Abstract
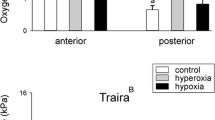
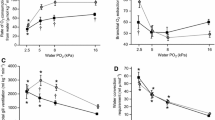
Hypoxic water and episodic air exposure are potentially life-threatening conditions that fish in tropical regions can face during the dry season. This study investigated the air-breathing behavior, oxygen consumption, and respiratory responses of the air-breathing (AB) armored catfish Pterygoplichthys anisitsi. The hematological parameters and oxygen-binding characteristics of whole blood and stripped hemoglobin and the intermediate metabolism of selected tissue in normoxia, different hypoxic conditions, and after air exposure were also examined. In normoxia, this species exhibited high activity at night and AB behavior (2–5 AB h−1). The exposure to acute severe hypoxia elicited the AB behavior (4 AB h−1) during the day. Under progressive hypoxia without access to the water surface, the fish were oxyregulators with a critical O2 tension, calculated as the inspired water O2 pressure, as 47 ± 2 mmHg. At water O2 tensions lower than 40 mmHg, the fish exhibited continuous apnea behavior. The blood exhibited high capacity for transporting O2, having a cathodic hemoglobin component with a high Hb–O2 affinity. Under severe hypoxia, the fish used anaerobic metabolism to maintain metabolic rate. Air exposure revealed physiological and biochemical traits similar to those observed under normoxic conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alton LA, White CR, Seymour RS (2007) Effect of aerial O2 partial pressure on bimodal gas exchange and air-breathing behaviour in Trichogaster leeri. J Exp Biol 210:2311–2319
Belão TC (2010) Respostas cardiorrespiratórias do teleósteo de respiração aérea, Clarias gariepinus exposto a hipóxia gradual. Ms thesis. Universidade Federal de São Carlos, São Carlos, SP, Brazil
Benesch RE, Benesch R, Yung S (1973) Equations for the spectrophotometric analysis of hemoglobin mixtures. Analyt Biochem 55:245–248
Bicudo JEPW, Johansen K (1979) Respiratory gas exchange in the airbreathing fish, Synbranchus marmoratus. Env Biol Fish 4:55–64
Bidinotto PM, Moraes G, Souza RHS (1997) Hepatic glycogen in eight tropical fresh w, ater teleost fish: a procedure for field determinations of micro samples. Bol Técn CEPTA 10:53–61
Caldwell CA, Hinshaw J (1994) Physiological and haematological responses in rainbow trout subjected to supplemental dissolved oxygen in fish culture. Aquaculture 126:183–193
CETESB (Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental) (2010) Relatório de qualidade das águas interiores do estado de São Paulo, São Paulo
Chapman LJ, McKenzie DJ (2009) Behavioral responses and ecological consequences. In: Richards JG, Farrel AP, Brauner CJ (eds), Fish physiology. Hypoxia, v 27, Academic Press, London, pp 24–77
Chippari-Gomes AR, Gomes LC, Lopes NP (2005) Metabolic adjustments in two Amazonian cichlids exposed to hypoxia and anoxia. Comp Biochem Physiol B 141:347–355
Clementi ME, Condò SG, Castagnola M, Giardina B (1994) Hemoglobin function under extreme life conditions. Eur J Biochem 223:309–317
Cruz AL (2007) O comportamento respiratório e a cascata de O2 no cascudo de respiração bimodal Pterygoplichthys anisitsi (Teleostei: Loricariidae). Ph D Thesis. Universidade Federal de São Carlos, São Carlos, SP, Brazil
Cruz AL, Langeani F (2000) Comportamento reprodutivo do cascudo Liposarcus anisitsi (Eigenmann & Kennedy, 1903) (Ostariophysi: Loricariidae: Hypostominae) em cativeiro. Comun Mus Ciênc Tecnol PUCRS 13:109–115
Cruz AL, Pedretti ACE, Fernandes MN (2009) Stereological estimation of the surface area and oxygen diffusing capacity of the respiratory stomach of the air-breathing armored catfish Pterygoplichthys anisitsi (Teleostei: Loricariidae). J Morphol 270:601–614
Dejours P (1981) Principles of comparative respiratory physiology. Elsevier, North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, New York, Oxford
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Fago A, Carratore V, Di Prisco G, Feuerlein RJ, Weber RE, Sottrup-Jensen L (1995) The cathodic hemoglobin of Anguilla anguilla. Amino acid sequence and oxygen equilibria of a reverse Bohr effect hemoglobin with high oxygen affinity and high phosphate sensitivity. J Biol Chem 270:18897–18902
Fernandes MN, Rantin FT (1989) Respiratory responses of Oreochromis niloticus (Pisces, Cichlidae) to environmental hypoxia under different thermal conditions. J Fish Biol 35:509–519
Fernandes MN, Rantin FT (1994) Relantionships between oxygen availability and metabolic cost of breathing in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): aquacultural consequences. Aquaculture 127:339–346
