Abstract
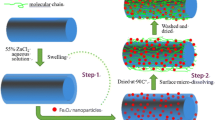
Magnetic nanoparticles were synthesized and embedded into the surface of cotton fibers via surface micro-dissolution method using NaOH/urea aqueous solution as dissolving agent, magnetic nanoparticles as the filler, and H2SO4/Na2SO4 aqueous solution as the coagulant. The magnetic nanoparticles and cotton fabrics were systematically studied by means of scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, thermal gravity, vibrating sample magnetometry, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and tensile testing. The results indicated that treated cotton fabrics contained about 12 wt% Fe3O4 and possessed durable magnetic response. Without using any adhesion agents, this surface micro-dissolution treatment provides a simple and green method to introduce nanoparticles into superficial layers of natural cotton fibers.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai J, Zhang L (2005) Rapid dissolution of cellulose in LiOH/Urea and NaOH/Urea aqueous solutions. Macromol Biosci 5:539–548
Cai J, Zhang L (2006) Unique gelation behavior of cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Biomacromolecules 7:183–189
Calvo S, Arias-Duque N, Giraldo O, Rosales-Rivera A (2012) Compositional, thermal and magnetic analysis of bamboo fibers covered with magnetite nanoparticles by in situ co-precipitation. Revista Mexicana de Física 58:134–137
Chen X, Burger C, Wan F, Zhang J, Rong L, Hsiao BS, Chu B, Cai J, Zhang L (2007) Structure study of cellulose fibers wet-spun from environmentally friendly NaOH/urea aqueous solutions. Biomacromolecules 8:1918–1926
Chen J, Wang F, Huang K, Liu Y, Liu S (2009) Preparation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with adjustable morphology. J Alloy Compd 475:898–902
Chia CH, Zakaria S, Ahamd S, Abdullah M, Jani SM (2006) Preparation of magnetic paper from kenaf: lumen loading and in situ synthesis method. Am J Appl Sci 3:1750–1754
Davidenko II (1996) High-density thermoremanent information recording in magnetic carrier and magneto-optical readout. J Inf Rec 23:315–323
de Rooij M, Crienen S, Witjes JA, Barentsz JO, Rovers MM, Grutters JPC (2014) Cost-effectiveness of magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and MR-guided targeted biopsy versus systematic transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy in diagnosing prostate cancer: a modelling study from a health care perspective. Eur Urol 66:430–436
Giri J, Guha Thakurta S, Bellare J, Kumar Nigam A, Bahadur D (2005) Preparation and characterization of phospholipid stabilized uniform sized magnetite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 293:62–68
Jiang Z, Fang Y, Xiang J, Ma Y, Lu A, Kang H, Huang Y, Guo H, Liu R, Zhang L (2014) Intermolecular interactions and 3D structure in cellulose-NaOH-urea aqueous system. J Phys Chem B 118:10250–10257
Katepetch C, Rujiravanit R (2011) Synthesis of magnetic nanoparticle into bacterial cellulose matrix by ammonia gas-enhancing in situ co-precipitation method. Carbohydr Polym 86:162–170
Katz E, Willner I (2006) A bis-quinone-functionalized Au-electrode subjected to hydrophobic magnetic nanoparticles acts as a three-state “Write-Read-Erase” information storage system. Electrochem Commun 8:879–882
Kraemer NA, Donker HCW, Otto J, Hodenius M, Senegas J, Slabu I, Klinge U, Baumann M, Muellen A, Obolenski B, Guenther RW, Krombach GA (2010) A concept for magnetic resonance visualization of surgical textile implants. Invest Radiol 45:477–483
Kraemer NA, Donker HCW, Kuehnert N, Otto J, Schrading S, Krombach GA, Klinge U, Kuhl CK (2013) In vivo visualization of polymer-based mesh implants using conventional magnetic resonance imaging and positive-contrast susceptibility imaging. Invest Radiol 48:200–205
Kumar P, Negi YS, Singh SP (2011) Filler loading in the lumen or/and cell wall of fibers—a literature review. BioResources 6:1635–1646
