Abstract
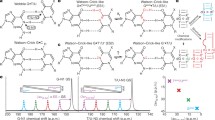
Transcriptase measurements of quantum expectations due to time-dependent coherent states populating informational DNA base-pair sites, designated by G–C → *G–*C, G–C → G′–C′, and A–T → *A–*T, provide a model for transcription and replication of time-dependent DNA lesions exhibited by bacteriophage T4. Coherent states are introduced as consequences of hydrogen bond arrangement, keto-amino → enol-imine, where product protons are shared between two sets of indistinguishable electron lone-pairs and thus participate in coupled quantum oscillations at frequencies of ~1013 s−1. The transcriptase deciphers and executes genetic specificity instructions by implementing measurements on superposition proton states at *G–*C, G′–C′, and *A–*T sites in an interval Δt ≪ 10−13 s. Decohered states participate in Topal–Fresco replication, which introduces substitutions *C → T, *G → A, G′ → T, and G′ → C, but superposition *A–*T states are deleted. These results imply an evolutionary shift favoring A–T richness.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002) Molecular biology of the cell, 4th edn. Garland, New York
Antequera F, Bird A (1993) Number of CpG islands and genes in human and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:11995–11999
Auerbach C (1959) Spontaneous mutations in dry spores of Neurospora crassa. Z Vererbungslehre 90:335–346
Baltz RH, Bingham PM, Drake JW (1976) Heat mutagenesis in bacteriophage T4: The transition pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:1269–1273
Bell NF, Sawyer RF, Volkas RR (2002) Entanglement and quantal coherence: study of two limiting cases of rapid systems-bath interactions. Phys Rev A65:052105-1–052105-12
Benzer S (1961) On the topography of the genetic fine structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 47:403–415
Bingham PM, Baltz RH, Ripley LS, Drake JW (1976) Heat mutagenesis in bacteriophage T4: The transversion pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:4159–4163
Bromham L, Penny D (2003) The modern molecular clock. Nat Rev Genet 4:216–224
Bromham LD, Rambaut A, Hamdy MD, Penny D (2000) The power of relative rates tests depends on the data. J Mol Evol 50:296–301
Caldin EF (1968) Tunneling in proton transfer reactions in solution. Chem Rev 69:135–156
Cooper WG (1993) Roles of evolution, quantum mechanics and point mutations in origins of cancer. Cancer Biochem Biophys 13:147–170
Cooper WG (1994) T4 phage evolution data in terms of a time-dependent Topal-Fresco mechanism. Biochem Genet 32:383–395
Cooper WG (1995) Evolutionary origin of expandable G-C rich triplet repeat DNA sequences. Biochem Genet 33:173–181
Cooper WG (1996) Hypothesis on a causal link between EMF and an evolutionary class of cancer and spontaneous abortion. Cancer Biochem Biophys 15:151–170
Cooper WG (2009) Evidence for transcriptase quantum processing implies entanglement and decoherence of superposition proton states. Biosystems 97(2):73–89
Cooper DN, Youssoufian H (1988) The CpG dinucleotide and human genetic diseases. Hum Genet 78:151–155
Cortopassi G, Liu Y (1995) Genotypic selection of mitochondrial and oncogenic mutations in human tissue suggest mechanisms of age-related pathophysiology. Mutat Res 338:151–159
Drake JW (1966) Spontaneous mutations accumulating in bacteriophage T4 in the complete absence of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 55:738–743
Drake JW, Baltz RH (1976) The biochemistry of mutagenesis. Ann Rev Biochem 45:11–37
Drake JW, McGuire J (1967) Characteristics of mutations appearing spontaneously in extracellular particles of bacteriophage T4. Genetics 55:387–398
Drake JW, Ripley LS (1994) Mutagenesis. In: Karam JD (ed) Molecular biology of bacteriophage T4. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 98–124
Drake JW, Charlesworth B, Charlesworth D, Crow JF (1998) Rates of spontaneous mutation. Genetics 148:1667–1686 (see p. 1671)
Drummond A, Pybus OG, Rambaut A (2003) Inference of viral evolutionary rates from molecular sequences. Adv Parasitol 54:331–358
Elango N, Kim S-H, NICS Program, Vigoda E, Yi SV (2008) Mutations of different molecular origins exhibit contrasting patterns of regional substitution rate variation. PLoS Comput Biol 4:e1000015. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000015
Evans D, Burbach J, van Leeuwen F (1995) Somatic mutations in the brain: relationship to aging? Mutat Res 338:173–182
Fitch WM, Leiter JM, Li XQ, Palese P (1991) Positive Darwinian evolution in human influenza A viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:4270–4274
Fu YH, Kuhl DAP, Pizzuti A, Pieretti M, Sutcliffe J, Richards S, Verkerk A, Holden J, Fenwick R Jr, Warren ST, Oostra BA, Nelson DL, Caskey CT (1991) Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: Resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell 67:1047–1058
