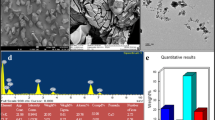
Abstract
Fluoride occurs in some drinking water sources at levels that are hazardous to health. Tests were conducted to assess the ability of a mineral-based adsorbent to take-up fluoride ion. Consequently, in search of novel adsorbent media, crystalline and hydrous iron(III)-zirconium(IV) hybrid oxide (IZHO) was synthesized, and tested to determine its capacity and kinetics for fluoride adsorption. The Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectrum of IZHO indicated the presence of Fe–O–Zr linkage which showed hybrid nature of the synthetic oxide. The optimum pH range for fluoride adsorption was ranged between 4.0 and 7.0. The analyses of the isotherm equilibrium data using the Langmuir and the Redlich–Peterson model equations by linear and non-linear methods showed that the data fitted better with latter model than the former. Thermodynamic analysis showed spontaneous nature of fluoride adsorption, and that took place with the increase of entropy. The kinetic data obtained for fluoride adsorption on IZHO at pH 6.8 (±0.1) and room temperature (303±2 K) described both the pseudo-first order and the reversible first-order equations equally well (r 2= ∼0.98–0.99), and better than pseudo second order equation (r 2= ∼0.96–0.98) for higher concentrations (12.5 and 25.0 mg/dm3) of fluoride. The kinetics of fluoride adsorption on the mixed oxide took place with boundary layer diffusion. External mass transport with intra-particle diffusion phenomena governed the rate limiting process, which has been confirmed from the Boyd poor non-linear kinetic plots.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C i :
-
The initial concentration (mg/dm3) of fluoride in solution
- C e :
-
The concentration of fluoride (mg/dm3) in solution at equilibrium
- C a :
-
The concentration of fluoride (mg/dm3) in solution at any time, t
- C b :
-
The concentration of fluoride in solid phase (mg/g) at any time, t
- C a0 :
-
The initial concentration of fluoride in solution (mg/dm3)
- C b0 :
-
The initial concentration of fluoride in adsorbent phase (mg/g)
- Cae :
-
The equilibrium concentration of solute in solution (mg/dm3)
- q e :
-
The adsorption capacity (mg/g) at equilibrium
- q m :
-
The monolayer adsorption capacity (mg/g)
- q t :
-
The adsorption capacity (mg/g) at any time, t
- B L :
-
The Langmuir adsorption equilibrium constant (dm3/mg)
- A L :
-
The Langmuir constant (dm3/g)
- A RP :
-
The Redlich–Peterson model isotherm constant (dm3/g)
- B RP :
-
The Redlich–Peterson model isotherm constant (dm3/mg) nRP
- n RP :
-
The Redlich–Peterson isotherm model exponent
- k 1 :
-
The pseudo-first order rate constant (time−1)
- k 2 :
-
The pseudo-second order rate constant (mg/g time)
- t :
-
time (min)
- Xa :
-
The fractional conversion of solute
- k # :
-
(=k 1+k 2) the overall rate constant (time−1)
- k 1 :
-
The rate of forward reaction (time−1)
- k 2 :
-
The rate of backward reaction (time−1)
- k B :
-
(=−k #) the rate constant (time−1) of Bhattacharya and Venkobachar model kinetics
- R L :
-
The equilibrium parameter
- Δ G 0 :
-
The Gibbs free energy change (kJ/mol)
- Δ H 0 :
-
The enthalpy change (kJ/mol)
- Δ S 0 :
-
The entropy change (kJ/mol/K)
- R :
-
The universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol/K)
- T :
-
The absolute temperature (K)
- D f :
-
The film diffusion coefficient (cm2/s)
- D p :
-
The pore diffusion coefficient (cm2/s)
- r 0 :
-
The mean radius (cm) of particles
- k i :
-
The diffusion rate constant (mg/g min0.5)
- F :
-
The fraction of solute adsorbed
- Bt :
-
A mathematical function of F
- C L :
-
Liquid phase equilibrium concentration of adsorbate (mg/dm3)
- C s :
-
Solid phase adsorbate concentration at equilibrium (mg/g)
References
Bhattarcharya, A.K., Venkobachar, C.: Removal of cadmium(II) by low costadsorbents. J. Environ. Eng. Div. ASCE Proc. 110, 110–122 (1984)
Bishop, P.L., Sansoucy, G.: Fluoride removal from drinking water by activated alumina. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 71, 554–561 (1979)
Castel, C., Schweizer, M., Simonnot, M.O., Sardin, M.: Selective removal of fluoride ions by a two-way ion-exchange cyclic process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 55, 3341–3352 (2000)
Cengeloglu, Y., Kir, E., Ersoz, M.: Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by using red mud. Sep. Purif. Technol. 28, 81–86 (2002)
Dey, S., Goswami, S., Ghosh, U.C.: Hydrous ferric oxide (HFO)—a scavenger for fluoride from contaminated water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 158, 311–323 (2004)
