Abstract
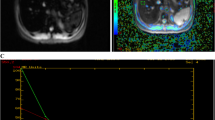
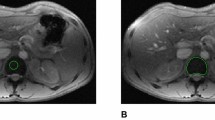
In b-thalassemia major (TM) multiple blood transfusions are needed for survival. As a consequence these patients present iron overload in different organs, including heart and liver. Magnetic resonance imaging using a bright blood gradient echo sequence has been successfully used for the quantification of tissue iron. The aim is to evaluate of the accuracy and precision in the evaluation of liver and myocardial T2* values in TM using two different analytical software solutions. Thirty TM patients aged 20–56 years (mean age 37, 11M/19F) were scanned in a GE 1.5 T CVI system. Each scan included the measurement of heart and liver T2* and the left ventricular ejection fraction using standard techniques. The analysis of T2* of heart and liver was done using the two different analytical software solutions: the “Functool” protocol by GE and the T2* module of QMassMR v7.4 by Medis medical imaging systems bv, Leiden, The Netherlands. The cardiac and liver T2* measurements showed that both software solutions allow reproducible measurements with low intra-observer variations (accuracy < 0.3 ms, precision < 2 ms). There is a small but significant difference between the two solutions of 2.4 ms in cardiac and of 1.5 ms in liver measurements. However, from the clinical point of view these differences (<2 ms) are small with negligible impact on the patient’s treatment management. The comparison of the T2* measurements using the two analytical software solutions proved that both techniques enable reproducible measurements for the evaluation of iron overload in heart and liver.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Modell B, Berdoukas V (1984) The clinical approach to Thalassemia. Grune & Stratton, New York, NY
Zurlo MG, De Stefano P, Borgna-pignatti C (1989) Survival and causes of death in thalassemia major. Lancet 2:27–30
Buja LM, Roberts WC (1971) Iron in the heart: etiology and clinical significance. Am J Med 51:209–221
Engle MA (1969) Cardiac involvement in Cooley’s anemia. Ann NY Acad Sci 119:694–702
Jacobs A (1980) The pathology of iron overload. In: Jacobs A, Worwood M (eds) Iron in biochemistry and medicine, II. Academic Press, New York, pp 439–452
Jacobs A, Miller F, Worwood M, Beamisch R, et al. Ferritin in the serum of normal subjects with iron deficiency and iron overload. Br Med J 1972: 206-11
Crosby WH (1976) Serum ferritin fails to indicate hemochromatosis: nothing gold can stay. N Engl J Med 294:333–334
Barry M, Sherlock S (1971) Measurement of liver iron concentration in liver biopsy specimens. Lancet 1:100–103
Brittenham GM, Badman DG (2003) Noninvasive measurement of iron: report of an NIDDK workshop. Blood 101:15–19
Liu P, Henkelman M, Joshi J et al (1996) Quantification of cardiac and tissue iron by nuclear magnetic resonance relaxometry in a novel murine thalassemia-cardiac iron overload model. Can J Cardiol 12:155–164
Mavrogeni S, Gotsis E, Ladis V, Berdousis E, Verganelakis D, Toulas P, Cokkinos DV (2008) Magnetic resonance evaluation of liver and myocardial iron deposition in thalassemia intermedia and b-thalassemia major. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 24:849–854
Anderson LJ, Holden S, Davis B, Prescott E, Charrier CC, Bunce NH, Firmin DN, Wonke B, Porter J, Walker JM et al (2001) Cardiovascular t2-star (t2*) magnetic resonance for the early diagnosis of myocardial iron overload. Eur Heart J 22:2171–2179
McKee PA, Castelli WP, McNamara PM et al (1971) The natural history of congestive heart failure the Framingham Study. N Engl J Med 285:1441–1446
Wood JC, Enriquez C, Ghugre N et al (2005) MRI R2 and R2* mapping accurately estimates hepatic iron concentration in transfusion-dependent thalassemia and sickle cell disease patients. Blood 106:1460–1465
Ramazzotti A, Pepe A, Positano V, Rossi G, De Marchi D, Brizi MG, Luciani A, Midiri M, Sallustio G, Valeri G, Caruso V, Centra M, Cianciulli P, De Sanctis V, Maggio A, Lombardi M (2009) Multicenter validation of the magnetic resonance T2* technique for segmental and global quantification of myocardial iron. J Magn Reson Imaging 30(1):62–68
Westwood MA, Firmin DN, Gildo M, Renzo G, Stathis G, Markissia K, Vasili B, Pennell DJ (2005) Intercentre reproducibility of magnetic resonance T2* measurements of myocardial iron in thalassaemia. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 21(5):531–538
Kirk P, He T, Anderson LJ, Roughton M, Tanner MA, Lam WW, Au WY, Chu WC, Chan G, Galanello R, Matta G, Fogel M, Cohen AR, Tan RS, Chen K, Ng I, Lai A, Fucharoen S, Laothamata J, Chuncharunee S, Jongjirasiri S, Firmin DN, Smith GC, Pennell DJ (2010) International reproducibility of single breathhold T2* MR for cardiac and liver iron assessment among five thalassemia centers. J Magn Reson Imaging 32:315–319
Pennell DJ, Berdoukas V, Karagiorga M, Ladis V, Piga A, Aessopos A et al (2006) Randomized controlled trial of deferiprone or deferoxamine in beta-thalassemia major patients with asymptomatic myocardial siderosis. Blood 107(9):3738–3744
Tanner MA, Galanello R, Dessi C, Smith GC, Westwood MA, Agus A et al (2007) A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of the effect of combined therapy with deferoxamine and deferiprone on myocardial iron in thalassemia major using cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Circulation 115(14):1876–1884
Kirk P, Roughton M, Porter JB, Walker JM, Tanner MA, Patel J et al (2009) Cardiac T2* magnetic resonance for prediction of cardiac complications in thalassemia major. Circulation 120(20):1961–1968
Smith GC, Carpenter JP, He T, Alam MH, Firmin DN, Pennell DJ (2011) Value of black blood T2* cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 13:21
Saiviroonporn P, Viprakasit V, Boonyasirinant T, Khuhapinant A, Wood JC, Krittayaphong R (2011) Comparison of the region-based and pixel-wise methods for cardiac T2* analysis in 50 transfusion-dependent Thai thalassemia patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr 35(3):375–381
Conflict of interest
Kees van Wijk is employed by Medis medical imaging systems bv. Johan H.C. Reiber is the CEO of Medis medical imaging systems bv, and has a part time appointment at the LUMC as Prof of Medical Imaging. Sophie Mavrogeni, Konstantinos Bratis, Louisa Kyrou and Antonios Kattamis declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mavrogeni, S., Bratis, K., van Wijk, K. et al. The reproducibility of cardiac and liver T2* measurement in thalassemia major using two different software packages. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 29, 1511–1516 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-013-0242-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-013-0242-6