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. ALS CNTF Treatment Study Group. 1996. Neurology 46 (5): 1244–1249.
Bluher, S., S. Moschos, J. Bullen Jr., E. Kokkotou, E. Maratos-Flier, S.J. Wiegand, M.W. Sleeman, and C.S. Mantzoros. 2004. Ciliary neurotrophic factorAx15 alters energy homeostasis, decreases body weight, and improves metabolic control in diet-induced obese and UCP1-DTA mice. Diabetes 53 (11): 2787–2796.
Ott, V., M. Fasshauer, A. Dalski, H.H. Klein, and J. Klein. 2002. Direct effects of ciliary neurotrophic factor on brown adipocytes: evidence for a role in peripheral regulation of energy homeostasis. The Journal of Endocrinology 173 (2): R1–R8.
Liu, Q.S., M. Gao, S.Y. Zhu, S.J. Li, L. Zhang, Q.J. Wang, and G.H. Du. 2007. The novel mechanism of recombinant human ciliary neurotrophic factor on the anti-diabetes activity. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 101 (2): 78–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2007.00092.x.
Watt, M.J., A. Hevener, G.I. Lancaster, and M.A. Febbraio. 2006. Ciliary neurotrophic factor prevents acute lipid-induced insulin resistance by attenuating ceramide accumulation and phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in peripheral tissues. Endocrinology 147 (5): 2077–2085. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2005-1074.
Watt, M.J., N. Dzamko, W.G. Thomas, S. Rose-John, M. Ernst, D. Carling, B.E. Kemp, M.A. Febbraio, and G.R. Steinberg. 2006. CNTF reverses obesity-induced insulin resistance by activating skeletal muscle AMPK. Nature Medicine 12 (5): 541–548. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1383.
Duff, E., C.L. Li, D.L. Hartzell, Y.H. Choi, M.A. Della-Fera, and C.A. Baile. 2004. Ciliary neurotrophic factor injected icv induces adipose tissue apoptosis in rats. Apoptosis 9 (5): 629–634. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:APPT.0000038042.31683.7b.
Kokoeva, M.V., H. Yin, and J.S. Flier. 2005. Neurogenesis in the hypothalamus of adult mice: potential role in energy balance. Science 310 (5748): 679–683. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1115360.
Jin, H., R. Yang, G.A. Keller, A. Ryan, A. Ko, D. Finkle, T.A. Swanson, W. Li, D. Pennica, W.I. Wood, and N.F. Paoni. 1996. In vivo effects of cardiotrophin-1. Cytokine 8 (12): 920–926. https://doi.org/10.1006/cyto.1996.0123.
Zvonic, S., J.C. Hogan, P. Arbour-Reily, R.L. Mynatt, and J.M. Stephens. 2004. Effects of cardiotrophin on adipocytes. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (46): 47572–47579. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M403998200.
Moreno-Aliaga, M.J., N. Perez-Echarri, B. Marcos-Gomez, E. Larequi, F.J. Gil-Bea, B. Viollet, I. Gimenez, J.A. Martinez, J. Prieto, and M. Bustos. 2011. Cardiotrophin-1 is a key regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism. Cell Metabolism 14 (2): 242–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.05.013.
Lopez-Yoldi, M., M. Fernandez-Galilea, L.M. Laiglesia, E. Larequi, J. Prieto, J.A. Martinez, M. Bustos, and M.J. Moreno-Aliaga. 2014. Cardiotrophin-1 stimulates lipolysis through the regulation of main adipose tissue lipases. Journal of Lipid Research 55 (12): 2634–2643. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M055335.
Lopez-Yoldi, M., B. Marcos-Gomez, M.A. Romero-Lozano, N. Sainz, J. Prieto, J.A. Martinez, M. Bustos, and M.J. Moreno-Aliaga. 2017. Cardiotrophin-1 Regulates Adipokine Production in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and Adipose Tissue From Obese Mice. Journal of Cellular Physiology 232 (9): 2469–2477. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25590.
Zhu, S., F. Sun, W. Li, Y. Cao, C. Wang, Y. Wang, D. Liang, R. Zhang, S. Zhang, H. Wang, and F. Cao. 2011. Apelin stimulates glucose uptake through the PI3K/Akt pathway and improves insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 353 (1–2): 305–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0799-0.
Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U., A. De Vincentis, J. Argemi, G. Galati, E. Anso, G. Patti, and A. Picardi. 2013. Cardiotrophin-1 is not associated with carotid or coronary disease and is inversely associated with obesity in patients undergoing coronary angiography. Archives of Medical Science 9 (4): 635–639. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2013.37272.
Hung, H.C., F.H. Lu, H.Y. Ou, H.T. Wu, J.S. Wu, Y.C. Yang, and C.J. Chang. 2013. Increased cardiotrophin-1 in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and newly diagnosed diabetes. International Journal of Cardiology 169 (3): e33–e34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.08.112.
