Abstract
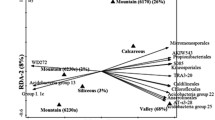
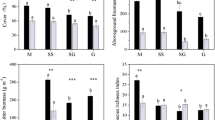
We investigated the temporal and among-site differentiation of soil functionality properties in fields under different grazing intensities (heavy and light) and compared them to those found in their adjacent hedgerows, consisting either of wooden shrubs (Rubus canescens) or of high trees (Populus sp.), during the cold and humid seasons of the year. We hypothesized that greater intensity of grazing would result in higher degradation of the soil system. The grazing factor had a significant effect on soil organic C and N, microbial biomass C, microbial biomass N, microbial activity, and β-glucosidase, while acid phosphatase and urease activity were not found to differ significantly among the management systems. The intensity of grazing affected mostly the chemical properties of soil (organic C and N) and altered significantly the composition of the soil microbial community, as lower C:N ratio of the microbial biomass indicates the dominance of bacteria over fungi in the heavily grazed fields. All estimated biological variables presented higher values in the humid period, although the pattern of differentiation was similar at both sampling times, revealing that site-specific variations were more pronounced than the time-specific ones. Our results indicate that not all C, N, and P dynamics were equally affected by grazing. Management plans applied to pastures, in order to improve soil quality properties and accelerate passive reforestation, should aim at the improvement of soil parameters related primarily to C and secondly to N cycle.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, P., Raff, D., & Lauenroth, W. (2001). The effect of grazing on the spatial heterogeneity of vegetation. Oecologia, 128(4), 465–479.
Aerts, R., & Chapin, F. S., III. (2000). The mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: a reevaluation of processes and patterns. Advances in Ecological Research, 30, 1–67.
Alexander, M. (1977). Introduction to soil microbiology. New York: Wiley.
Allen, S. E. (1974). Chemical analysis of ecological materials. Oxford: Blackwell.
Allison, S. D., & Jastrow, J. D. (2006). Activities of extracellular enzymes in physically isolated fractions of restored grassland soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38(11), 3245–3256.
Altesor, A., Piñeiro, G., Lezama, F., Jackson, R. B., Sarasola, M., & Paruelo, J. M. (2006). Ecosystem changes associated with grazing in subhumid South American grasslands. Journal of Vegetation Science, 17(3), 323–332.
Bardgett, R. D., Jones, A. C., Jones, D. L., Kemmitt, S. J., Cook, R., & Hobbs, P. J. (2001). Soil microbial community patterns related to the history and intensity of grazing in sub-montane ecosystems. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 33(12–13), 1653–1664.
Bardgett, R. D., Lovell, R. D., Hobbs, P. J., & Jarvis, S. C. (1999). Seasonal changes in soil microbial communities along a fertility gradient of temperate grasslands. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 31(7), 1021–1030.
Bardgett, R. D., Wardle, D. A., & Yeates, G. W. (1998). Linking above-ground and below-ground interactions: how plant responses to foliar herbivory influence soil organisms. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 30(14), 1867–1878.
Berg, M. P., & Hemerik, L. (2004). Secondary succession of terrestrial isopod, centipede, and millipede communities in grasslands under restoration. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 40(3), 163–170.
Breiman, L., Friedman, J. H., Olshen, R. A., & Stone, C. J. (1984). Classification and regression trees. New York: Chapman and Hall.
Brookes, P. C., Landman, A., Pruden, G., & Jenkinson, D. S. (1985). Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 17(6), 837–842.
Buka, E. (2012). Patterns of plant diversity in areas surrounding Lake Pamvotis (undergraduate thesis). University of Ioannina (In Greek, abstract in English).
Carrera, A. L., Vargas, D. N., Campanella, M. V., Bertiller, M. B., Sain, C. L., & Mazzarino, M. J. (2005). Soil nitrogen in relation to quality and decomposability of plant litter in the Patagonian Monte, Argentina. Plant Ecology, 181(1), 139–151.
Chodak, M., & Niklińska, M. (2010). Effect of texture and tree species on microbial properties of mine soils. Applied Soil Ecology, 46(2), 268–275.
Cingolani, A. M. I., Cabido, M. R., Renison, D., & Solís Neffa, V. (2003). Combined effects of environment and grazing on vegetation structure in Argentine granite grasslands. Journal of Vegetation Science, 14(2), 223–232.
