Abstract
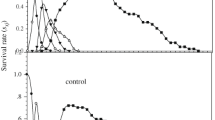
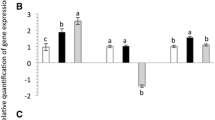
The soybean aphid, Aphis glycines Matsumura, is a major pest in soybean crop. Current management of this pest relies mainly on insecticides applications, and the neonicotinoid imidacloprid has been proposed as an effective insecticide to control A. glycines in soybean field. Imidacloprid at lethal concentrations not only exerts acute toxicity to A. glycines, but also cause various biological changes when aphids are chronically exposed to lower concentrations. In this study, we assessed the effects of a low-lethal (0.20 mg L−1) and two sublethal (0.05 and 0.10 mg L−1) imidacloprid concentrations on various A. glycines life history traits. Aphid exposure to 0.20 mg L−1 imidacloprid caused slower juvenile development, shorter reproductive period, and reduced adult longevity, fecundity and total lifespan. Stimulatory effects, i.e. hormesis, on reproduction and immature development duration were observed in aphids exposed to the lower sublethal imidacloprid concentrations. Consequently, the net reproduction rate (R 0) was significantly higher than in the control aphids. These findings stress the importance of the actual imidacloprid concentration in its toxicological properties on A. glycines. Therefore, our results would be useful for assessing the overall effects of imidacloprid on A. glycines and for optimizing integrated pest management programs targeting this pest.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agatz A, Cole TA, Preuss TG, Zimmer E, Brown CD (2013) Feeding inhibition explains effects of imidacloprid on the growth, maturation, reproduction, and survival of Daphnia magna. Environm Sci Technol 47:2909–2917
Agatz A, Ashauer R, Brown CD (2014) Imidacloprid perturbs feeding of Gammarus pulex at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:648–653
Ali A, Ahmad F, Biondi A, Wang Y, Desneux N (2012) Potential for using Datura alba leaf extracts against two major stored grain pests, the khapra beetle Trogoderma granarium and the rice weevil Sitophillus oryzae. J Pest Sci 85:359–366
Ayyanath M-M, Cutler GC, Scott-Dupree CD, Sibley PK (2013) Transgenerational shifts in reproduction hormesis in green peach aphid exposed to low concentrations of imidacloprid. PLoS One 8:e74532
Bao HB, Liu SH, Gu JH, Wang XZ, Liang XL, Liu ZW (2009) Sublethal effects of four insecticides on the reproduction and wing formation of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Pest Manag Sci 65:170–174
Bengochea P, Budia F, Viñuela E, Medina P (2014) Are kaolin and copper treatments safe to the olive fruit fly parasitoid Psyttalia concolor? J Pest Sci 87:351–359
Biondi A, Mommaerts V, Smagghe G, Vinuela E, Zappalà L, Desneux N (2012) The non-target impact of spinosyns on beneficial arthropods. Pest Manag Sci 68:1523–1536
Biondi A, Zappalà L, Stark JD, Desneux N (2013a) Do biopesticides affect the demographic traits of a parasitoid wasp and its biocontrol services through sublethal effects? PLoS 8:e76548
Biondi A, Desneux N, Amiens-Desneux E, Siscaro G, Zappalà L (2013b) Biology and developmental strategies of the Palaearctic parasitoid Bracon nigricans (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) on the Neotropical moth Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J Econ Entomol 106:1638–1647
Boina DR, Onagbola EO, Salyani M, Stelinski LL (2009) Antifeedant and sublethal effects of imidacloprid on Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri. Pest Manag Sci 65:870–877
Cai EX (2009) Residue and safe application of imidacloprid on vegetable soybean. Fujian J Agr Sci 24:241–245
Calabrese EJ, Baldwin LA (2001) Hormesis: a generalizable and unifying hypothesis. Crit Rev Toxicol 31:353–424