Li L, Leung CW, Pong PWT (2013a) Magnetism of iron oxide nanoparticles and magnetic biodetection. J Nanoelectron Optoelectron 8:397–414
Li Y, Zhu H, Gu H, Dai H, Fang Z, Weadock NJ, Guo Z, Hu L (2013b) Strong transparent magnetic nanopaper prepared by immobilization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in a nanofibrillated cellulose network. J Mater Chem A 1:15278–15283
Li R, Wang S, Lu A, Zhang L (2015) Dissolution of cellulose from different sources in an NaOH/urea aqueous system at low temperature. Cellulose 22:339–349
Lin H, Watanabe Y, Kimura M, Hanabusa K, Shirai H (2003) Preparation of magnetic poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) materials by in situ synthesis of magnetite in a PVA matrix. J Appl Polym Sci 87:1239–1247
Lue A, Zhang L (2007) Advance in solvents of cellulose. Acta Polym Sin 10:937–944
Munawar RF, Zakaria S, Radiman S, Hua C-C, Abdullah M, Yamauchi T (2010) Properties of magnetic paper prepared via in situ synthesis method. Sains Malays 39:593–598
O’Handley RC (1999) Modern magnetic materials: principles and applications. Wiley, Hoboken
Qi H, Chang C, Zhang L (2008) Effects of temperature and molecular weight on dissolution of cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Cellulose 15:779–787
Saini P, Choudhary V, Vijayan N, Kotnala RK (2012) Improved electromagnetic interference shielding response of poly(aniline)-coated fabrics containing dielectric and magnetic nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 116:13403–13412
Shi X, Zhang L, Cai J, Cheng G, Zhang H, Li J, Wang X (2011) A facile construction of supramolecular complex from polyaniline and cellulose in aqueous system. Macromolecules 44:4565–4568
Shyr T-W, Shie J-W (2012) Electromagnetic shielding mechanisms using soft magnetic stainless steel fiber enabled polyester textiles. J Magn Magn Mater 324:4127–4132
Small AC, Johnston JH (2009) Novel hybrid materials of magnetic nanoparticles and cellulose fibers. J Colloid Interface Sci 331:122–126
Tartaj P (2009) Superparamagnetic composites: magnetism with no memory. Eur J Inorg Chem 2009:333–343
Wang J, Zhang K, Peng Z, Chen Q (2004) Magnetic properties improvement in Fe3O4 nanoparticles grown under magnetic fields. J Cryst Growth 266:500–504
Xu F, Yang Y, Zhang G, Zhang F, Zhang Y (2015) A self-stiffness finishing for cotton fabric with N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide. Cellulose 22:2837–2844
Yan H, Zhang J, You C, Song Z, Yu B, Shen Y (2009) Influences of different synthesis conditions on properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys 113:46–52
Zakaria S, Ong BH, Ahmad SH, Abdullah M, Yamauchi T (2005) Preparation of lumen-loaded kenaf pulp with magnetite (Fe3O4). Mater Chem Phys 89:216–220
Zhang L (2012) Novel materials with advanced properties constructed from cellulose solution dissolved at low temperature. In: Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society, p 243
Zhang H, Zheng JY (2012) Immobilization of magnetic magnetite nanoparticle film on polyamide fabric. J Appl Polym Sci 125:3770–3777
Zhang B, Tu Z, Zhao F, Wang J (2013) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles prepared by using an improved polyol method. Appl Surf Sci 266:375–379
Zhong W, Liu P, Shi HG, Xue DS (2010) Ferroferric oxide/polystyrene (Fe3O4/PS) superparamagnetic nanocomposite via facile in situ bulk radical polymerization. Express Polym Lett 4:183–187
Acknowledgment
This work was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2013B026), National Training Programs of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates (201510635046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, M., Li, L., Xie, R. et al. Preparation of magnetic cotton fabric by surface micro-dissolution treatment. Cellulose 24, 1099–1106 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1152-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1152-2