Abstract
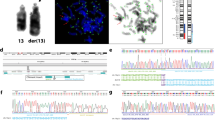
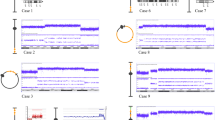
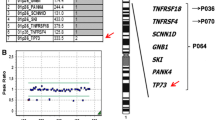
Deletion of the distal band of the short arm of chromosome 1 (monosomy 1p36) is the most common terminal deletion syndrome, occurring in about 1 in 5000 newborns. Of the 121 subjects ascertained for our study to date, 12 (9.9%) have interstitial deletions, three of which are complex rearrangements showing more than one deletion. Herein we report the characterization of a complex rearrangement with two interstitial deletions in the same chromosome 1p36.33-p36.23. We narrowed and analyzed the breakpoints and junctions between the sequence fragments involved in the rearrangement to determine the structure of this deleted chromosome 1. The analyses of the DNA sequence at the junctions showed additional complexity: an inversion and a third de-novo interstitial deletion. We reconstructed this complex rearrangement of 1p36 to understand the mechanism of formation. Analysis of the breakpoint junctions revealed that three of the four breakpoints each interrupted a gene. Alignments of the junctions showed the lack of any sequence similarity between the breakpoints, suggesting the involvement of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) in the ligation of broken ends following deletion. The identification of translin recognition sites in the breakpoints suggests translin involvement in the repair of broken chromosomes. This report is one of the first to examine constitutional chromosomal rearrangements at the DNA sequence level. The discovery of cryptic events in seemingly simple chromosome rearrangements may provide the basis for proposing mechanisms of formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeysinghe SS, Chuzhanova N, Krawczak M, Ball EV, Cooper DN (2003) Translocation and gross deletion breakpoints in human inherited disease and cancer – I: Nucleotide composition and recombination-associated motifs. Hum Mutat 22: 229–244.
Aoki K, Suzuki K, Sugano T et al. (1995) A novel gene, Translin, encodes a recombination hotspot binding protein associated with chromosomal translocations. Nat Genet 10: 167–174.
Ballif BC, Kashork CD, Shaffer LG (2000) FISHing for mechanisms of cytogenetically defined terminal deletions using chromosome-specific subtelomeric probes. Eur J Hum Genet 8: 764–770.
Ballif BC, Yu W, Shaw CA, Kashork CD, Shaffer LG (2003) Monosomy 1p36 breakpoint junctions suggest pre-meiotic breakage–fusion–bridge cycles are involved in generating terminal deletions. Hum Mol Genet 12: 2153–2165.
Ballif BC, Gajecka M, Shaffer LG (2004a) Monosomy 1p36 breakpoints indicate repetitive DNA sequence elements may be involved in generating and/or stabilizing some terminal deletions. Chromosome Res 12: 133–141.
Ballif BC, Wakui K, Gajecka M, Shaffer LG (2004b) Translocation breakpoint mapping and sequence analysis in three monosomy 1p36 subjects with der(1)t(1;1)(p36;q44) suggest mechanisms for telomere capture in stabilizing de novo terminal rearrangements. Hum Genet 114: 198–206.
Benson G (1999) Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 27: 573–580.
Gajecka M, Yu W, Ballif BC et al. (2005) Delineation of mechanisms and regions of dosage imbalance in complex rearrangements of 1p36 leads to a putative gene for regulation of cranial suture closure. Eur J Hum Genet 13: 139–149.
Heilstedt HA, Ballif BC, Howard LA et al. (2003) Physical map of 1p36, placement of breakpoints in monosomy 1p36, and clinical characterization of the syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 72: 1200–1212.
Jurka J (2000) Repbase update: a database and an electronic journal of repetitive elements. Trends Genet 16: 418–420.
Kent WJ (2002) BLAT—the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res 12: 656–664.
Page SL, Shaffer LG (1997) Nonhomologous Robertsonian translocations form predominantly during female meiosis. Nat Genet 15: 231–232.
Rice P, Longden I, Bleasby A (2000) EMBOSS: the European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet 16: 276–277.
Shaffer LG, Lupski JR (2000) Molecular mechanisms for constitutional chromosomal rearrangements in humans. Annu Rev Genet 34: 297–329.
Shaffer LG, McCaskill C, Han JY et al. (1994) Molecular characterization of de novo secondary trisomy 13. Am J Hum Genet 55: 968–974.
Yu W, Ballif BC, Kashork CD et al. (2003) Development of a comparative genomic hybridization microarray and demonstration of its utility with 25 well-characterized 1p36 deletions. Hum Mol Genet 12: 2145–2152.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gajecka, M., Glotzbach, C.D. & Shaffer, L.G. Characterization of a complex rearrangement with interstitial deletions and inversion on human chromosome 1. Chromosome Res 14, 277–282 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-006-1044-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-006-1044-7