Abstract
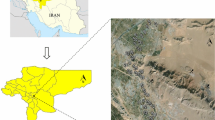
The main objective of this study was to determine the concentration of cadmium, chromium, copper, nickel, lead, and zinc in surface soils of two land uses including agricultural and urban green space in Semnan Province, Iran. For this purpose, the soil samples of 27 urban green space and 47 agricultural fields were collected and analyzed. The correlation coefficients, analysis of variance, principal component analysis, cluster analysis, and geoaccumulation index were utilized to compare the mean values in the two land uses and pinpoint the possible sources of contamination in the study area. The average contents of Cd, Cu, Cr, Ni, Pb, and Zn in green space soils were 0.1, 24.9, 78.7, 28.2, 22.1, and 82.1 mg/kg, respectively, while the mean concentrations of Cd, Cu, Cr, Ni, Pb, and Zn in agricultural soils were 0.3, 24.3, 83.7, 33.3, 18.1, and 80.4 mg/kg, respectively. The mean concentrations of lead, copper, and zinc were higher in urban green space in comparison with those of agricultural fields, while it was vice versa for chromium, cadmium, and nickel. In general, significant, but weak, correlations were observed between Zn with Pb (r = 0.53) and Cu (r = 0.61) and Ni with Cr (r = 0.55) and Cu(r = 0.51). The main sources of contamination turned out to be both natural and anthropogenic as the results of correlation coefficients, principal component analysis, and cluster analysis showed. That is to say, chromium and nickel had emanated from natural while the sources of cadmium, lead, and zinc could be attributed to anthropogenic activities. For the case of copper, both natural and anthropogenic activities were influential; however, the role of human activities was more effective. The results of contamination assessment showed that heavy metal contamination in agricultural land use was higher than green space indicating the role of human activities in this respect.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams, P. W. (2002). Soils: their implications to human health. Science of the Total Environment, 291, 1–32.
Amini, M., Afyuni, M., Khademi, H., Abbaspour, K. C., & Schulin, R. (2005). Mapping risk of cadmium and lead contamination to human health in soils of central Iran. Science of the Total Environment, 347(1), 64–77.
Bai, L. Y., Zeng, X. B., Li, L. F., Pen, C., & Li, S. H. (2010). Effects of land use on heavy metal accumulation in soils and sources analysis. Agricultural Sciences in China, 9(11), 1650–1658.
Banerjee, A. D. K. (2002). Heavy metal levels and solid phase speciation in street dusts of Delhi, India. Environmental Pollution, 123, 95–105.
Biasioli, M., Barberis, R., & Ajmone-Marsan, F. (2006). The influence of a large city on some soil properties and metals content. Science of the Total Environment, 356, 154–164.
Brūmelis, G., Lapiņa, L., Nikodemus, O., & Tabors, G. (2002). Use of the O horizon of forest soils in monitoring metal deposition in Latvia. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 135(1–4), 291–309.
Chen, T. B., Wong, J. W. C., Zhou, H. Y., & Wong, M. H. (1997). Assessment of trace metal distribution and contamination in surface soils of Hong Kong. Environmental Pollution, 96, 61–68.
Chen, T. B., Zheng, Y. M., Lei, M., Huang, Z. C., Wu, H. T., Chen, H., et al. (2005). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere, 60(4), 542–551.
Dankoub, Z., Ayoubi, S., Khademi, H., & Lu, S. G. (2012). Spatial distribution of magnetic properties and selected heavy metal s in calcareous soils as affected by land use in the Isfahan region, central Iran. Pedosphere, 22, 33–47.
Dayani, M., & Mohammadi, J. (2010). Geostatistical assessment of Pb, Zn and Cd contamination in near-surface soils of the urban-mining transitional region of Isfahan, Iran. Pedosphere, 20, 568–577.
De Kimpe, C. R., & Morel, J. L. (2000). Urban soil management: a growing concern. Soil Science, 165(1), 31–40.
Esmaeili, A., Moore, F., Keshavarzi, B., Jaafarzadeh, N., & Kermani, M. (2014). A geochemical survey of heavy metal s in agricultural and background soils of the Isfahan industrial zone, Iran. Jurnal of Catena, 121, 88–98.
