Abstract
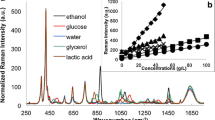
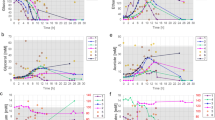
Cultivations of Streptomyces peucetius in two types of medium were monitored on-line using a Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer combined with an attenuated total reflection probe. The quantitative measurements of the glucose, starch and acetate concentrations were implemented using partial least squares calibration models. These were regressed on spectral and concentration information obtained by adding together single constituent spectra of the main constituents in the medium according to a full factorial design. The accuracy achieved was considered to be satisfactory, with an average root mean square error of prediction of 1.5 g/l for glucose and 0.25 g/l for acetate. The methodology used is considered to be a rapid technique for generation of calibration data, and a step towards the use of library type data for calibration purposes in quantitative FTIR spectroscopy applications in bioprocesses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung H, Arnold MA (1995) Monitoring the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of starch with near-infrared spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc 49:1097–1102
Dahlbacka J, Weegar J, von Weymarn N, Fagervik K (2012) On-line measurement of the substrate concentrations in Pichia pastoris fermentations using FT-IR/ATR. Biotechnol Lett 34:1009–1017
Doak DL, Phillips JA (1999) In situ monitoring of an Escherichia coli fermentation using a diamond composition ATR probe and mid-infrared spectroscopy. Biotechnol Prog 15:529–539
Kornmann H, Rhiel M, Cannizzaro C, Marison I, von Stockar U (2003) Methodology for real-time, multianalyte monitoring of fermentations using an in-situ mid-infrared sensor. Biotechnol Bioeng 82:702–709
Kornmann H, Valentinotti S, Duboc P, Marison I, von Stockar U (2004) Monitoring and control of Gluconacetobacter xylinus fed-batch cultures using in situ mid-IR spectroscopy. J Biotechnol 113:231–245
Landgrebe D, Haake C, Höpfner T, Beutel S, Hitzmann B, Scheper T, Rhiel M, Reardon KF (2010) On-line infrared spectroscopy for bioprocess monitoring. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:11–20
Næs T, Isaksson T, Fearn T, Davies T (2002) A user friendly guide to multivariate calibration and classification. NIR Publications, Chichester
Roychoudhury P, Harvey LM, McNeil B (2006) The potential of mid infrared spectroscopy (MIRS) for real time bioprocess monitoring. Anal Chim Acta 571:159–166
Schenk J, Marison IW, von Stockar U (2007) Simplified Fourier-transform mid-infrared spectroscopy calibration based on a spectra library for the on-line monitoring of bioprocesses. Anal Chim Acta 591:132–140
Acknowledgments
This study was made possible by funding from Tekes—the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahlbacka, J., Kiviharju, K., Eerikäinen, T. et al. Monitoring of Streptomyces peucetius cultivations using FTIR/ATR spectroscopy and quantitative models based on library type data. Biotechnol Lett 35, 337–343 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1093-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1093-2