Abstract
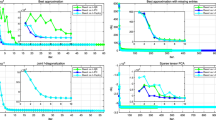
When optimizing on a Riemannian manifold, it is important to use an efficient retraction, which maps a point on a tangent space to a point on the manifold. In this paper, we prove a map based on the QR factorization to be a retraction on the generalized Stiefel manifold. In addition, we propose an efficient implementation of the retraction based on the Cholesky QR factorization. Numerical experiments show that the proposed retraction is more efficient than the existing one based on the polar factorization.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Absil, P.A., Mahony, R., Sepulchre, R.: Optimization Algorithms on Matrix Manifolds. Princeton University Press, Princeton (2008)
Absil, P.A., Malick, J.: Projection-like retractions on matrix manifolds. SIAM J. Optim. 22(1), 135–158 (2012)
Adler, R.L., Dedieu, J.P., Margulies, J.Y., Martens, M., Shub, M.: Newton’s method on Riemannian manifolds and a geometric model for the human spine. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 22(3), 359–390 (2002)
Aihara, K., Sato, H.: A matrix-free implementation of Riemannian Newton’s method on the Stiefel manifold. Optim. Lett. 11(8), 1729–1741 (2017)
Bendory, T., Eldar, Y.C., Boumal, N.: Non-convex phase retrieval from STFT measurements. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 64(1), 467–484 (2018)
Boumal, N., Absil, P.A., Cartis, C.: Global rates of convergence for nonconvex optimization on manifolds. IMA J. Numer. Anal. https://doi.org/10.1093/imanum/drx080 (2018)
Boumal, N., Mishra, B., Absil, P.A., Sepulchre, R.: Manopt, a Matlab toolbox for optimization on manifolds. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 15, 1455–1459 (2014)
Edelman, A., Arias, T.A., Smith, S.T.: The geometry of algorithms with orthogonality constraints. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 20(2), 303–353 (1998)
Imakura, A., Yamamoto, Y.: Efficient implementations of the modified Gram–Schmidt orthogonalization with a non-standard inner product. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.10440 (2017)
Kasai, H., Sato, H., Mishra, B.: Riemannian stochastic recursive gradient algorithm with retraction and vector transport and its convergence analysis. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 2521–2529 (2018)
Lowery, B.R., Langou, J.: Stability analysis of QR factorization in an oblique inner product. arXiv preprint arXiv:1401.5171 (2014)
Manton, J.H.: Optimization algorithms exploiting unitary constraints. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 50(3), 635–650 (2002)
Mishra, B., Sepulchre, R.: Riemannian preconditioning. SIAM J. Optim. 26(1), 635–660 (2016)
Ring, W., Wirth, B.: Optimization methods on Riemannian manifolds and their application to shape space. SIAM J. Optim. 22(2), 596–627 (2012)
Rozložník, M., Tůma, M., Smoktunowicz, A., Kopal, J.: Numerical stability of orthogonalization methods with a non-standard inner product. BIT Numer. Math. 52(4), 1035–1058 (2012)
Sato, H.: A Dai–Yuan-type Riemannian conjugate gradient method with the weak Wolfe conditions. Comput. Optim. Appl. 64(1), 101–118 (2016)
Sato, H., Iwai, T.: A Riemannian optimization approach to the matrix singular value decomposition. SIAM J. Optim. 23(1), 188–212 (2013)
Sato, H., Sato, K.: Riemannian optimal system identification algorithm for linear MIMO systems. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 1(2), 376–381 (2017)
Yger, F., Berar, M., Gasso, G., Rakotomamonjy, A.: Adaptive canonical correlation analysis based on matrix manifolds. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 299–306 (2012)
Yger, F., Berar, M., Gasso, G., Rakotomamonjy, A.: Oblique principal subspace tracking on manifold. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 2429–2432. IEEE (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editor and the reviewer for their careful reading and constructive comments, especially on Theorem 3.2. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Akira Imakura (University of Tsukuba) and Dr. Yusaku Yamamoto (The University of Electro-Communications) for their helpful advice. This study was supported in part by Grant Numbers JP16K17647 and JP18K18064 from the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research Program (KAKENHI) of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, H., Aihara, K. Cholesky QR-based retraction on the generalized Stiefel manifold. Comput Optim Appl 72, 293–308 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-018-0046-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10589-018-0046-7