Abstract
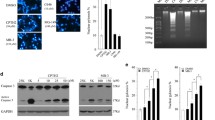
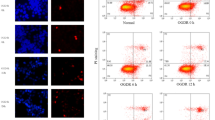
Contrary to cell cycle-associated cyclin-dependent kinases, CDK5 is best known for its regulation of signaling processes in regulating mammalian CNS development. Studies of CDK5 have focused on its phosphorylation, although the diversity of CDK5 functions in the brain suggests additional forms of regulation. Here we expanded on the functional roles of CDK5 glycosylation in neurons. We showed that CDK5 was dynamically modified with O-GlcNAc in response to neuronal activity and that glycosylation represses CDK5-dependent apoptosis by impairing its association with p53 pathway. Blocking glycosylation of CDK5 alters cellular function and increases neuronal apoptosis in the cell model of the ICH. Our findings demonstrated a new role for O-glycosylation in neuronal apoptosis and provided a mechanistic understanding of how glycosylation contributes to critical neuronal functions. Moreover, we identified a previously unknown mechanism for the regulation of activity-dependent gene expression, neural development, and apoptosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barros-Minones L et al (2013) Inhibition of calpain-regulated p35/cdk5 plays a central role in sildenafil-induced protection against chemical hypoxia produced by malonate. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832:705–717. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.02.002
Bhattacharjee RN, Banks GC, Trotter KW, Lee HL, Archer TK (2001) Histone H1 phosphorylation by Cdk2 selectively modulates mouse mammary tumor virus transcription through chromatin remodeling. Mol Cell Biol 21:5417–5425. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.16.5417-5425.2001
Bradl M, Lassmann H (2010) Oligodendrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 119:37–53. doi:10.1007/s00401-009-0601-5
Cruz JC, Tseng HC, Goldman JA, Shih H, Tsai LH (2003) Aberrant Cdk5 activation by p25 triggers pathological events leading to neurodegeneration and neurofibrillary tangles. Neuron 40:471–483
Dhavan R, Tsai LH (2001) A decade of CDK5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:749–759. doi:10.1038/35096019
Ducruet AF, Zacharia BE, Hickman ZL, Grobelny BT, Yeh ML, Sosunov SA, Connolly ES Jr (2009) The complement cascade as a therapeutic target in intracerebral hemorrhage. Exp Neurol 219:398–403. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.07.018
Francisco H, Kollins K, Varghis N, Vocadlo D, Vosseller K, Gallo G (2009) O-GLcNAc post-translational modifications regulate the entry of neurons into an axon branching program. Dev neurobiol 69:162–173. doi:10.1002/dneu.20695
Haltiwanger RS, Grove K, Philipsberg GA (1998) Modulation of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine levels on nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins in vivo using the peptide O-GlcNAc-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase inhibitor o-(2-acetamido-2-deoxy-d-glucopyranosylidene)amino-n-phenylcarbamate. J Biol Chem 273:3611–3617
Hart GW (1997) Dynamic O-linked glycosylation of nuclear and cytoskeletal proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 66:315–335. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.66.1.315
Hart GW, Housley MP, Slawson C (2007) Cycling of O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine on nucleocytoplasmic proteins. Nature 446:1017–1022. doi:10.1038/nature05815
Karabiyikoglu M, Hua Y, Keep RF, Ennis SR, Xi G (2004) Intracerebral hirudin injection attenuates ischemic damage and neurologic deficits without altering local cerebral blood flow. J cereb blood flow metabol 24:159–166. doi:10.1097/01.WCB.0000100062.36077.84
Lazarus BD, Love DC, Hanover JA (2009) O-GlcNAc cycling: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Int J biochem cell biol 41:2134–2146. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2009.03.008
Levy YS, Streifler JY, Panet H, Melamed E, Offen D (2002) Hemin-induced apoptosis in PC12 and neuroblastoma cells: implications for local neuronal death associated with intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurotox Res 4:609–616. doi:10.1080/1029842021000045624
Li BS, Zhang L, Takahashi S, Ma W, Jaffe H, Kulkarni AB, Pant HC (2002) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 prevents neuronal apoptosis by negative regulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3. EMBO J. 21:324–333. doi:10.1093/emboj/21.3.324
Li BS et al (2003) Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 is involved in neuregulin-dependent activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt activity mediating neuronal survival. J Biol Chem 278:35702–35709. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302004200
Li L et al (2013) Up-regulation of NFATc4 involves in neuronal apoptosis following intracerebral hemorrhage. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33:893–905. doi:10.1007/s10571-013-9955-2
Lin S et al (2012) Heme activates TLR4-mediated inflammatory injury via MyD88/TRIF signaling pathway in intracerebral hemorrhage. J neuroinflam 9:46. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-9-46