Hung, H.C., F.H. Lu, H.T. Wu, H.Y. Ou, Y.C. Yang, J.S. Wu, and C.J. Chang. 2015. Cardiotrophin-1 is inversely associated with obesity in non-diabetic individuals. Scientific Reports 5: 17438. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17438.
Natal, C., M.A. Fortuno, P. Restituto, A. Bazan, I. Colina, J. Diez, and N. Varo. 2008. Cardiotrophin-1 is expressed in adipose tissue and upregulated in the metabolic syndrome. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism 294 (1): E52–E60. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00506.2007.
Rendo-Urteaga, T., S. Garcia-Calzon, E. Martinez-Anso, M. Chueca, M. Oyarzabal, M.C. Azcona-Sanjulian, M. Bustos, M.J. Moreno-Aliaga, J.A. Martinez, and A. Marti. 2013. Decreased cardiotrophin-1 levels are associated with a lower risk of developing the metabolic syndrome in overweight/obese children after a weight loss program. Metabolism 62 (10): 1429–1436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2013.05.011.
Rose, T.M., and A.G. Bruce. 1991. Oncostatin M is a member of a cytokine family that includes leukemia-inhibitory factor, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and interleukin 6. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 88 (19): 8641–8645.
Rose, T.M., M.J. Lagrou, I. Fransson, B. Werelius, O. Delattre, G. Thomas, P.J. de Jong, G.J. Todaro, and J.P. Dumanski. 1993. The genes for oncostatin M (OSM) and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) are tightly linked on human chromosome 22. Genomics 17 (1): 136–140. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1993.1294.
Tanaka, M., T. Hara, N.G. Copeland, D.J. Gilbert, N.A. Jenkins, and A. Miyajima. 1999. Reconstitution of the functional mouse oncostatin M (OSM) receptor: molecular cloning of the mouse OSM receptor beta subunit. Blood 93 (3): 804–815.
Sanchez-Infantes, D., U.A. White, C.M. Elks, R.F. Morrison, J.M. Gimble, R.V. Considine, A.W. Ferrante, E. Ravussin, and J.M. Stephens. 2014. Oncostatin m is produced in adipose tissue and is regulated in conditions of obesity and type 2 diabetes. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 99 (2): E217–E225. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2013-3555.
Komori, T., M. Tanaka, E. Senba, A. Miyajima, and Y. Morikawa. 2013. Lack of oncostatin M receptor beta leads to adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance by switching macrophage phenotype. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 288 (30): 21861–21875. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.461905.
Komori, T., M. Tanaka, E. Senba, A. Miyajima, and Y. Morikawa. 2014. Deficiency of oncostatin M receptor beta (OSMRbeta) exacerbates high-fat diet-induced obesity and related metabolic disorders in mice. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 289 (20): 13821–13837. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.542399.
Komori, T., M. Tanaka, H. Furuta, T. Akamizu, A. Miyajima, and Y. Morikawa. 2015. Oncostatin M is a potential agent for the treatment of obesity and related metabolic disorders: a study in mice. Diabetologia 58 (8): 1868–1876. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-015-3613-9.
Hattori, K., T. Sumi, T. Yasui, M. Morimura, H. Nobeyama, E. Okamoto, M. Noriyuki, K. Honda, H. Kiyama, and O. Ishiko. 2004. VEGF mRNA in adipocytes increase with rebound weight-gain after diet-restriction. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 13 (3): 395–399.
Rega, G., C. Kaun, S. Demyanets, S. Pfaffenberger, K. Rychli, P.J. Hohensinner, S.P. Kastl, W.S. Speidl, T.W. Weiss, J.M. Breuss, A. Furnkranz, P. Uhrin, J. Zaujec, V. Zilberfarb, M. Frey, R. Roehle, G. Maurer, K. Huber, and J. Wojta. 2007. Vascular endothelial growth factor is induced by the inflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 and oncostatin m in human adipose tissue in vitro and in murine adipose tissue in vivo. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 27 (7): 1587–1595. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.107.143081.
Miyaoka, Y., M. Tanaka, T. Naiki, and A. Miyajima. 2006. Oncostatin M inhibits adipogenesis through the RAS/ERK and STAT5 signaling pathways. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 281 (49): 37913–37920. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M606089200.
Heinrich, P.C., I. Behrmann, S. Haan, H.M. Hermanns, G. Muller-Newen, and F. Schaper. 2003. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. The Biochemical Journal 374 (Pt 1): 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20030407.
Funding
This work was supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (No. 81673970 and No. 81874449).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, D., Wang, Y., Zhou, G. et al. Review: the Roles and Mechanisms of Glycoprotein 130 Cytokines in the Regulation of Adipocyte Biological Function. Inflammation 42, 790–798 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-00959-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-00959-6