Cordeiro EMG, de Moura ILT, Fadini MAM, Guedes RNC (2013) Beyond selectivity: are behavioral avoidance and hormesis likely causes of pyrethroid-induced outbreaks of the southern red mite Oligonychus ilicis? Chemosphere 93:1111–1116
Cutler GC, Ramanaidu K, Astatkiec T, Ismana MB (2009) Green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae), reproduction during exposure to sublethal concentrations of imidacloprid and azadirachtin. Pest Manag Sci 65:205–209
Damsteegt VD, Stone AL, Kuhlmann M, Gildow FE, Domier LL, Sherman DJ, Schneider WL (2011) Acquisition and transmissibility of U.S. soybean dwarf virus isolates by the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines. Plant Dis 95:945–950
Desneux N, Pham-Delegue MH, Kaiser L (2004) Oviposition behaviour and patch-time allocation in two aphid parasitoids exposed to deltamethrin residues. Entomol Exp Appl 112:227–235
Desneux N, Fauvergue X, Dechaume-Moncharmont FX, Kerhoas L, Ballanger Y, Kaiser L (2005) Diaeretiella rapae limits Myzus persicae populations following applications of deltamethrin in oilseed rape. J Econ Entomol 98:9–17
Desneux N, Ramirez-Romero R, Kaiser L (2006a) Multistep bioassay to predict recolonization potential of emerging parasitoids after a pesticide treatment. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2675–2682
Desneux N, O’Neil RJ, Yoo HJS (2006b) Suppression of population growth of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines Matsumura, by predators: the identification of a key predator and the effects of prey dispersion, predator abundance, and temperature. Environ Entomol 35:1342–1349
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech JM (2007) The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 52:81–106
Desneux N, Barta RJ, Hoelmer KA, Hopper KR, Heimpel GE (2009) Multifaceted determinants of host specificity in an aphid parasitoid. Oecologia 160:387–398
Di Prisco G, Cavaliere V, Annoscia D, Varricchio P, Caprio E, Nazzi F, Gargiulo G, Pennacchio F (2013) Neonicotinoid clothianidin adversely affects insect immunity and promotes replication of a viral pathogen in honey bees. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:18466–18471
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fogel MN, Schneider MI, Desneux N, Gonzalez B, Ronco AE (2013) Impact of the neonicotinoid acetamiprid on immature stages of the predator Eriopis connexa (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ecotoxicology 22:1063–1071
Forbes VE, Calow P (1999) Is the per capita rate of increase a good measure of population-level effects in ecotoxicology? Environ Toxicol Chem 18:1544–1556
Gerami S, Jahromi KT, Ashouri A, Rasoulian G, Heidari A (2005) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid and pymetrozine on the life table parameters of Aphis Gpssypii Glover (Homoptera: Aphididae). Comm Appl Biol Sci 70:779–785
Gontijo PC, Moscardini VF, Michaud JP, Carvalho GA (2014) Non-target effects of chlorantraniliprole and thiamethoxam on Chrysoperla carnea when employed as sunflower seed treatments. J Pest Sci 87:711–719
Guedes RNC, Cutler GC (2014) Insecticide-induced hormesis and arthropod pest management. Pest Manag Sci 70:690–697
Han P, Niu CY, Lei CL, Cui JJ, Desneux N (2010a) Quantification of toxins in a Cry1Ac + CpTI cotton cultivar and its potential effects on the honey bee Apis mellifera L. Ecotoxicology 19:1452–1459
Han P, Niu CY, Lei CL, Cui JJ, Desneux N (2010b) Use of an innovative T-tube maze assay and the proboscis extension response assay to assess sublethal effects of GM products and pesticides on learning capacity of the honey bee Apis mellifera L. Ecotoxicology 19:1612–1619
He YX, Zhao J, Zheng Y, Zhan Z, Desneux N, Wu KM (2012) Lethal effect of imidacloprid on the coccinellid predator Serangium japonicum and sublethal effects on predator voracity and on functional response to the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Ecotoxicology 21:1291–1300