Fernandes MN, Sanchez JR, Matsuzaki M, Panepucci L, Rantin FT (1999) Aquatic respiration in facultative air-breathing fish: effects of temperature and hypoxia. In: Val AL, Almeida-Val VMF (eds) Biology of tropical fishes. Manaus, INPA, pp 341–353
Gee JH (1980) Respiratory patterns and antipredator responses in the central mudminnow, Umbra limi, a continuous, facultative, air-breathing fish. Can J Zool 58:819–827
Gee JH, Graham JB (1978) Respiratory and hidrostatic functions of the intestine of the catfishes Hoplosternum thoracatum and Brochis splendens (Callichthyidae). J Exp Biol 74:1–16
Giardina B, Amiconi G (1981) Measurement of binding of gaseous and nongaseous ligands to hemoglobins by conventional spectrophotometric procedures. Methods Enzymol 76:417–427
Graham JB (1983) The transition to air breathing in fishes. II. Effects of hypoxia acclimation on the bimodal gas exchange of Ancistrus chagresi (Loricariidae). J Exp Biol 102:157–173
Graham JB (1997) Air-breathing fishes: evolution, diversity, and adaptation. Academic Press, San Diego
Graham JB, Baird TA (1984) The transition to air breathing in fishes. III. Effects o body size and aquatic hypoxia on the aerial gas exchange of the swamp eel Synbranchus marmoratus. J Exp Biol 108:357–375
Graham JB, Wegner NC (2010) Breathing air in water and in air: the air-breathing fishes. In: Nilsson GE (ed) Respiratory Physiology of Vertebrates. Life with and without oxygen. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 174–221
Graham JB, Baird TA, Stockmann W (1987) The transition to air breathing in fishes. IV. Impact of branchial specializations for an air breathing on the aquatic respiratory mechanisms and ventilatory costs of the swamp eel Synbranchus marmoratus. J Exp Biol 129:83–106
Harrower JR, Brown CH (1972) Blood lactic acid. A micro method adapted to field collection of microliter samples. J Appl Physiol 32:224–228
Hebert NA, Wells RMG (2001) The anaerobic physiology of the air-breathing blue gourami, Trichogaster trichopterus, necessitates behavioural regulation of breath-hold limits during hypoxic stress and predatory challenge. J Comp Physiol B 171:603–612
Hochachka PW, Lutz PL (2001) Mechanism, origin, and evolution of anoxia tolerance in animals. Comp Biochem Physiol B 130:435–459
Hochachka PW, Somero GN (2002) Biochemical adaptation: mechanism and process in physiological evolution. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Hughes GM, Singh BH (1971) Gas exchange in air and water in an air breathing catfish, Saccobranchus (Heteropneustes) fossilis. J Comp Biol 55:667–682
Ip YK, Lim CB, Chew SF, Wilson JM, Randall DJ (2001) Partial aminoacid catabolism leading to the formation of alanine in Periophthalmodon schlosseri: a strategy that facilitates the use of aminoacids as an energy source during locomotory activity on land. J Exp Biol 204:1615–1624
Jensen FB (2004) Red blood cell pH, the Bohr effect, and other oxygenation-linked phenomena in blood O2 and CO2 transport. Acta Physiol Scand 182:215–227
Johansen K, Mangum CP, Lykkeboe G (1978) Respiratory properties of the blood of Amazon fishes. Can J Zool 56:898–906
Karim MR, Sekini M, Ukita M (2003) A model of fish preference and mortality under hypoxic water in the coastal environment. Mar Pollut Bull 47:25–29
Lu GD (1939) The metabolism of piruvic acid in normal and vitamin B- deficient state. I. A rapid specific and sensitive method for the estimation of blood pyruvate. Biochem J 33:249–254
MacCormack TJ, McKinley RS, Roubach R, Almeida-Val VMF, Val AL, Driedzic WR (2003) Changes in ventilation, metabolism, and behaviour, but not bradycardia, contribute to hypoxia survival in two species of Amazonian armoured catfish. Can J Zool 81:272–280
MacCormack TJ, Lewis JM, Almeida-Val VMF (2006) Carbohydrate management, anarobic metabolism and adenosine levels in the armoured catfish Liposarcus pardalis (Castelnau) during hypoxia. J Exp Zool A 305:363–375
Mattias AT, Perna SA, Moron SE, Rodrigues JAO, Fernandes MN (1996) Comparação entre a estrutura morfológica e a morfometria das brânquias do cascudo Hypostomus regani e Hypostomus plecostomus (Loricariidae). Anais VII Sem Reg Ecol 7:223–236
Mattias AT, Rantin FT, Fernandes MN (1998) Gill respiratory parameters during progressive hypoxia in the facultative air-breathing fish, Hypostomus regani (Loricariidae). Comp Biochem Physiol A 120:311–315
Milsson WK (1991) Intermittent breathing in vertebrates. Annu Rev Physiol 53:87–105
Moraes G, Oliveira MA, Rantin FT (1996) The metabolic pattern changes of Hoplias malabaricus from normoxia to hypoxia conditions. Rev Bras Biol 56:191–196