Geranian, H., Mokhtari, A. R., & Cohen, D. R. (2013). A comparison of fractal methods and probability plots in identifying and mapping soil metal contamination near an active mining area, Iran. Science of Total Environment, 463-464, 845–854.
Ghaderian, S. M., & GhotbiRavandi, A. A. (2012). Accumulation of copper and other heavy metals by plants growing on Sarcheshmeh copper mining area, Iran. Geochemical Exploration, 123, 25–32.
Hafezimoghaddas, N., Namaghi, H. H., Ghorbani, H., & Dahrazma, B. (2013). The effects of agricultural practice and land-use on the distribution and origin of some potentially toxic metals in the soils of Golestan province, Iran. Environmental Earth sciences, 68(2), 487–497.
Hani, A., & Pazira, E. (2011). Heavy metal s assessment and identification of their sources in agricultural soils of Southern Tehran, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 176(1–4), 677–691.
Huang, S. S., Liao, Q. L., Hua, M., Wu, X. M., Bi, K. S., Yan, C. Y., et al. (2007). Survey of heavy metal contamination and assessment of agricultural soil in Yangzhong district, Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere, 67(11), 2148–2155.
Imperato, M., Adamo, P., Naimo, D., Arienzo, M., Stanzione, D., & Violante, P. (2003). Spatial distribution of heavy metal s in urban soils of Naples city (Italy). Environmental Pollution, 124, 247–256.
Jalali, M., & Hemati, N. (2013). Chemical fractionation of seven heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn) in selected paddy soils of Iran. Paddy and Water Environment, 11(1–4), 299–309.
Kapungwe, E. M. (2011). Industrial land use and heavy metal contaminated wastewater used for irrigation in periurban Zambia, Singapore. Tropical Geography, 32(1), 71–84.
Karim, Z., Qureshi, B. A., Mumtaz, M., & Qureshi, S. (2014). Heavy metal content in urban soils as an indicator of anthropogenic and natural influences on landscape of Karachi a multivariate spatio-temporal analysis. Ecological Indicators, 42, 20–31.
Karimi, R., Ayoubi, S., Jalalian, A., Sheikh-Hosseini, A. R., & Afyuni, M. (2011). Relationships between magnetic susceptibility and heavy metals in urban topsoils in the arid region of Isfahan, central Iran. Applied Geophysics, 74, 1–7.
KarimiNezhad, M. T., Tabatabaei, S. M., & Gholami, A. (2015). Geochemical assessment of steel smelter-impacted urban soils, Ahvaz, Iran. Geochemical Exploration, 152, 91–109.
Kelepertzis, E. (2014). Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Mediterranean: insights from Argolida basin, Peloponnese, Greece. Geoderma, 221, 82–90.
Lacerda, L. D., de Souza, M., & Ribeiro, M. G. (2004). The effects of land use change on mercury distribution in soils of Alta Floresta, Southern Amazon. Environmental Pollution, 129(2), 247–255.
Lorenz, K., & Lal, R. (2005). The depth distribution of organic soil carbon in relation to land use and management and the potential of carbon sequestration in subsoil horizons. Advances in Agronomy, 88, 35–66.
Lee, C. S. L., Li, X., Shi, W., Cheung, S. C. N., & Thornton, I. (2006). Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: a study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Science of the Total Environment, 356(1), 45–61.
Luo, X. S., Ding, J., Xu, B., Wang, Y. J., Li, H. B., & Yu, S. (2012). Incorporating bioaccessibility into human health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban park soils. Science of the Total Environment, 424, 88–96.
Madrid, L., Diaz-Barrientos, E., & Madrid, F. (2002). Distribution of heavy metal contents of urban soils in parks of Seville. Chemosphere, 49, 1301–1308.
Melaku, S., Dams, R., & Moens, L. (2005). Determination of heavy metals in agricultural soil samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry: microwave acid digestion versus aqua regia extraction. Analytica Chimica Acta, 543(1), 117–123.
Micó, C., Recatalá, L., Peris, M., & Sánchez, J. (2006). Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere, 65(5), 863–872.
