Abstract
Aims
Activation of the PI3K/Akt signal transduction pathway has been linked to endocrine resistance in tamoxifen treated breast cancer patients. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway causes phosphorylation of Bad leading to modulation of cellular apoptosis. The present study was carried out to test the hypothesis that disruption of apoptosis in breast cancer, via Akt activation, is linked with hormone resistance.
Methods
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed on 402 oestrogen receptor (ER) positive breast cancers using antibodies against Bad, pBad (ser 112), Bcl-2, Bcl-xl and Bax.
Results
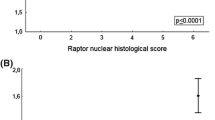
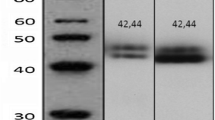
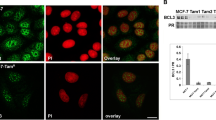
Bad, pBad (ser 112), Bcl-2 and Bax expression was observed in the cellular cytoplasmic compartment only. Patients, whose tumours had high levels of Bad expression, had a significantly improved disease-free survival when compared to patients whose tumours had low levels of Bad expression (P = 0.049). Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway by either heregulin or oestrogen had no effect on expression of Bad, Bcl-2, Bax or Bcl-xl. However, heregulin increased pBad (ser 112) expression.
Discussion
Data presented here shows that Bad expression is associated with relapse in tamoxifen-treated breast cancer patients, supporting our hypothesis that the apoptosis pathway is involved in tamoxifen resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gradishar WJ (2004) Tamoxifen—what next? Oncologist 9:378–384
Coombes RC, Hall E, Gibson LJ, Paridaens R, Jassem J, Delozier T, Jones SE, Alvarez I, Bertelli G, Ortmann O, Coates AS, Bajetta E, Dodwell D, Coleman RE, Fallowfield LJ, Mickiewicz E, Andersen J, Lonning PE, Cocconi G, Stewart A, Stuart N, Snowdon CF, Carpentieri M, Massimini G, Bliss JM (2004) A randomized trial of exemestane after two to three years of tamoxifen therapy in postmenopausal women with primary breast cancer. N Engl J Med 350:1081–1092
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) (2005) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 365:1687–1717
Dowsett M (2003) Analysis of time to recurrence in the ATAC (arimidex, tamoxifen, alone or in combination) trial according to estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status. Breast Cancer Res Treat 82:S7–S7
Shou J, Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Wakeling AE, Ali S, Weiss H, Schiff R (2004) Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:926–935
Jordan NJ, Gee JM, Barrow D, Wakeling AE, Nicholson RI (2004) Increased constitutive activity of PKB/Akt in tamoxifen resistant breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 87:167–180
Knuefermann C, Lu Y, Liu B, Jin W, Liang K, Wu L, Schmidt M, Mills GB, Mendelsohn J, Fan Z (2003) HER2/PI-3K/Akt activation leads to a multidrug resistance in human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Oncogene 22:3205–3212
Schiff R, Massarweh SA, Shou J, Bharwani L, Mohsin SK, Osborne CK (2004) Cross-talk between estrogen receptor and growth factor pathways as a molecular target for␣overcoming endocrine resistance. Clin Cancer Res 10:331S–336S
Fleming FJ, Myers E, Kelly G, Crotty TB, McDermott EW, O’Higgins NJ, Hill AD, Young LS (2004) Expression of SRC-1, AIB1, and PEA3 in HER2 mediated endocrine resistant breast cancer; a predictive role for SRC-1. J Clin Pathol 57:1069–1074
Osborne CK, Bardou V, Hopp TA, Chamness GC, Hilsenbeck SG, Fuqua SA, Wong J, Allred DC, Clark GM, Schiff R (2003) Role of the estrogen receptor coactivator AIB1 (SRC-3) and HER-2/neu in tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:353–361
McKenna NJ, Lanz RB, O’Malley BW (1999) Nuclear receptor coregulators: cellular and molecular biology. Endocr Rev 20:321–344
Johnston SR, Head J, Pancholi S, Detre S, Martin LA, Smith IE, Dowsett M (2003) Integration of signal transduction inhibitors with endocrine therapy: an approach to overcoming hormone resistance in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9:524S–532S
Clark AS, West K, Streicher S, Dennis PA (2002) Constitutive and inducible Akt activity promotes resistance to chemotherapy, trastuzumab, or tamoxifen in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 1:707–717
West KA, Castillo SS, Dennis PA (2002) Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and chemotherapeutic resistance. Drug Resist Updat 5:234–248
Tsuruo T, Naito M, Tomida A, Fujita N, Mashima T, Sakamoto H, Haga N (2003) Molecular targeting therapy of cancer: drug resistance, apoptosis and survival signal. Cancer Sci 94:15–21
Tovey SM, Witton CJ, Bartlett JM, Stanton PD, Reeves JR, Cooke TG (2004) Outcome and human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER) 1–4 status in invasive breast carcinomas with proliferation indices evaluated by bromodeoxyuridine labelling. Breast Cancer Res 6:R246–R251