Moraes G, Altran AE, Avilez IM, Barbosa CC, Bidinotto PM (2005) Metabolic adjustments during semi-aestivation of the marble eel (Synbranchus marmoratus), a facultative air-breathing fish. Braz J Biol 65:305–312
Nelson JA, Rios FS, Sanches JR, Fernandes MN, Rantin FT (2007) Environmental influences on the respiratory physiology and gut chemistry of a facultatively air-breathing, tropical herbivorous fish Hypostomus regani (Ihering, 1905). In: Fernandes MN, Rantin FT, Glass ML, Kapoor BG (eds) Fish respiration and environment, Science Publisher, Enfield, Jersey, Plymouth, pp 191–218
Nikinmaa M (1997) Oxygen and carbon dioxide transport in vertebrate erythrocytes: an evolutionary change in the role of membrane transport. J Exp Biol 200:369–380
Nikinmaa M (2002) Oxygen-dependent cellular functions: why fishes and their aquatic environment are a prime choice of study. Comp Biochem Physiol A 133:1–16
Oliveira RD, Lopes JM, Sanches JR, Kalinin AL, Glass ML, Rantin FT (2004) Cardiorespiratory responses of the facultative air breathing fish jeju, Hoplerythrinus unitaeniatus (Teleostei, Erythrinidae), exposed to graded ambient hypoxia. Comp Biochem Physiol A 139:479–485
Perna SA, Fernandes MN (1996) Gill morphometry of the facultative air-breathing loricariid fish, Hypostomus plecostomus (Walbaum) with special emphasis to aquatic respiration. Fish Physiol Biochem 15:213–220
Rantin FT, Kalinin AL, Glass ML, Fernandes MN (1992) Respiratory responses to hypoxia in relation to mode of life of two erythrinid species (Hoplias malabaricus and Hoplias lacerdae). J Fish Biol 41:805–812
Smithies O (1955) Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variation in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J 61:629–641
Smithies O (1959) An improved procedure for starch gel electrophoresis. Biochem J 71:585–587
Souza RHS, Soncini R, Glass ML, Sanches JR, Rantin FT (2001) Ventilation, gill perfusion and blood gases in dourado, Salminus maxillosus Valenciennes (Teleostei, Characidae), exposed to graded hypoxia. J Comp Physiol B 171:483–489
Takasusuki J, Fernandes MN, Severi W (1998) The occurrence of aerial respiration in Rhinelepis strigosa during progressive hypoxia. J Fish Biol 52:369–379
Tamburrini M, Verde C, Olianas A, Giardina B, Corda M, Sanna MT, Fais A, Deianna AM, Di Prisco G, Pellegrini M (2001) The hemoglobin system of the brown moray Gymnothorax unicolor. Eur J Biochem 268:4104–4111
Trinder P (1969) Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with the alternative oxygen acceptor. Analyt Clinic Biochem 6:24–25
Val AL, Schwantes AR, Schwantes MLB, De Luca PH (1981) Amido hidrolisado em milho como suporte eletroforético. Ciênc Cult 33:992–996
van den Thillart GEEJM, van Waarde A (1985) Teleosts in hypoxia: aspects of anaerobic metabolism. Mol Physiol 8:393–409
van Hesswijk JCF, van Pelt J, van den Thillart GEEJM (2005) Free fatty acid metabolism in the air-breathing African catfish Clarias gariepinus during asphyxia. Comp Biochem Physiol A 141:15–21
Wang T, Hicks JW (2002) An integrative model to predict maximum O2 uptake in animals with central vascular shunts. Zoology 105:45–53
Weber RE, Ostojic H, Fago A (2002) Novel mechanism for high-altitude adaptation in haemoglobin of the Andean frog Telmatobius peruvianus. Am J Physiol R 283:1052–1060
Weibel ER, Taylor CR, Hoppeller H (1992) Variations in function and designed: testing by symmorphosis in the respiratory system. Respir Physiol 87:325–348
Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grants from the Brazilian research funding institutions National Council of Technological and Scientific Development (CNPq), Foundation for Supporting Research in the State of São Paulo (FAPESP), and Coordination of Improvement of Higher Education Personal (CAPES) to MN Fernandes. The authors thank the Aquaculture Center of the São Paulo State University (CAUNESP), Jaboticabal, SP, for providing the fish. A.L. Cruz and W. Klein, and M.N. Fernandes are, respectively, research members of National Institute of Science and Technology in Comparative Physiology (INCT-Fisiologia Comparada) and National Institute of Science and Technology in Aquatic Toxicology (INCT-Toxicologia Aquática). A.L. Cruz acknowledges CAPES for awarding scholarships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Cruz, A.L., da Silva, H.R., Lundstedt, L.M. et al. Air-breathing behavior and physiological responses to hypoxia and air exposure in the air-breathing loricariid fish, Pterygoplichthys anisitsi . Fish Physiol Biochem 39, 243–256 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-012-9695-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-012-9695-0