Liu F, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Hart GW, Gong CX (2004) O-GlcNAcylation regulates phosphorylation of tau: a mechanism involved in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10804–10809. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400348101
Lopes JP, Agostinho P (2011) Cdk5: multitasking between physiological and pathological conditions. Prog Neurobiol 94:49–63. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.03.006
Ma Y et al (2013) Activated cyclin-dependent kinase 5 promotes microglial phagocytosis of fibrillar beta-amyloid by up-regulating lipoprotein lipase expression Molecular & cellular proteomics. MCP 12:2833–2844. doi:10.1074/mcp.M112.026864
Marshall S, Bacote V, Traxinger RR (1991) Discovery of a metabolic pathway mediating glucose-induced desensitization of the glucose transport system Role of hexosamine biosynthesis in the induction of insulin resistance. J biol chem 266:4706–4712
Prabhakaran S, Naidech AM (2012) Ischemic brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage: a critical review Stroke. J Cereb Circ 43:2258–2263. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.655910
Rashidian J et al (2009) Essential role of cytoplasmic cdk5 and Prx2 in multiple ischemic injury models, in vivo. J.Neurosci 29:12497–12505. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3892-09.2009
Rexach JE, Clark PM, Hsieh-Wilson LC (2008) Chemical approaches to understanding O-GlcNAc glycosylation in the brain. Nat Chem Biol 4:97–106. doi:10.1038/nchembio.68
Sansing LH, Messe SR, Cucchiara BL, Cohen SN, Lyden PD, Kasner SE, Investigators C (2009) Prior antiplatelet use does not affect hemorrhage growth or outcome after ICH. Neurology 72:1397–1402. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000342709.31341.88
Selim M (2009) Deferoxamine mesylate: a new hope for intracerebral hemorrhage: from bench to clinical trials Stroke. J Cereb Circ 40:S90–S91. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.533125
Sharma P et al (2002) Phosphorylation of MEK1 by cdk5/p35 down-regulates the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 277:528–534. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109324200
Sundaram JR et al (2013) Specific inhibition of p25/Cdk5 activity by the Cdk5 inhibitory peptide reduces neurodegeneration in vivo. J.Neurosci 33:334–343. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3593-12.2013
Tallent MK, Varghis N, Skorobogatko Y, Hernandez-Cuebas L, Whelan K, Vocadlo DJ, Vosseller K (2009) In vivo modulation of O-GlcNAc levels regulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity through interplay with phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 284:174–181. doi:10.1074/jbc.M807431200
Wang J, Dore S (2008) Heme oxygenase 2 deficiency increases brain swelling and inflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neuroscience 155:1133–1141. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.07.004
Zeidan Q, Hart GW (2010) The intersections between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: implications for multiple signaling pathways. J Cell Sci 123:13–22. doi:10.1242/jcs.053678
Zhang J, Krishnamurthy PK, Johnson GV (2002) Cdk5 phosphorylates p53 and regulates its activity. J Neurochem 81:307–313
Zheng YL, Li BS, Kanungo J, Kesavapany S, Amin N, Grant P, Pant HC (2007) Cdk5 Modulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling regulates neuronal survival. Mol Biol Cell 18:404–413. doi:10.1091/mbc.E06-09-0851
Zhu J, Li W, Mao Z (2011) Cdk5: mediator of neuronal development, death and the response to DNA damage. Mech Ageing Dev 132:389–394. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2011.04.011
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81371299, 31300902, 81471188), the Colleges and Universities in Natural Science Research Project of Jiangsu Province (13KJB310009), a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), Technology Innovation Programme of Jiangsu Province (No. CXLX13_876), and Technology Innovation Programme of Nantong University (Nos. YKC13075, YKC13086).
Author’s Contribution
Xiaojin Ning, Jianhong Shen, Yuteng Ji, Lili Xie, Hongmei Wang, Ning Liu, Xide Xu, and Chi Sun did the experiments; Tao Tao did the statistic work; Dongmei Zhang designed the experimental plans; and Aiguo Shen and Kaifu Ke wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Xiaojin Ning and Tao Tao contributed equally to this work.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10571_2016_391_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Figure S1. (A) Hemin treatment at different concentrations (25, 50, 75, 100, and 150 μM) reduced cellular viability in a dose-dependent manner at indicative time point (3, 6, and 12 h) compared to untreated cells (control) assayed by CCK-8. (B) Hemin treatment (75 μM) reduced cellular viability in a time-dependent manner compared to untreated cells assayed by CCK-8.Supplementary material 1 (TIFF 182 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ning, X., Tao, T., Shen, J. et al. The O-GlcNAc Modification of CDK5 Involved in Neuronal Apoptosis Following In Vitro Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37, 527–536 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0391-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-016-0391-y