He YX, Zhao JW, Zheng Y, Weng QY, Biondi A, Desneux N, Wu KM (2013) Assessment of potential sublethal effects of various insecticides on key biological traits of the tobacco whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. Int J Biol Sci 9:246–255
Heimpel GE, Ragsdale DW, Venette R, Hopper KR, O’Neil RJ, Rutledge CE, Wu Z (2004) Prospects for importation biological control of the soybean aphid: anticipating potential costs and benefits. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:249–258
Heimpel GE, Yang Y, Hill JD, Ragsdale DW (2013) Environmental consequences of invasive species: greenhouse gas emissions of insecticide use and the role of biological control in reducing emissions. PLoS One 8:e72293
Jager T, Barsi A, Ducrot V (2013) Hormesis on life-history traits: is there such thing as a free lunch? Ecotoxicology 22:263–270
James DG (1997) Imidacloprid increase egg production in Amblyseius Victoriensis (Acari; Phytoseiidae). Expl Appl Acarol 21:75–82
James DG, Price TS (2002) Fecundity in twospotted spider mite (Acari: Tetranychidae) is increased by direct and systemic exposure to imidacloprid. J Econ Entomol 95:729–732
Lashkari MR, Sahragard A, Ghadamyari M (2007) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid and pymetrozine on population growth parameters of cabbage aphid, Brevicoryne brassicae on rapeseed, Brassica napus L. Insect Sci 14:207–212
Laycock I, Lenthall KM, Barratt AT, Cresswell JE (2012) Effects of imidacloprid, a neonicotinoid pesticide, on reproduction in worker bumble bees (Bombus terrestris). Ecotoxicology 21:1937–1945
Li Y, Hill CB, Hartman GL (2004) Effect of three resistant soybean genotypes on the fecundity, mortality, and maturation of soybean aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 97:1106–1111
Liang P, Tian YA, Biondi A, Desneux N, Gao XW (2012) Short-term and transgenerational effects of the neonicotinoid nitenpyram on susceptibility to insecticides in two whitefly species. Ecotoxicology 21:1889–1898
Magalhaes LC, Hunt TE, Siegfried BD (2009) Efficacy of neonicotinoid seed treatments to reduce soybean aphid populations under field and controlled conditions in Nebraska. J Econ Entomol 102:187–195
Malaquias JB, Ramalho FS, Omoto C, Godoy WAC, Silveira RF (2013) Imidacloprid affects the functional response of predator Podisus nigrispinus (Dallas) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) to strains of Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) on Bt cotton. Ecotoxicology 23:192–200
Mensah C, Di Fonzo C, Nelson RL, Wang D (2005) Resistance to soybean aphid in early maturing soybean germplasm. Crop Sci 45:2228–2233
Miao J, Du ZB, Wu YQ, Gong ZJ, Jiang YL, Duan Y, Li T, Lei CL (2013) Sub-lethal effects of four neonicotinoid seed treatments on the demography and feeding behaviour of the wheat aphid Sitobion avenae. Pest Manag Sci 70:55–59
Moores GD, Gao XW, Denholm I, Devonshire AL (1996) Characterisation of insensitive acetylcholinesterase in insecticide resistant cotton aphids, Aphis gossypii Glover (Homoptera: Aphididae). Pestic Biochem Physiol 56:102–110
Nauen R, Tietjen K, Wagner K, Elbert A (1998a) Efficacy of plant metabolites of imidacloprid against Myzus persicae and Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae). Pestic Sci 52:53–57
Nauen R, Koob B, Elbert A (1998b) Antifeedant effects of sublethal dosages of imidacloprid on Bemisia tabaci. Entomol Exp Appl 88:287–293
Nyman AM, Hintermeister A, Schirmer K, Ashauer R (2013) The insecticide imidacloprid causes mortality of the freshwater amphipod Gammarus pulex by interfering with feeding behavior. PLoS One 8(5):e62472
Pan H, Liu Y, Liu B, Lu Y, Xu X, Qian X, Wu K, Desneux N (2014) Lethal and sublethal effects of cycloxaprid, a novel cis-nitromethylene neonicotinoid insecticide, on the mirid bug Apolygus lucorum. J Pest Sci 87:731–738
