Abstract
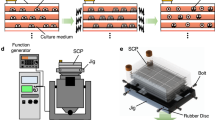
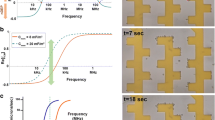
Low intensity (< 2 Vpp/cm (peak to peak voltage/cm)), high frequency (10–30 MHz), and 10 min alternating electric fields (sine wave with no DC component) induce non-contact and enzyme-free cell detachment of anchorage-dependent cells directly from commercially available cell culture flasks and stack plates. 0.25 Vpp/cm, 20 MHz alternating electric field for 10 min at room temperature (RT) induced maximum detachment and separated 99.5 ± 0.1% (mean ± SEM, n = 6) of CHO-K1 and 99.8 ± 0.2% of BALB/3T3 cells from the culture flasks. Both vertical and lateral alternating electric field applications for 10 min at RT detach the CHO-K1 cells from 25 cm2 culture flasks. The alternating electric field application induced cell detachment is almost noncytotoxic, and over 90% of the detached cells remained alive. The alternating electric field applied CHO-K1 cells for 90 min showed little or no lag phase and immediately enter exponential phase in cell growth. Combination of the 20 MHz alternating electric field and enzymatic treatment for 4 min at 37 °C showed synergetic effect and quickly detached human induced pluripotent stem cells from a laminin-coated culture flask compared with the only enzymatic treatment. These results indicate that the rapid cell detachment with both the electric field application and the enzymatic treatment could be applied to subcultures of cells that are susceptible to prolonged enzymatic digestion damage for mass culture of sustainable clinical use.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen AK-L, Reuveny S, Oh SKW (2013) Application of human mesenchymal and pluripotent stem cell microcarrier cultures in cellular therapy: achievements and future direction. Biotech Adv 31:1032–1046
Cheng Z, Cheng K, Weng W (2017) SiO2/TiO2 nanocomposite films on polystyrene for light-induced cell detachment application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:2130–2137
Elson E (1995) Biologic effects of radiofrequency and microwave fields: in vivo and in vitro experimental results. In: Bronzino JD (ed) The biomedical engineering handbook. CRC Press Inc, Boca Raton, pp 1417–1423
Goh TK-P, Zhang Z-Y, Chen AK-L, Reuveny S, Choolan M, Chan JKY, Oh SK-W (2013) Microcarrier culture for efficient expansion and osteogenic differentiation of human fetal mesenchymal stem cells. Biores Open Access 2:84–97
Guedes JC, Park J-H, Lakhkar NJ, Kim H-W, Knowles JC, Wall IB (2012) TiO2-doped phosphate glass microcarriers: a stable bioactive substrate for expansion of adherent mammalian cells. J Biomater Appl 28:2–11
Heathman TRJ, Glyn VAM, Picken A, Rafiq QA, Coopman K, Nienow AW, Kara B, Hewitt CJ (2015) Expansion, harvest and cryopreservation of human mesenchymal stem cells in a serum-free microcarrier process. Biotech Bioeng 112:1696–1706
Hendrick V, Muniz E, Geuskens G, Wérenne J (2001) Adhesion, growth and detachment of cells on modified polystyrene surface. Cytotechnology 36:49–53
Hippel RV (1954) Dielectric materials and applications. MIT Press, Cambridge, p 438
Hirai H, Umegaki R, Kino-Oka M, Taya M (2002) Characterization of cellular motions through direct observation of individual cells at early stage in anchorage-dependent culture. J Biosci Bioeng 94:351–356
Hirano K, Konagaya S, Turner A, Noda Y, Kitamura S, Kotera H, Iwata H (2017) Closed-channel culture system for efficient and reproducible differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into islet cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 487:344–350
Hong Y, Yu M, Weng W, Cheng K, Wang H, Lin J (2013) Light-induced cell detachment for cell sheet technology. Biomaterials 34:11–18
Kakegawa T, Mochizuki N, Sadr N, Suzuki H, Fukuda J (2013) Cell-adhesive and cell-repulsive zwitterionic oligopeptides for micropatterning and rapid electrochemical detachment of cells. Tisssue Eng A 19:290–298
Kirson ED, Gurvich Z, Schneiderman R, Dekel E, Itzhaki A, Wasserman Y, Schatzberger R, Palti Y (2004) Disruption of cancer cell replication by alternating electric fields. Cancer Res 64:3288–3295
Koyama S (2011) Electrically modulated attachment and detachment of animal cells cultured on an optically transparent patterning electrode. J Biosci Bioeng 111:578–583. (Corrigendum in: Koyama S (2012) J Biosci Bioeng 114:240)
Kurashina Y, Hirano M, Imashiro C, Totani K, Komotori J, Takemura K (2017) Enzyme-free cell detachment mediated by resonance vibration with temperature modulation. Biotech Bioeng 114:2279–2288
Merten O-W (2015) Advances in cell culture: anchorage dependence. Philos Trans R Soc B 370:20140040
Nakagawa M, Taniguchi Y, Senda S, Takizawa N, Ichisaka T, Asano K, Morizane A, Doi D, Takahashi J, Nishizawa M, Yoshida Y, Toyoda T, Osafune K, Sekiguchi K, Yamanaka S (2014) A novel efficient feeder-free culture system for the derivation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci Rep 4:3594
Nakajima K, Honda S, Nakamura Y, López-Redondo F, Kohsaka S, Yamato M, Kikuchi A, Okano T (2001) Intact microglia are cultured and non-invasively harvested without pathological activation using a novel cultured cell recovery method. Biomaterials 22:1213–1223
Nienow AW, Rafiq QA, Coopman K, Hewitt CJ (2014) A potentially scalable method for the harvesting of hMSCs from microcarriers. Biochem Eng J 85:79–88
Potapova IA, Brink PR, Cohen IS, Doronin SV (2008) Culturing of human mesenchymal stem cells as three-dimensional aggregates induces functional expression of CXCR4 that regulates adhesion to endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 283:13100–13107
Yang HS, Jeon O, Bhang SH, Lee S-H, Kim B-S (2010) Suspension culture of mammalian cells using thermosensitive microcarrier that allows cell detachment without proteolytic enzyme treatment. Cell Transpl 19:1123–1132
Yoon SH, Mofrad MR (2011) Cell adhesion and detachment on gold surfaces modified with a thiol-functionalized RGD peptide. Biomaterials 32:7286–7296
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koyama, S., Wada, M., Tamura, Y. et al. Alternating electric field application induced non-contact and enzyme-free cell detachment. Cytotechnology 71, 583–597 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-019-00307-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-019-00307-4