Conn, C., & Dighton, J. (2000). Litter quality influences on decomposition, ectomycorrhizal community structure and mycorrhizal root surface acid phosphatase activity. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 32(4), 489–496.
Craine, J. M., Ballantyne, F., Peel, M., Zambatis, N., Morrow, C., & Stock, W. D. (2009). Grazing and landscape controls on nitrogen availability across 330 South African savanna sites. Austral Ecology, 34, 731–740.
Deng, L., Sweeney, S., & Shangguan, Z. P. (2014). Grassland responses to grazing disturbance: plant diversity changes with grazing intensity in a desert steppe. Grass and Forage Science, 69(3), 524–533.
Diaz-Fierros, F., Villar, M. C., Gil, F., Carballas, M., Leiros, M. C., Carballas, T., & Cabaneiro, A. (1988). Effect of cattle slurry fractions on nitrogen mineralization in soil. Journal of Agricultural Science, 110, 491–497.
Dilly, O., Blume, H. P., & Munch, J. C. (2003). Soil microbial activities in Luvisols and Anthrosols during 9 years of region-typical tillage and fertilisation practices in northern Germany. Biogeochemistry, 65(3), 319–339.
Friedl, M. A., & Brodley, C. E. (1997). Decision tree classification of land cover from remotely sensed data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 61(3), 399–409.
Fterich, A., Mahdhi, M., & Mars, M. (2012). Impact of grazing on soil microbial communities along a chronosequence of Acacia tortilis subsp. raddiana in arid soils in Tunisia. European Journal of Soil Biology, 50, 56–63.
Gao, Y. Z., Giese, M., Lin, S., Sattelmacher, B., Zhao, Y., & Brueck, H. (2008). Belowground net primary productivity and biomass allocation of a grassland in Inner Mongolia is affected by grazing intensity. Plant and Soil, 307(1–2), 41–50.
Hellenic National Meteorological Service (2011). Ioannina—data period:1956–1997. The climate of Greece. http://www.hnms.gr/hnms/english/climatology/climatologyregiondiagramshtml?dr city=Ioannina
Hiltbrunner, D., Schulze, S., Hagedorn, F., Schmidt, M. W. I., & Zimmmermann, S. (2012). Cattle trampling alters soil properties and changes soil microbial communities in a Swiss sub-alpine pasture. Geoderma, 170, 369–377.
Islam, K. R., & Weil, R. R. (2000). Soil quality indicator properties in mid-Atlantic soils as influenced by conservation management. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 55(1), 69–78.
Jenkinson, D. S. (1976). The effects of biocidal treatments on metabolism in soil-IV. The decomposition of fumigated organisms in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 8(3), 203–208.
Katsalirou, E., Deng, S., Nofziger, D. L., Gerakis, A., & Fuhlendorf, S. D. (2010). European journal of soil biology spatial structure of microbial biomass and activity in prairie soil ecosystems. European Journal of Soil Biology, 46(3–4), 181–189.
Keeler, B. L., Hobbie, S. E., & Kellogg, L. E. (2009). Effects of long-term nitrogen addition on microbial enzyme activity in eight forested and grassland sites: implications for litter and soil organic matter decomposition. Ecosystems, 12(1), 1–15.
Köhler, B., Gigon, A., Edwards, P. J., Krüsi, B., Langenauer, R., Lüscher, A., & Ryser, P. (2005). Changes in the species composition and conservation value of limestone grasslands in Northern Switzerland after 22 years of contrasting managements. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 7(1), 51–67.
Krämer, S., & Green, D. M. (2000). Acid and alkaline phosphatase dynamics and their relationship to soil microclimate in a semiarid woodland. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 32(2), 179–188.
Laskurain, N. A., Aldezabal, A., Olano, J. M., Loidi, J., & Escudero, A. (2013). Intensification of domestic ungulate grazing delays secondary forest succession: evidence from exclosure plots. Journal of Vegetation Science, 24(2), 320–331.
Liu, N., Kan, H. M., Yang, G. W., & Zhang, Y. J. (2015). Changes in plant, soil, and microbes in a typical steppe from simulated grazing: explaining potential change in soil C. Ecological Monographs, 85(2), 269–286.
Liu, Z., Li, Z., Nijs, I., & Bogaert, J. (2005). Fine-scale spatial pattern of Cleistogenes squarrosa population under different grazing intensities. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 14(1), 11–17.
