Abstract
Purpose of work
Mutation of the p53 gene is the most common genetic alteration in human cancers. Our study proposes to rationally design a p53 antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) repository, which contains a series of ASOs containing single nucleotide differences to discriminate between each mutant and wild type (WT) p53.
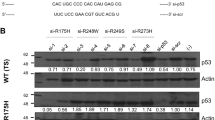
The Sfold software was used to predict target-accessibility and we designed an initial series of antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) that target the p53 mutants A161T, R175H and R249S. Western-blot analysis indicated that ASOs strongly inhibited the expression of p53 mutants in a panel of human tumor cell lines (SNU-449, SK-BR-3 and PLC/PRF/5) while having little effect on the expression of WT p53 (HepG2 cells). In three cancer lines harboring each of the p53 mutations, mutant-specific ASO treatment led to a dose-dependent inhibition of cell growth, cell viability, colony formation and invasion, and expression of mutant p53-dependent survival proteins. Our preliminary results indicate that a single nucleotide difference in ASOs can discriminate between mutant and WT p53. These observations support the hypothesis that a p53 ASO repository can be a potentially valuable tool to knock down oncogenic mutant p53 and warrant the testing of a p53 ASO repository in in vivo settings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beeram M, Patnaik A, Rowinsky EK (2005) Raf: a strategic target for therapeutic development against cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(27):6771–6790
Blandino G, Levine AJ, Oren M (1999) Mutant p53 gain of function: differential effects of different p53 mutants on resistance of cultured cells to chemotherapy. Oncogene 18(2):477–485
Bullock AN, Fersht AR (2001) Rescuing the function of mutant p53. Nat Rev Cancer 1(1):68–76
Cadwell C, Zambetti GP (2001) The effects of wild-type p53 tumor suppressor activity and mutant p53 gain-of-function on cell growth. Gene 277(1–2):15–30
Joerger AC, Fersht AR (2007) Structure-function-rescue: the diverse nature of common p53 cancer mutants. Oncogene 26(15):2226–2242
Keats JJ, Reiman T, Maxwell CA, Taylor BJ, Larratt LM, Mant MJ, Belch AR, Pilarski LM (2003) In multiple myeloma, t(4;14)(p16;q32) is an adverse prognostic factor irrespective of FGFR3 expression. Blood 101(4):1520–1529
Lane DP (2005) Exploiting the p53 pathway for the diagnosis and therapy of human cancer. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 70:489–497
Littlejohn JE, Cao X, Miller SD, Ozvaran MK, Jupiter D, Zhang L, Rodarte C, Smythe WR (2008) Bcl-xl antisense oligonucleotide and cisplatin combination therapy extends survival in SCID mice with established mesothelioma xenografts. Int J Cancer 123(1):202–208
Mack GS (2008) Genzyme and Isis strike megadeal. Nat Biotechnol 26(3):251–253
Martinez LA, Naguibneva I, Lehrmann H, Vervisch A, Tchenio T, Lozano G, Harel-Bellan A (2002) Synthetic small inhibiting RNAs: efficient tools to inactivate oncogenic mutations and restore p53 pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(23):14849–14854
Miletti-Gonzalez KE, Chen S, Muthukumaran N, Saglimbeni GN, Wu X, Yang J, Apolito K, Shih WJ, Hait WN, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L (2005) The CD44 receptor interacts with p-glycoprotein to promote cell migration and invasion in cancer. Cancer Res 65(15):6660–6667
O’Connor OA, Smith EA, Toner LE, Teruya-Feldstein J, Frankel S, Rolfe M, Wei X, Liu S, Marcucci G, Chan KK, Chanan-Khan A (2006) The combination of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and the Bcl-2 antisense molecule oblimersen sensitizes human b-cell lymphomas to cyclophosphamide. Clin Cancer Res 12(9):2902–2911
Opalinska JB, Gewirtz AM (2002) Nucleic-acid therapeutics: basic principles and recent applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1(7):503–514
Ozvaran MK, Cao XX, Miller SD, Monia BA, Hong WK, Smythe WR (2004) Antisense oligonucleotides directed at the Bcl-xl gene product augment chemotherapy response in mesothelioma. Mol Cancer Ther 3(5):545–550
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55(2):74–108
Petitjean A, Achatz MI, Borresen-Dale AL, Hainaut P, Olivier M (2007) Tp53 mutations in human cancers: functional selection and impact on cancer prognosis and outcomes. Oncogene 26(15):2157–2165
Sahu NK, Shilakari G, Nayak A, Kohli DV (2007) Antisense technology: a selective tool for gene expression regulation and gene targeting. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 8(5):291–304
Scian MJ, Stagliano KE, Anderson MA, Hassan S, Bowman M, Miles MF, Deb SP, Deb S (2005) Tumor-derived p53 mutants induce NF-kappaB2 gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 25(22):10097–10110
Selivanova G, Wiman KG (2007) Reactivation of mutant p53: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Oncogene 26(15):2243–2254
Sigal A, Rotter V (2000) Oncogenic mutations of the p53 tumor suppressor: the demons of the guardian of the genome. Cancer Res 60(24):6788–6793
Strano S, Dell’Orso S, Di Agostino S, Fontemaggi G, Sacchi A, Blandino G (2007) Mutant p53: an oncogenic transcription factor. Oncogene 26(15):2212–2219
Tamm I, Dorken B, Hartmann G (2001) Antisense therapy in oncology: new hope for an old idea? Lancet 358(9280):489–497
Vousden KH, Lu X (2002) Live or let die: the cell’s response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer 2(8):594–604
Wacheck V, Zangemeister-Wittke U (2006) Antisense molecules for targeted cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 59(1):65–73
Wiman KG (2006) Strategies for therapeutic targeting of the p53 pathway in cancer. Cell Death Differ 13(6):921–926
Xie Z, Choong PF, Poon LF, Zhou J, Khng J, Jasinghe VJ, Palaniyandi S, Chen CS (2008) Inhibition of CD44 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells enhances apoptosis, chemosensitivity, and reduces tumorigenesis and invasion. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 62(6):949–957
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by the Singapore Cancer Syndicate Grant (TN0031, AN0038), and the Terry Fox Run Cancer Research Grant 2004 (Chien-Shing Chen). Wee Joo Chng was supported in part by the National Medical Research Council of Singapore Clinician Scientist Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Z., Chng, W.J., Tay, K.G. et al. Therapeutic potential of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides in downregulating p53 oncogenic mutations in cancers. Biotechnol Lett 33, 221–228 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0423-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0423-5