Papachristos DP, Milonas PG (2008) Adverse effects of soil applied insecticides on the predatory coccinellid Hippodamia undecimnotata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol Control 47:77–81
Planes L, Catalan J, Tena A, Porcuna JL, Jacas JA, Izquierdo J, Urbaneja A (2013) Lethal and sublethal effects of spirotetramat on the mealybug destroyer, Cryptolaemus montrouzieri. J Pest Sci 86:321–327
Ragsdale DW, McCornack BP, Venette RC, Potter DB, Macrae IV et al (2007) Economic threshold for soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 100:1258–1267
Ragsdale DW, Landis DA, Brodeur J, Heimpel GE, Desneux N (2011) Ecology and magement of the soybean aphid in North America. Annu Rev Entomol 56:375–399
Saber M, Abedi Z (2013) Effects of methoxyfenozide and pyridalyl on the larval ectoparasitoid Habrobracon hebetor. J Pest Sci 86:685–693
Shi X, Jiang L, Wang H, Qiao K, Wang D, Wang K (2011) Toxicities and sublethal effects of seven neonicotinoid insecticides on survival, growth and reproduction of imidacloprid-resistant cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii. Pest Manag Sci 67:1528–1533
Shirvani-Farsani N, Zamani AA, Abbasi AA, Kheradmand K (2013) Toxicity of three insecticides and tobacco extract against the fungus gnat, Lycoriella auripila and the economic injury level of the gnat on button mushroom. J Pest Sci 86:591–597
Stark JD, Banks JE (2003) Population-level effects of pesticides and other toxicants on arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 48:505–519
Stark JD, Banks JE, Vargas R (2004) How risky is risk assessment: the role that life history strategies play in susceptibility of species to stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:732–736
Tan Y, Biondi A, Desneux N, Gao XW (2012) Assessment of physiological sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the mirid bug Apolygus lucorum (Meyer-Dür). Ecotoxicology 21:1989–1997
Tomizawa M, Casida JE (2001) Structure and diversity of insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Pest Manag Sci 57:914–922
Vernon RS, van Herk WG, Clodius M, Harding C (2013) Crop protection and mortality of Agriotes obscurus wireworms with blended insecticidal wheat seed treatments. J Pest Sci 86:137–150
Wang AH, Wu JC, Yu YS, Liu JL, Yue JF, Wang MY (2005) Selective insecticide-induced stimulation on fecundity and biochemical changes in Tryporyza incertulas (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Econ Entomol 98:1144–1149
Widiarta IN, Matsumura M, Suzuki Y, Nakasuji F (2001) Effects of sublethal doses of imidacloprid on the fecundity of green leafhoppers, Nephotettix spp. (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) and their natural enemies. Appl Entomol Zool 36:501–507
Wu ZS, Schenk-Hamlin D, Zhan WY, Ragsdale DW, Heimpel GE (2004) The soybean aphid in China: a historical review. Ann Entomol Soc Am 97:209–218
Yu YS, Shen GQ, Zhu HL, Lu YT (2010) Imidacloprid-induced hormesis on the fecundity and juvenile hormone levels of the green peach aphid Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Pest Biochem Physiol 98:238–242
Zotti MJ, Grutzmacher AD, Lopes IH, Smagghe G (2013) Comparative effects of insecticides with different mechanisms of action on Chrysoperla externa (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae): lethal, sublethal and dose-response effects. Insect Sci 20:743–752
Acknowledgments
This research was mainly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31272077).
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yanyan Qu and Da Xiao have contributed equally to the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., Xiao, D., Li, J. et al. Sublethal and hormesis effects of imidacloprid on the soybean aphid Aphis glycines . Ecotoxicology 24, 479–487 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1396-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1396-2