Abstract
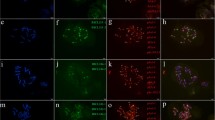
A genome specific DNA sequence that detects Secale africanum chromatin incorporated into wheat was developed in this study. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis was used to search for genome specific DNA sequences of S. africanum in lines, R111, “mianyang11” (MY11) and wheat-rye 1RS/1BL translocations R25 and R57. A high copy rye-specific DNA segment pSaD15940 of the S. africanum genome was obtained. The sequence of pSaD15 did not show any significant homology to other reported sequences in databases and it is therefore a new repetitive sequence of Secale. PCR primers were designed for pSaD15940, which amplify a clear 887 bp fragment in S. africanum but not in any wheat. The primers also amplified an 887 bp fragment in other accessions of rye, Chinese Spring-Imperial rye chromosome additions and a diverse range of material carrying different rye chromosomes or chromosomal segments. In situ hybridization showed that probe pSaD15940 was specifically hybridized throughout all rye chromosomes arms except for the terminal regions. The advantage of the rye-specific probe developed herein compared to those of previous reports is that it has been shown to be widely applicable to other Secale species. The probe will be useful as a molecular marker for the introgression of S. africanum and other rye chromosome segments into the wheat genome.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkhimova OG, Mazurok NA, Potapova TA, Zakian SM, Heslop-Harrison JS, Vershinin AV (2004) Diverse patterns of the tandem repeats organization in rye chromosomes. Chromosoma 113:42–52
Alves E, Ballesteros I, Linacero R, Vazquez AM (2005) RYS1, a foldback transposon, is activated by tissue culture and shows preferential insertion points into the rye genome. Theor Appl Genet 111:431–436
Appels R, Dennis ES, Smyth DR, Peacock WJ (1981) Two repeated DNA sequences from the heterochromatic region of rye (Secale cereal) chromosomes. Chromosoma 84:265–277
Appels R, Driscoll C, Peacock WJ (1978) Hetero-chromatin and highly repeated DNA sequences in rye (Secale cereal). Chromosoma 70:67–89
Aragon-Alcaide L, Miller T, Schwarzacher T, Reader S, Moore G (1996) A cereal centromere sequence. Chromosoma 105:261–268
Bedbrook JR, Jones J, O’Dell M, Thompson R, Flavell RB (1980a) A molecular description of telomeric heterochromatin in Secale species. Cell 19:540–560
Bedbrook JR, O’Dell M, Flavell RB (1980b) Amplification of rearranged sequences in cereal plant. Nature (London) 288:133–137
Brunell MS, Lukaszewski AJ, Whitkus R (1999) Development of arm specific RAPD markers for rye chromosome 2R in wheat. Crop Sci 39:1702–1706
Cheng ZJ, Murata M (2003) A centromeric tandem repeat family originating from a part of Ty3/gypsy-retroelement in wheat and its relatives. Genetics 164:665–672
Chikmawati T, Skovmand B, Gustafson JP (2005) Phylogenetic relationships among Secale species revealed by amplified fragment length polymorphisms. Genome 48:792–801
Contento A, Heslop-Harrison JS, Schwarzacher T (2005) Diversity of a major repetitive DNA sequence in diploid and polyploid Triticeae. Cytogenet Gen Res 109:34–42
Flavell RB, Bennett MD, Smith JB, Smith DB (1974) Genome size and the proportion of repeated nucleotide sequence DNA in plants. Biochem Genet 12:257–269
Francis HA, Leitch AR, Koebner MDR (1995) Conversion of a RAPD-generated PCR product, containing a novel dispersed repetitive element, into a fast and robust assay for the presence of rye chromatin in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 90:636–642