Liu, X., Lindemann, W., Whitford, W., et al. (2000). Microbial diversity and activity of disturbed soil in the northern Chihuahuan Desert. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 32, 243–249.
Lodge, G. M., & Whalley, R. D. B. (1989). Native and natural pastures on the tablelands of New South Wales: a review and annotated bibliography. NSW Agriculture, Technical Bulletin, 35.
Mastrogianni, A., Papatheodorou, E. M., Monokrousos, N., Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U., & Stamou, G. P. (2014). Reclamation of lignite mine areas with Triticum aestivum: the dynamics of soil functions and microbial communities. Applied Soil Ecology, 80, 51–59.
Matthews, A. (2013). Greening agricultural payments in the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy. Bio-based and Applied Economics, 2(1), 1–27.
McLean, E. O. (1982). Soil pH and lime requirement. In A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, & D. R. Kenney (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis, part 2 (pp. 199–224). American Society of Agronomy: Madison.
Monokrousos, N., Boutsis, G., & Diamantopoulos, J. D. (2014). Development of soil chemical and biological properties in the initial stages of post-mining deposition sites. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(12), 9065–9074.
Moore, J. C., & Hunt, H. W. (1988). Resource compartmentation and the stability of real ecosystems. Nature, 333, 261–263.
Morgan, J. A., Pataki, D. E., Körner, C., Clark, H., Del Grosso, S. J., Grünzweig, J. M., Knapp, A. K., Mosier, A. R., Newton, P. C. D., Niklaus, P. A., Nippert, J. B., Nowak, R. S., Parton, W. J., Polley, H. W., & Shaw, M. R. (2004). Water relations in grassland and desert ecosystems exposed to elevated atmospheric CO2. Oecologia, 140(1), 11–25.
Nautiyal, C. S., Chauhan, P. S., & Bhatia, C. R. (2010). Changes in soil physico-chemical properties and microbial functional diversity due to 14 years of conversion of grassland to organic agriculture in semi-arid agroecosystem. Soil and Tillage Research, 109(2), 55–60.
Nyssen, J., Temesgen, H., Lemenih, M., Zenebe, A., Haregeweyn, N., & Haile, M. (2008). Spatial and temporal variation of soil organic carbon stocks in a lake retreat area of the Ethiopian Rift Valley. Geoderma, 146(1–2), 261–268.
Ohtonen, R., Fritze, H., Pennanen, T., Jumpponen, A., & Trappe, J. (1999). Ecosystem properties and microbial community changes in primary succession on a glacier forefront. Oecologia, 119(2), 239–246.
Papatheodorou, E. M. (2008). Responses of soil microbial communities to climatic and human impacts in Mediterranean regions. In T. X. Liu (Ed.), Soil ecology research developments (pp. 63–87). New York: Nova Science Publishers.
Papatheodorou, E. M., Kapagianni, P., Georgila, E. D., Monokrousos, N., & Stamou, G. P. (2013). Predictability of soil succession patterns under different agricultural land use practices: continual conventional cultivation versus transformation to organic cultivation or fallow periods. Pedobiologia, 56(4–6), 233–239.
Pavel, R., Doyle, J., & Steinberger, Y. (2004). Seasonal pattern of cellulase concentration in desert soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36, 549–554.
Peco, B., Carmona, C. P., de Pablos, I., & Azcárate, F. M. (2012). Effects of grazing abandonment on functional and taxonomic diversity of Mediterranean grasslands. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 152, 27–32.
Peco, B., Sánchez, A. M., & Azcárate, F. M. (2006). Abandonment in grazing systems: consequences for vegetation and soil. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 113(1–4), 284–294.
Pineiro, G., Paruelo, J. M., Jobbágy, E. G., Jackson, R. B., & Oesterheld, M. (2009). Grazing effects on belowground C and N stocks along a network of cattle exclosures in temperate and subtropical grasslands of South America. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 23(2).
Prieto, L. H., Bertiller, M. B., Carrera, A. L., & Olivera, N. L. (2011). Soil enzyme and microbial activities in a grazing ecosystem of Patagonian Monte, Argentina. Geoderma, 162(3–4), 281–287.
Ross, D. J. (1990). Influence of soil mineral nitrogen content on soil respiratory activity and measurements of microbial carbon and nitrogen by fumigation-incubation procedures. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 28, 311–321.