Mirzaei, R., Ghorbani, H., Moghaddas, N. H., & Martín, J. A. R. (2014). Ecological risk of heavy metal hotspots in topsoils in the province of Golestan, Iran. Geochemical Exploration, 147, 268–276.
Muller, G. (1979). Schwermetalle in den sediments des Rheins-Veran-derungenseitt 1971. Umschan., 79, 778–783.
Nael, M., Khademi, H., Jalalian, A., Schulin, R., Kalbasi, M., & Sotohian, F. (2009). Effect of geopedological conditions on the distribution and chemical speciation of selected heavy metals in forest soils of western Alborz, Iran. Geoderma, 152, 157–170.
Naimi, S., & Ayoubi, S. (2013). Vertical and horizontal distribution of magnetic susceptibility and metal contents in an industrial district of central Iran. Applied Geophysics, 96, 55–66.
Parizanganeh, A., Hajisoltani, P., & Zamani, A. (2010). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in surficial soils surrounding zinc industrial complex in Zanjan-Iran. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2, 162–166.
Qishlaqi, A., Moore, F., & Forghani, G. (2009). Characterization of metal contamination in soils under two landuse patterns in the Angouran region, NW Iran; a study based on multivariate data analysis. Hazardous Materials, 172(1), 374–384.
Rodríguez Martín, J. A., Ramos-Miras, J. J., Boluda, R., & Gil, C. (2013). Spatial relations of heavy metals in arable and greenhouse soils of a Mediterranean environment region (Spain). Geoderma, 200–201, 180–188.
Rodríguez Martín, J. A., Nanos, N., Grau, J. M., Gil, L., & Lopez-Arias, M. (2008). Multiscale analysis of heavy metal contents in Spanish agricultural topsoils. Chemosphere, 70(6), 1085–1096.
Sun, C., Bi, C., Chen, Z., Wang, D., Zhang, C., Sun, Y., Zhongjie, Y., & Dong, Z. (2010). Assessment on environmental quality of heavy metal s in agricultural soils of Chongming Island, Shanghai City. Geographical Sciences, 20(1), 135–147.
Teng, Y., Wu, J., Lu, S., Wang, Y., Jiao, X., & Song, L. (2014). Soil and soil environmental quality monitoring in China: a review. Environment International, 69, 177–199.
USEPA (1998). Method 3051A. Microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils and oils. Revision1, US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), Washington, DC.
Wong, S. C., Li, X. D., Zhang, G., et al. (2002). Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environmental Pollution, 119, 33–44.
Xia, X., Chen, X., Liu, R., & Liu, H. (2011). Heavy metals in urban soils with various types of land use in Beijing, China. Hazardous Materials, 186(2), 2043–2050.
Yang, L., Li, Y., Peng, K., & Wu, S. (2014). Nutrients and heavy metal s in urban soils under different green space types in Anji, China. Catena, 115, 39–46.
Yeganeh, M., Afyuni, M., Khoshgoftarmanesh, A. H., Khodakarami, L., Amini, M., Soffyanian, A., & Schulin, R. (2013). Mapping of human health risks arising from soil nickel and mercury contamination. Hazardous Materials, 244, 225–239.
Yesilonis, I. D., Pouyat, R. V., & Neerchal, N. K. (2008). Spatial distribution of metals in soils in Baltimore, Maryland: role of native parent material, proximity to major roads, housing age and screening guidelines. Environmental Pollution, 156, 723–731.
Zhao, L., Xu, Y., Hou, H., Shangguan, Y., & Li, F. (2014). Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China. Science of the Total Environment, 468, 654–662.
Zhao, Y., Wang, Z., Sun, W., Huang, B., Shi, X., & Ji, J. (2010). Spatial interrelations and multiscale sources of soil heavy metal variability in a typical urban–rural transition area in Yangtze River Delta region of China. Geoderma, 156, 216–227.
Acknowledgments
The financial support of this project has been provided by the grant number 100-2164 offered by Geological Survey of Iran. The authors are grateful to Geological Survey of Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirzaei, R., Teymourzade, S., Sakizadeh, M. et al. Comparative study of heavy metals concentration in topsoil of urban green space and agricultural land uses. Environ Monit Assess 187, 741 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4973-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4973-9