Francki MG (2001) Identification of Bilby, a diverged centromeric Ty1-copia retrotransposon family from cereal rye (Secale cereale L.). Genome 44:266–274
Graybosch RA (2001) Uneasy Unions: quality effects of rye chromatin transfer to wheat. J Cereal Sci 33:3–16
Gu YQ, Coleman-Derr D, Kong X, Anderson OD (2004) Rapid genome evolution revealed by comparative sequence analysis of orthologous regions from four Triticeae genomes. Plant Physiol 135:459–470
Guidet F, Rogowsky P, Taylor C, Song W, Langridge P (1991) Cloning and characterization of a new rye-specific repeated sequence. Genome 34:81–87
Heslop-Harrison JS (2000) Comparative genome organization in plants: from sequence and markers to chromatin and chromosomes. Plant Cell 12:617–636
Iqbal MJ, Rayburn AL (1995) Identification of the 1RS rye chromosomal segment in wheat by RAPD analysis. Theor Appl Genet 91:1048–1053
Ito H, Nasuda S, Endo TR (2004) A direct repeat sequence associated with the centromeric retrotransposons in wheat. Genome 47:747–756
Jiang HR, Dai DQ, Sun DF (1992) Creation of special germaplasm resources in Triticum. J Sichuan Agric Univ 10:255–259
Jiang J, Friebe B, Gill BS (1994) Recent advances in alien gene transfer in wheat. Euphytica 73:199–212
Jiang JM, Nasuda SH, Dong FG, Scherrer CW, Woo SS, Wing RA, Gill BS, Ward DC (1996) A conserved repetitive DNA element located in the centromeres of cereal chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14210–14213
Katto MC, Endo TR, Nasuda S (2004) A PCR-based marker for targeting small rye segments in wheat background. Genes Genet Syst 79:245–250
Kiyotaka N, Hisashi T, Tetsuo S (1999) A novel repetitive sequence, termed the JNK repeat family, located on an extra heterochromatic region of chromosome 2R of Japanese rye. Chromosome Res 6:95–101
Ko JM, Do GS, Suh DY, Seo BB, Shin DC, Moon HP (2002) Identification and chromosomal organization of two rye genome-specific RAPD products useful as introgression markers in wheat. Genome 45:157–164
Koebner RMD (1995) Generation of PCR-based markers for the detection of rye chromatin in a wheat background. Theor Appl Genet 90:740–745
Lapitan NLV, Sears RG, Gill BS (1988) Amplification of repeated DNA sequences in wheat × rye hybrids regenerated from tissue culture. Theor Appl Genet 75:381–388
Lapitan NLV, Sears RG, Rayburn AL, Gill BS (1986) Wheat-rye translocations. J Hered 77:415–419
Lee JH, Graybosch RA, Lee DJ (1994) Detection of rye chromosome 2R using the polymerase chain reaction and sequence-specific DNA primers. Genome 37:19–22
Lelley T, Josifek KJ, Kaltsikes PJ (1978) Polymorphism in the Giemsa C-banding pattern of rye chromosomes. Can J Genet Cytol 20:307–312
Li WL, Zhang P, Feller JP, Friebe B, Gill BS (2004) Sequence composition, organization and evolution of core Triticeae genome. Plant J 40:500–511
Liu C, Li GR, Yang ZJ, Feng J, Zhou JP, Ren ZL (2006a) Specific DNA band isolation and SCAR marker construction of rye genome. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin 26:2434–2438
Liu C, Yang ZJ, Feng J, Zhou JP, Chi SH, Ren ZL (2006b) Development of Dasypyrum genome specific marker by using wheat microsatellites. Hereditas (Beijing) 28:1573–1579
Lukaszewski AJ, Gustafson JP (1987) Cytogenetics of Triticale. Plant Breed Rev 5:41–93
Mao L, Zhai WX, Hu H, Zhu LH (1994) Cloning and characterization of a repetitive sequence in rye (Secale cereal). Plant Sci 100:51–57
McIntyre CL, Pereira S, Moran LB, Appels R (1990) New Secale cereale (rye) DNA derivatives for the detection of rye chromosome segments in wheat. Genome 33:635–640
