Abstract
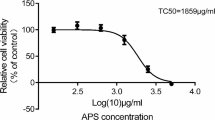
Grifola frondosa is an important fungal research resource. However, there was little report about hyperglycemic activity of Grifola frondosa polysaccharide on insulin resistance in vitro. In this study, the hypoglycemic activity of a polysaccharide obtained from Grifola frondosa (GFP) on HepG2 cell and hpyerglycemic mechanism were investigated. The purity of the isolated polysaccharides was examined by HPLC. In this research, it was found that GFP enhanced the absorption of glucose of HepG2 cells in a dose dependent manner at 24 h of 30 ugmL−1. GC-MS and FT-IR spectroscopy analysis results showed that glucose and galactose were the dominant monosaccharides in GFP and the major component of GFP was β-pyranoside. Western-blotting results showed that the HepG2 cell model treated with GFP activated the insulin receptor protein (IRS) in the cell membrane and increased phosphorylated-AktSer473 expression, which had an inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase (GSK-3). The down-regulation of GSK-3 stimulated synthesis of intracellular glycogen. The results above suggested that the GFP increased the metabolism of glucose and stimulated synthesis of intracellular glycogen through the Akt/GSK-3 pathway.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, I.Y., Kim, H.Y., Lee, S., Lee, H.G.: Effect of the degree of oxidation on the physicochemical and biological properties of Grifola frondosa polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 83, 1298–1302 (2011)
Cao, X.H., Wang, A.H., Jiao, R.Z., Wang, C.L., Mao, D.Z., Yan, L., et al.: Surfactin induces apoptosis and G2/M arrest in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells through cell cycle factor regulation. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 55(3), 163–171 (2009)
Chen, Q., Xia, Y.P., Qu, Z.Y.: Effects of ecdysteron on insulin sensitivity and Glc metabolism in insulin resistant cell model. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 22(4), 465–470 (2006)
Cross, D.A., Alessi, D.R., Cohen, P., Andjelkovich, M., Hemmings, B.A.: Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378, 785–789 (1995)
Cui, F.J., Tao, W.Y., Xu, Z.H., Guo, W.J., Xu, H.Y., Ao, Z.H., et al.: Structural analysis of anti-tumor heteropolysaccharide GFPS1b from the cultured mycelia of Grifola frondosa GF9801. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 395–401 (2007)
Defronzo, R.A., Bondonna, R.C., Ferranini, E.: Pathogenesis of NIDDM: a balanced overview. Diabetes Care 15, 318–337 (1992)
Eldar-Finkelman, H., Krebs, E.G.: Phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 by glycogen synthase kinase 3 impairs insulin action. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 94, 960–9664 (1997)
Elstrom, R.L., Bauer, D.E., Buzzai, M., Karnauskas, R., Harris, M.H., Plas, D.R., Zhuang, H., Cinalli, R.M., Alavi, A., Rudin, C.M., Thompson, C.B.: Akt stimulates aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 64, 3892–3899 (2004)
Fellah, A., Anjukandi, P., Waterland, M.R., Williams, M.A.K.: Determining the degree of methylesterification of pectin by ATR/FT-IR: Methodology optimization and comparison with theoretical calculations. Carbohydr. Polym. 78, 847–853 (2009)
Li, F., Yuan, Q., Rashid, F.: Isolation, purification and immunobiological activity of an new water-soluble bee pollen polysaccharide from Crataegus pinnatifida Bge. Carbohydr. Polym. 78, 80–88 (2009)
Ge, Y., Duan, Y.F., Fang, G.Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, S.: Polysaccharides from fruit calyx of Physalis alkekengi var. francheti: Isolation, purification, structural features and antioxidant activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 77, 188–193 (2009)
Gu, C.Q., Li, J., Chao, F.H.: Inhibition of hepatitis B virus by D-fraction from Grifola frondosa: Synergistic effect of combination with interferon-alpha in HepG2.2.15. Antivir. Res. 72(2), 162–165 (2006)
Guo, L.M., Zhang, R.X., Jia, Z.P., et al.: Effects of rehmannia glutinosa oligosaccharides on pro liferation of HepG2 and insulin resistant. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 32(13), 1328–1332 (2007)
Hnatyszyn, O., Mino, J., Ferraro, G., Acevedo, C.: The hypoglycemic effect of Phyllanthus sellowianus fractions in streptozotocin- induced diabetic mice. Phytomedicine 9, 556–559 (2002)
Kurushima, H., Kodama, N., Nanba, H.: Activities of polysaccharides obtain form Grifola frondosa on insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus induced by streptozotocin in mice. Mycoscience 41, 437–480 (2000)
Kubo, K.: Anti-diabetic activity present in the fruit body of Grifola frondosa (Maitake). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 17, 1106 (1990)
LeRoith, D., Gavrilova, O.: Mouse models created to study the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 38, 904–912 (2006)
Wang, L.-Y., Wang, Y., De-Sheng, X., Ruan, K.-F., Feng, Y., Wang, S.: MDG-1, a polysaccharide from Ophiopogon japonicus exerts hypoglycemic effects through the PI3K/Akt pathway in a diabetic KKAy mouse model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 143, 347–354 (2012)
Liu, X.H., Dong, Z., Fu, J.M., et al.: Effects of batephrine on insulin resisitance in HepG2 cells and its mechanism. Chin. J. New. Drugs. 17(12), 1026–1029 (2008)
Manning, B.D., Cantley, L.C.: AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129, 1261–1274 (2007)
Mu, Y.M., Jin, M.M., Chi, C., Lu, J.M., Pan, C.Y.: Therapeutic effects of rhein on the insulin resistance in liver of diabetic rats induced by streptozotocin. Diabetes 57, 717 (2008)
Xie, J.T., Zhou, Y.P.: Ginseng beery reduces blood glucose and body weight in db/db mice. Phytomedicine 9, 254–258 (2002)
Xu, J.S., Ma, M.W., Purcell, W.M.: Characterisation of some cytotoxic endpoints using rat liver and HepG2 spheroids as in vitro models and their application in hepatotoxicity studies. I. Glucose metabolism and enzyme release as cytotoxic markers. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 189, 100–111 (2003)
Xu, D.S., Feng, Y., Lin, X., Deng, H.L., Fang, J.N., Dong, Q.: Isolation, purification and structural analysis of a polysaccharide MDG-1 from Ophiopogon japonicus. Acta. Pharmacol. Sin. 40, 636–639 (2005)
Whiteman, E.L., Cho, H., Birnbaum, M.J.: Role of Akt/protein kinase B in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 13, 444–451 (2002)
Zhu, M.Y., Mo, J.G., He, C.S., Xie, H.P., Ma, N., Wang, C.J.: Extraction, characterization of polysaccharides from lycium barbarum and its effect on bone gene expression in rats. Carbohydr. Polym. 80, 672–676 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by these projects in China (2012BAD33B04, 2012AA022108, 2012GB2A100016, IRT1166, 31000768, 31171731 and 10ZCZDSY07000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Zhou, F., Chen, Y. et al. A polysaccharide from Grifola frondosa relieves insulin resistance of HepG2 cell by Akt-GSK-3 pathway. Glycoconj J 31, 355–363 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-014-9526-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-014-9526-x