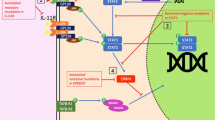
Abstract
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF-21) has been previously judged as a major metabolic regulator. In this paper, we show that FGF-21 has a potential role in anti-inflammation and immunoregulation. In vivo, treatment with exogenous FGF-21 can alleviate LPS-induced inflammation. In vitro, FGF-21 inhibited LPS-induced IL-1β expression in THP-1 cells. Furthermore, besides the NF-κB pathway, the mechanism of action of FGF-21 was observed to involve the elevation of IL-10 in the ERK1/2 pathway. This study clearly indicates that FGF21 can be used as an attractive target for the management of inflammatory disorders. This piece of research indicates that FGF-21 could have much value in the management of inflammatory disorders.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gariani, K., G. Drifte, I. Dunn-Siegrist, J. Pugin, and F.R. Jornayvaz. 2013. Increased FGF21 plasma levels in humans with sepsis and SIRS. Endocrine Connection. 2 (3): 146–153.
Dreiher, J., Y. Almog, C.L. Sprung, et al. 2012. Temporal trends in patient characteristics and survival of intensive care admissions with sepsis: a multicenter analysis. Critical Care Medicine 40 (3): 855–860.
Longo, C.J., D.K. Heyland, H.N. Fisher, et al. 2007. A long-term follow-up study investigating health-related quality of life and resource use in survivors of severe sepsis: comparison of recombinant human activated protein C with standard care. Critical Care 11 (6): R128.
Camporez, J.P., F.R. Jornayvaz, M. Petersen, D. Pesta, B.A. Guigni, J. Serr, D. Zhang, M. Kahn, V.T. Samuel, M.J. Jurczak, et al. 2013. Cellular mechanisms by which FGF21 improves insulin sensitivity in male mice. Endocrinology 154: 3099–3109.
Coskun, T., H.A. Bina, M.A. Schneider, J.D. Dunbar, C.C. Hu, Y. Chen, D.E. Moller, and A. Kharitonenkov. 2008. Fibroblast growth factor 21 corrects obesity in mice. Endocrinology 149: 6018–6027.
Kharitonenkov, A., T.L. Shiyanova, A. Koester, A.M. Ford, R. Micanovic, E.J. Galbreath, G.E. Sandusky, L.J. Hammond, J.S. Moyers, R.A. Owens, et al. 2005. FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. Journal of Clinical Investigation 115: 1627–1635.
Kharitonenkov, A., V.J. Wroblewski, A. Koester, Y.F. Chen, C.K. Clutinger, X.T. Tigno, B.C. Hansen, A.B. Shanafelt, and G.J. Etgen. 2007. The metabolic state of diabetic monkeys is regulated by fibroblast growth factor-21. Endocrinology 148: 774–781.
Wang, Wen-Fei, Si-Ming Li, Gui-Ping Ren, Wei Zheng, Yu-Jia Lu, Yin-Hang Yu, et al. 2014. Recombinant murine fibroblast growth factor 21 ameliorates obesity-related inflammation in monosodium glutamate-induced obesity rats. Endocrine. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0433-5.
Feingold, Kenneth R., Carl Grunfeld, Josef G. Heuer, Akanksha Gupta, Martin Cramer, Tonghai Zhang, et al. 2012. FGF21 is increased by inflammatory stimuli and protects leptin-deficient ob/ob mice from the toxicity of sepsis. Endocrinology 153 (6): 2689–2700.
Johnson, C.L., J.Y. Weston, S.A. Chadi, E.N. Fazio, M.W. Huff, A. Kharitonenkov, et al. 2009. Fibroblast growth factor 21 reduces the severity of cerulein-induced pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology 137: 1795–1804.
Li, S.M., W.F. Wang, L.H. Zhou, L. Ma, Y. An, W.J. Xu, T.H. Li, Y.H. Yu, D.S. Li, and Y. Liu. 2014, 2014. Fibroblast growth factor 21 expressions in white blood cells and sera of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus during gestation and postpartum. Endocrine. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0309-8.
Wang, Wen-fei, Lei Ma, Ming-yao Liu, Ting-ting Zhao, Tong Zhang, Yong-bi Yang, Hong-xue Cao, Xiao-hui Han, and De-shan Li. 2014. A novel function for fibroblast growth factor 21: stimulation of NADPH oxidase-dependent ROS generation. Endocrine. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0502-9.
Koch, L., D. Frommhold, K. Buschmann, et al. 2014, 2014. LPS-and LTA-induced expression of IL-6 and TNF-α in neonatal and adult blood: role of MAPKs and NF-κB. Mediators of Inflammation.
Kim, H.J., J. Hart, N. Knatz, et al. 2004. Janus kinase 3 down-regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-1 beta-converting enzyme activation by autocrine IL-10[J]. Journal of Immunology 172 (8): 4948–4955.
Cao, Z., M. Tanaka, C. Regnier, et al. 1999. NF-κB activation by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology 64 (1): 473–484.
Jacobs, R.F., D.R. Tabor, A.W. Burks, et al. 1989. Elevated interleukin-1 release by human alveolar macrophages during the adult respiratory distress syndrome[J]. American Review of Respiratory Disease 140 (6): 1686–1692.
Siler, T.M., J.E. Swierkosz, T.M. Hyers, et al. 2009. Immunoreactive interleukin-1 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of high-risk patients and patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Experimental Lung Research 15 (6): 881–894.
Kowluru, R.A., Q. Zhong, J.M. Santos, et al. 2014. Beneficial effects of the nutritional supplements on the development of diabetic retinopathy[J]. Nutrition and Metabolism 11 (1): 8.
Lee, M.S., S.E. Choi, E.S. Ha, et al. 2012. Fibroblast growth factor-21 protects human skeletal muscle myotubes from palmitate-induced insulin resistance by inhibiting stress kinase and NF-κB[J]. Metabolism 61 (8): 1142–1151.
Yu, Y., F. Bai, W. Wang, et al. 2015. Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects mouse brain against d-galactose induced aging via suppression of oxidative stress response and advanced glycation end products formation.[J]. Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 133 (1): 122.
Robertson, S.A., R.J. Skinner, and A.S. Care. 2006. Essential role for IL-10 in resistance to lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm labor in mice[J]. Journal of Immunology 177 (7): 4888–4896.
Guarda, G., M. Braun, F. Staehli, et al. 2011. Type I interferon inhibits interleukin-1 production and inflammasome activation[J]. Immunity 34 (2): 213–223.
Saraiva, Margarida, and Anne O’Garra. 2010. The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells[J]. Nature Reviews Immunology 10 (3): 170.
Lin, X.L., X.L. He, J.F. Zeng, et al. 2014. FGF21 increases cholesterol efflux by upregulating ABCA1 through the ERK1/2-PPARγ-LXRα pathway in THP1 macrophage-derived foam cells[J]. DNA and Cell Biology 33 (8): 514–521.
Funding
This study was funded by the “Young Talents” Project of Northeast Agricultural University (grant number 16QC27) and Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (grant number C2017023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Northeast Agricultural University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Jy., Wang, N., Khoso, M.H. et al. FGF-21 Elevated IL-10 Production to Correct LPS-Induced Inflammation. Inflammation 41, 751–759 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0729-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0729-3