Kirkegaard T, Witton CJ, McGlynn LM, Tovey SM, Dunne B, Lyon A, Bartlett JM (2005) AKT activation predicts outcome in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. J Pathol 207:139–146
Kato S, Endoh H, Masuhiro Y, Kitamoto T, Uchiyama S, Sasaki H, Masushige S, Gotoh Y, Nishida E, Kawashima H, Metzger D, Chambon P (1995) Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science 270:1491–1494
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem 276:9817–9824
Stoica GE, Franke TF, Moroni M, Mueller S, Morgan E, Iann MC, Winder AD, Reiter R, Wellstein A, Martin MB, Stoica A (2003) Effect of estradiol on estrogen receptor-alpha gene expression and activity can be modulated by the ErbB2/PI 3-K/Akt pathway. Oncogene 22:7998–8011
Sun M, Paciga JE, Feldman RI, Yuan Z, Coppola D, Lu YY, Shelley SA, Nicosia SV, Cheng JQ (2001) Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH Kinase (PI3K)/AKT2, activated in breast cancer, regulates and is induced by estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) via interaction between ERalpha and PI3K. Cancer Res 61:5985–5991
Yu D, Hung MC (2000) Overexpression of ErbB2 in cancer and ErbB2-targeting strategies. Oncogene 19:6115–6121
Tan Y, Ruan H, Demeter MR, Comb MJ (1999) p90(RSK) blocks bad-mediated cell death via a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 274:34859–34867
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Sanchez B, Martinou JC (2001) Bax is present as a high molecular weight oligomer/complex in the mitochondrial membrane of apoptotic cells. J Biol Chem 276:11615–11623
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ (2004) Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116:205–219
Willis SN, Adams JM (2005) Life in the balance: how BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:617–625
Harada H, Andersen JS, Mann M, Terada N, Korsmeyer SJ (2001) p70S6 kinase signals cell survival as well as growth, inactivating the pro-apoptotic molecule BAD. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9666–9670
McLaughlin MM, Kumar S, McDonnell PC, Van Horn S, Lee JC, Livi GP, Young PR (1996) Identification of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase-activated protein kinase-3, a novel substrate of CSBP p38 MAP kinase. J Biol Chem 271:8488–8492
Naresh A, Long W, Vidal GA, Wimley WC, Marrero L, Sartor CI, Tovey S, Cooke TG, Bartlett JM, Jones FE (2006) The ERBB4/HER4 intracellular domain 4ICD is a BH3-only protein promoting apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 66:6412–6420
Coombes RC, Hall E, Gibson LJ, Paridaens R, Jassem J, Delozier T, Jones SE, Alvarez I, Bertelli G, Ortmann O, Coates AS, Bajetta E, Dodwell D, Coleman RE, Fallowfield LJ, Mickiewicz E, Andersen J, Lonning PE, Cocconi G, Stewart A, Stuart N, Snowdon CF, Carpentieri M, Massimini G, Bliss JM (2004) A randomized trial of exemestane after two to three years of tamoxifen therapy in postmenopausal women with primary breast cancer. N Engl J Med 350:1081–1092
Treeck O, Zhou R, Diedrich K, Ortmann O (2004) Tamoxifen long-term treatment in vitro alters the apoptotic response of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs 15:787–793
Fernando RI, Wimalasena J (2004) Estradiol abrogates apoptosis in breast cancer cells through inactivation of BAD: Ras-dependent nongenomic pathways requiring signaling through ERK and Akt. Mol Biol Cell 15:3266–3284
Kim R (2005) Unknotting the roles of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL in cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 333:336–343
Linjawi A, Kontogiannea M, Halwani F, Edwardes M, Meterissian S (2004) Prognostic significance of p53, bcl-2, and Bax expression in early breast cancer. J Am Coll Surg 198:83–90
Baccouche S, Daoud J, Frikha M, Mokdad-Gargouri R, Gargouri A, Jlidi R (2003) Immunohistochemical status of p53, MDM2, bcl2, bax, and ER in invasive ductal breast carcinoma in Tunisian patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1010:752–763
Cameron DA, Keen JC, Dixon JM, Bellamy C, Hanby A, Anderson TJ, Miller WR (2000) Effective tamoxifen therapy of breast cancer involves both antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic changes. Eur J Cancer 36:845–851
Bukholm IR, Bukholm G, Nesland JM (2002) Reduced expression of both Bax and Bcl-2 is independently associated with lymph node metastasis in human breast carcinomas. APMIS 110:214–220
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cannings, E., Kirkegaard, T., Tovey, S. et al. Bad expression predicts outcome in patients treated with tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat 102, 173–179 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9323-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9323-8