Nagaki K, Tsujimoto H, Sasakuma T (1999) A novel repetitive sequence, termed the JNK repeat family, located on an extra heterochromatic region of chromosome 2R of Japanese rye. Chromosome Res 7:95–101
Presting GG, Malysheva L, Fuchs J, Schubert I (1998) A TY3-GYPSY retrotransposon-like sequence localizes to the centromeric regions of cereal chromosomes. Plant J 16:721–728
Rayburn AL, Gill BS (1985) Use of biltin-labeled probes to map specific DNA sequences on wheat chromosomes. J Hered 76:78–81
Rogowsky PM, Manning S, Liu JY, Langridge P (1991) The R173 family of rye-specific repetitive DNA sequences: a structure analysis. Genome 34:88–95
Rogowsky PM, Liu JY, Manning S, Taylor C, Langridge P (1992) Structural heterogeneity in the R173 family of rye-specific repetitive DNA sequences. Plant Mol Biol 20:95–102
Saal B, Wricke G (1999) Development of simple sequence repeat markers in rye (Secale cereale L.). Genome 42:964–972
Sharma HC, Gill BS (1983) Current status of wide hybridization in wheat. Euphytica 32:17–31
Singh RJ, Robbelen G (1977) Identification by Giemsa technique of the translocations separating cultivated rye from three wild species of Secale. Chromosoma (Berl) 59:217–225
Van Campenhout S, Volckaert G (1999) The fortuitous cloning of retroelement-like sequences from wheat and rye as by-products of a specific polymerase chain reaction. DNA Seq 10:173–178
Vershinin AV, Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1995) The large-scale genomic organization of repetitive DNA family at the telomeres of rye chromosomes. Plant Cell 7:1823–1833
Wan XQ, Yang ZJ, Feng J, Liu Y, Ren ZL (2005) Generation of a rye chromosomes specific PCR-based marker. Southwest China J Agric Sci 18(suppl):50–53
Wang J, Wang XP, Ji J, Wang ZG, An TG, Li JM, Zhang ZQ (2006) Creation of novel wheat-rye 1BS/1RS translocation lines and characterization by molecular cytogenetics. Acta Agron Sin 32:30–33
Yang ZJ, Ren ZL (2000) Genetic specification on rye chromatin transferred to wheat line 85-DH5304. J Sichuan Agric Univ 18:109–112
Yang ZJ, Li GR, Ren ZL (2001a) Identification of a Triticum durum-Secale africanum amphiploid and its crossability with common wheat. J Genet Breed 5:45–50
Yang ZJ, Li GR, Jiang HR, Ren ZL (2001b) Expression of nucleolus, endosperm storage proteins and disease resistance in an amphiploid between Aegilops tauschii and Secale silvestre. Euphytica 119:317–321
Yang ZJ, Li GR, Jiang HR, Ren ZL (2001c) Intergenomic interaction of Nucleolus, gliadin and disease resistance in a Triticum aestivum-Secale africanum amphiploid. J Sichuan Agric Univ 19:340–343
Zhou JP, Yang ZJ, Feng J, Tang ZX, Ren ZL (2005) Isolation and identification of rye special DNA sequences. Southwest China J Agric Sci 18:598–602
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30671288 and 30671136), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-06-0810) and the Science and Technology Committee of Sichuan Province, China for their financial support. We particular thank Dr I. Dundas (The University of Adelaide, Australia), Prof. B. Friebe (Kansas State University, USA), Dr. S.M. Reader (John Innes Center, Britain) and NPGS for kindly providing seeds. We are grateful to Dr I. Dundas for his helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Yang, ZJ., Li, GR. et al. Isolation of a new repetitive DNA sequence from Secale africanum enables targeting of Secale chromatin in wheat background. Euphytica 159, 249–258 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9484-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9484-5