Rutigliano, F. A., D’Ascoli, R., & Virzo De Santo, A. (2004). Soil microbial metabolism and nutrient status in a Mediterranean area as affected by plant cover. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36(11), 1719–1729.
Shand, C. A., Williams, B. L., Dawson, L. A., Smith, S., & Young, M. E. (2002). Sheep urine affects soil solution nutrient composition and roots: differences between field and sward box soils and the effects of synthetic and natural sheep urine. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 34(2), 163–171.
Singh, B. K., Millard, P., Whiteley, A. S., & Murrell, J. C. (2004). Unravelling rhizosphere-microbial interactions: opportunities and limitations. Trends in Microbiology, 12(8), 386–393.
Sinsabaugh, R. L., Reynolds, H., & Long, T. M. (2000). Rapid assay for amidohydrolase (urease) activity in environmental samples. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 32(14), 2095–2097.
Somda, I., Harkous, S., & Brun, H. (1997). Bipolar heterothallism in B-group isolates of Leptosphaeria maculans. Plant Pathology, 46(6), 890–896.
Srivastava, A. K. (2012). Advances in citrus nutrition. Maharashtra: National Research Centre for Citrus Nagpur.
Stephens, S. E., Walker, J. A., Blunck, D. R., Jayaraman, A., Naugle, D. E., Ringelman, J. K., & Smith, A. J. (2008). Predicting risk of habitat conversion in native temperate grasslands. Conservation Biology, 22(5), 1320–1330.
Su, Y. Z., Li, Y. L., Cui, J. Y., & Zhao, W. Z. (2005). Influences of continuous grazing and livestock exclusion on soil properties in a degraded sandy grassland, Inner Mongolia, northern China. Catena, 59(3), 267–278.
Su, Y. Z., Zhao, H. L., Zhang, T. H., & Zhao, X. Y. (2004). Soil properties following cultivation and non-grazing of a semi-arid sandy grassland in northern China. Soil & Tillage Research, 75, 27–36.
Thornes, J. B. (2007). Modelling soil erosion by grazing: recent developments and new approaches. Geographical Research, 45(1), 13–26.
Trasar-Cepeda, C., Leirós, M. C., & Gil-Sotres, F. (2008). Hydrolytic enzyme activities in agricultural and forest soils. Some implications for their use as indicators of soil quality. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40, 2146–2155.
Tzialla, C. E., Veresoglou, D. S., Papakosta, D., & Mamolos, A. P. (2006). Changes in soil characteristics and plant species composition along a moisture gradient in a Mediterranean pasture. Journal of Environmental Management, 80(1), 90–98.
Wade, J. (1997). A study of vegetation composition and soil chemistry on five year non-rotational set-aside under four management regimes, (Ph.D dissertation), Essex, UK.
Wan, Y., Bao, Y., & Zhou, Q. (2010). Simultaneous adsorption and desorption of cadmium and tetracycline on cinnamon soil. Chemosphere, 80(7), 807–812.
Wang, L., Wang, D., Liu, J., Huang, Y., & Hodgkinson, K. C. (2011). Diet selection variation of a large herbivore in a feeding experiment with increasing species numbers and different plant functional group combinations. Acta Oecologica, 37(3), 263–268.
Wang, D., Wu, G. L., Zhu, Y. J., & Shi, Z. H. (2014). Grazing exclusion effects on above- and below-ground C and N pools of typical grassland on the Loess Plateau (China). Catena, 123, 113–120.
Wardle, D. A. (1992). A comparative assessment of factors which influence microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen levels in soil. Biological Reviews, 67(3), 321–358.
Wu, G. L., Du, G. Z., Liu, Z. H., & Thirgood, S. (2009). Effect of fencing and grazing on a Kobresia-dominated meadow in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Plant and Soil, 319, 115–126.
Zhu, G. Y., Deng, L., Zhang, X. B., & Shangguan, Z. P. (2016). Effects of grazing exclusion on plant community and soil physicochemical properties in a desert steppe on the Loess Plateau, China. Ecological Engineering, 90, 372–381.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panayiotou, E., Dimou, M. & Monokrousos, N. The effects of grazing intensity on soil processes in a Mediterranean protected area. Environ Monit Assess 189, 441 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6161-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6161-6