Garcia-Viloca M, Gao J, Karplus M, Truhlar DG (2004) How enzymes work: analysis by modern rate theory and computer simulations. Science 303:186–195
Ghosh S, Rosenbaum TF, Aeppll G, Coppersmith SN (2003) Entangled quantum states of magnetic dipoles. Nature 425:48–51
Gillispie JH (1991) The causes of molecular evolution. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK
Grace M, Brif C, Rabitz H, Walmsley IA, Kosut RL, Lidar DA (2007) Optimal control of quantum gates and suppression of decoherence in a system of interacting two-level particles. J Phys B At Mol Opt Phys 40:S103–S125
Hwang DG, Green P (2004) Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo sequence analysis reveals varying neutral substitution patterns in mammalian evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13994–14001
Kadenbach B, Munscher C, Frank V, Muller-Hocker J, Napiwotzki J (1995) Human aging is associated with stochastic somatic mutations of mitochondrial DNA. Mutat Res 338:161–172
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Korber B, Muldoon M, Theiler J, Gao F, Gupta R, Lapedes A, Hahn BH, Wolinsky S, Bhattacharya T (2000) Timing the ancestor of the HIV-1 pandemic strains. Science 288:1789–1796
Kricker M, Drake JW (1990) Heat mutagenesis in bacteriophage T4: another walk down the transversion pathway. J Bacteriol 172:3037–3039
Löwdin PO (1965) Quantum genetics and the aperiodic solid: some aspects on the biological problems of heredity, mutations, aging and tumors in view of the quantum theory of the DNA molecule. Adv Quantum Chem 2:213–359
Matsuura T, Fang P, Pearson CE, Jayakar P, Ashizawa T, Roa BB, Nelson DL (2006) Interruptions in the expanded ATTCT repeat of spinocerebellar ataxia type 10: repeat purity as a disease modifier. Am J Hum Genet 78:125–129
McFadden J, Al-Khalili J (1999) A quantum mechanical model of adaptive mutations. Biosystems 50:203–211
Merzbacher E (1997) Quantum mechanics, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Metzler R, Ambjörnsson T (2005) Dynamic approach to DNA breathing. J Biol Phys 31:339–350
Modrich P (1997) Strand-specific mismatch repair in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 272:24727–24730
Nei M, Glazko GV (2002) Estimation of divergence times for a few mammalian and several primate species. J Hered 93:157–164
Nielson MA, Chuang IL (2000) Quantum computation and quantum information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Ohta T (2002) Near-neutrality in evolution of genes and gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16134–16137
Ono T, Miyamura Y, Ikehata H (1995) Spontaneous mutant frequency of lacZ gene in spleen of transgenic mouse increases with age. Mutat Res 338:183–188
Pollard E, Lemke M (1965) Rate of mutation to phage resistance in 2H2O medium. Mutat Res 2:213–217
Reif F (1965) Fundamentals of statistical and thermal physics. McGraw Hill, New York
Ripley LS (1988) Estimation of in vivo miscoding rates. Quantitative behavior of two classes of heat-induced DNA lesions. J Mol Biol 202:17–34
Smith AB, Peterson KJ (2002) Dating the time of origin of major clades: molecular clocks and the fossil record. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 30:65–88
Sueoka N (2002) Wide intra-genomic G + C heterogeneity in human and chicken is mainly due to strand-symmetric directional mutation pressures: dGTP-oxidation and symmetric cytosine-deamination hypothesis. Gene 30:141–154
Topal MD, Fresco JR (1976) Complementary base pairing and the origin of base substitutions. Nature 263:285–289
Twiddy SS, Holmes EC, Rambuat A (2003) Inferring the rate and time-scale of dengue virus evolution. Mol Biol Evol 20:122–129
Vedral V (2003) Entanglements hit the big time. Nature 425:28–29
Zhang XB, Urlando C, Tao KS, Heddle JA (1995) Factors affecting somatic mutation frequencies in vivo. Mutat Res 338:189–201
Zurek WH (1991) Decoherence and the transition from quantum to classical. Phys Today 44:36–44
Zurek WH (2003) Decoherence, einselection and the quantum origins of the classical. Rev Mod Phys 75:715–775
Acknowledgments
Insightful questions and discussions by Altonie Barber and Nikolay Sarychev are sincerely appreciated. I am grateful to an anonymous reviewer for calling my attention to an important reference and for identifying quantum coherence and decoherence as central issues in this report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooper, W.G. Necessity of Quantum Coherence to Account for the Spectrum of Time-Dependent Mutations Exhibited by Bacteriophage T4. Biochem Genet 47, 892–910 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-009-9293-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-009-9293-8