Fan, X., Parker, D.J., Smith, M.D.: Adsorption kinetics of fluoride on low cost materials. Water Res. 37, 4929—4937 (2003)
Ghorai, S., Pant, K.K.: Equilibrium, kinetics and breakthrough studies for adsorption of fluoride on activated alumina. Sep. Purif. Technol. 42(3), 265–271 (2005)
Goswami, S., Dey, S., Ghosh, U.C.: Studies on removal of fluoride by hydrated zirconium oxide (HZO). Chem. Environ. Res. 13, 117–126 (2004)
Gupta, V.K., Ali, I.: Removal of DDD and DDE from wastewater using bagasse fly ash, a sugar industry waste. Water Res. 35, 33–40 (2001)
Helfferich, F.: Ion-Exchange. McGraw–Hill, New York (1962)
Hichour, M., Persin, F., Molenat, J., Sandeaux, J., Gavach, C.: Desalination 122, 53–62 (1999)
Hichour, M., Persin, F., Sandeaux, J., Gavach, C.: Fluoride removal from waters by Donnan dialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 18, 1–11 (2000)
Ho, Y.S., McKay, G.: Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem. Eng. J. 70, 115–124 (1998)
Jamode, A.V., Sapkal, V.S., Jamode, V.S.: Defluoridation of water using inexpensive adsorbents. J. Ind. Inst. Sci. 84, 163–171 (2004)
Kumar, V.K., Ramamurthi, V., Sivanesan, S.: Modeling the mechanism involved during the sorption of methylene blue onto fly ash. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 284, 14–21 (2005)
Lagergren, S.: Zur Theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 24(4), 1–39 (1898)
Langmuir, I.: The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 38, 2221–2295 (1916)
Li, Y.H., Wang, S., Cao, A., Zhao, D., Zhang, X., Xu, C., Luan, Z., Ruan, D., Liang, J., Wu, D., Wei, B.: Adsorption of fluoride from water by amorphous alumina supported on carbon nanotube. Chem. Phys. Lett. 350, 412–416 (2001)
Michelson, L.D., Gideon, P.G., Pace, E.G., Kutal, L.H.: Removal of soluble mercury from wastewater by complexing techniques. Bull No. 74, US Dept. Industry, Office of Water Research and Technology (1975)
Pervov, A.G., Dudkin, E.V., Sidorenko, O.A., Antipov, V.V., Khakhnov, S.A., Makarov, R.I.: RO and RF membrane systems for drinking water production and their maintenance techniques. Desalination 132, 315–321 (2000)
Piekos, R., Paslawaska, S.: Fluoride uptake characteristics of fly ash. Fluoride 32, 14–19 (1999)
Pietrelli, L.: Fluoride wastewater treatment by adsorption onto Metallurgical grade alumina. Ann. Chim. 95(5), 303–312 (2005)
Reardon, E.J., Wang, Y.: Limestone reactor for fluoride removal from wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 34(15), 3247–3253 (2000)
Redlich, O., Peterson, D.L.: A useful adsorption isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 63, 1024 (1959)
Saha, S.: Treatment of aqueous effluent for fluoride removal. Water Res. 27, 1347–1350 (1993)
Saxena, V.K., Ahmed, S.: Dissolution of fluoride in groundwater: a water-rock interaction study. Environ. Geol. 40, 1084–1087 (2001)
Sivasamy, A., Singh, K.P., Mohan, D., Muruthamuthu: Studies on defluoridationof water by coal-based sorbents. J. Chem. Tech. Biotech. 76, 717–722 (2001)
Srimurali, M., Pragathi, A., Karthikeyan, J.: A study on removal of fluorides from drinking water by adsorption onto low cost materials. Environ. Pollut. 99, 285—289 (1998)
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th edn. AWWA/APHA/WEF, Washington (1998)
Sujana, M.G., Thakur, R.S., Rao, S.B.: Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by using alum sludge. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 206(1), 94–101 (1998)
Tramfloc, Inc.: Fluoride removal by activated alumina. PO Box 350, Tempe, AZ 85280–0350, water@tramfloc.com, copyright© 1997–2005, Tramfloc, Inc. (2005)
Wang, S., Li, H.: Kinetic modelling and mechanism of dye adsorption of dye adsorption on unburned carbon. Dyes Pigments. Available online at www.sciencedirect.com (2005)
Wasay, S.A., Haron, Md.J., Tokunaga, S.: Adsorption of fluoride, phosphate and arsenate ions on lanthanum impregnated silica gel. Water Environ. Res. 68, 295–300 (1996)
Wu, Y.C.: Activated alumina removes fluoride from water. J. Water Sew. Works 125, 76–87 (1978)
Yang, C.L., Dluhy, R.: Electrochemical generation of aluminium sorbent for fluoride adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 94(3), 223–238 (2002)
Yang, M., Hashimoto, T., Hoshi, N., Myoga, H.: Fluoride removal in a fixed bed packed with granular calcite. Water Res. 33(16), 3395–3402 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biswas, K., Bandhoyapadhyay, D. & Ghosh, U.C. Adsorption kinetics of fluoride on iron(III)-zirconium(IV) hybrid oxide. Adsorption 13, 83–94 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-007-9000-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-007-9000-1