Abstract
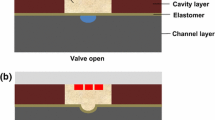
This paper reports design, fabrication, and characterization of an air-actuated microvalve and a micropump made of thermoplastic materials. The bonding process was carried out by thermal fusion process with no particular surface treatment. The developed microvalve was used as a reversible switch for controlling both liquid flow and electrical field. Bonding strength of the fabricated microvalves could withstand liquid and air pressures of up to 600 kPa with no burst failure. The micropump made of three connected microvalves, actuated by compressed air, could generate a liquid flow rate of up to 85 µl/min. The proposed microvalve and micropump can be used as pre-fabricated off-the-shelf microfluidic functional elements for easy and rapid integration with thermoplastic microfluidic circuitries in a plug-and-play arrangement.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker H, Gärtner C (2008) Polymer microfabrication technologies for microfluidic systems. Anal Bioanal Chem 390:89–111. doi:10.1007/s00216-007-1692-2
Berthier E, Young EWK, Beebe D (2012) Engineers are from PDMS-land, Biologists are from Polystyrenia. Lab Chip 12:1224–1237. doi:10.1039/c2lc20982a
Byrne MB, Leslie MT, Gaskins HR, Kenis PJA (2014) Methods to study the tumor microenvironment under controlled oxygen conditions. Trends Biotechnol 32:556–563. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.09.006
Chin CD, Linder V, Sia SK (2012) Commercialization of microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 12:2118–2134. doi:10.1039/c2lc21204h
Elizabeth Hulme S, Shevkoplyas SS, Whitesides GM (2009) Incorporation of prefabricated screw, pneumatic, and solenoid valves into microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 9:79–86. doi:10.1039/b809673b
Frimat J-P, Becker M, Chiang Y-Y et al (2011) A microfluidic array with cellular valving for single cell co-culture. Lab Chip 11:231–237. doi:10.1039/c0lc00172d
Gómez-Sjöberg R, Leyrat AA, Pirone DM et al (2007) Versatile, fully automated, microfluidic cell culture system. Anal Chem 79:8557–8563. doi:10.1021/ac071311w
Grover WH, von Muhlen MG, Manalis SR (2008) Teflon films for chemically-inert microfluidic valves and pumps. Lab Chip 8:913–918. doi:10.1039/b800600h
Gu P, Liu K, Chen H et al (2010) Chemical-assisted bonding of thermoplastics/elastomer for fabricating microfluidic valves. Anal Chem 83:446–452. doi:10.1021/ac101999w
Gu P, Nishida T, Fan ZH (2013) The use of polyurethane as an elastomer in thermoplastic microfluidic devices and the study of its creep properties. Electrophoresis. doi:10.1002/elps.201300160
Hong TF, Ju WJ, Wu MC et al (2010) Rapid prototyping of PMMA microfluidic chips utilizing a CO2 laser. Microfluid Nanofluidics 9:1125–1133. doi:10.1007/s10404-010-0633-0
Hulme SE, Shevkoplyas SS, McGuigan AP et al (2010) Lifespan-on-a-chip: microfluidic chambers for performing lifelong observation of C. elegans. Lab Chip 10:589–597. doi:10.1039/b919265d
Irimia D (2010) Microfluidic technologies for temporal perturbations of chemotaxis. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 12:259–284. doi:10.1146/annurev-bioeng-070909-105241
Jiang L, Erickson D (2013) Light-governed capillary flow in microfluidic systems. Small 9:107–114. doi:10.1002/smll.201201778
Kang DH, Kim SM, Lee B et al (2013) Stimuli-responsive hydrogel patterns for smart microfluidics and microarrays. Analyst 138:6230–6242. doi:10.1039/c3an01119d
Lee JN, Park C, Whitesides GM (2003) Solvent compatibility of poly(dimethylsiloxane)-based microfluidic devices. Anal Chem 75:6544–6554. doi:10.1021/ac0346712
Lii J, Hsu W-J, Parsa H et al (2008) Real-time microfluidic system for studying mammalian cells in 3D microenvironments. Anal Chem 80:3640–3647. doi:10.1021/ac8000034
Ma H, Jiang L, Shi W et al (2009) A programmable microvalve-based microfluidic array for characterization of neurotoxin-induced responses of individual C. elegans. Biomicrofluidics 10(1063/1):3274313
Melin J, Quake SR (2007) Microfluidic large-scale integration: the evolution of design rules for biological automation. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 36:213–231. doi:10.1146/annurev.biophys.36.040306.132646
Nguyen N-T, Huang X, Chuan TK (2002) MEMS-micropumps: a review. J Fluids Eng 124:384. doi:10.1115/1.1459075
Nguyen N-T, Shaegh SAM, Kashaninejad N, Phan D-T (2013) Design, fabrication and characterization of drug delivery systems based on lab-on-a-chip technology. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:1403–1419. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2013.05.008
Ochs CJ, Kasuya J, Pavesi A, Kamm RD (2014) Oxygen levels in thermoplastic microfluidic devices during cell culture. Lab Chip 14:459–462. doi:10.1039/c3lc51160j
Ogilvie IRG, Sieben VJ, Cortese B et al (2011) Chemically resistant microfluidic valves from Viton® membranes bonded to COC and PMMA. Lab Chip 11:2455–2459. doi:10.1039/c1lc20069k
Oh KW, Ahn CH (2006) A review of microvalves. J Micromechanics Microengineering 16:R13–R39. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/16/5/R01
Piccin E, Coltro WKT, Fracassi da Silva JA et al (2007) Polyurethane from biosource as a new material for fabrication of microfluidic devices by rapid prototyping. J Chromatogr A 1173:151–158. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.09.081
Qin L, Vermesh O, Shi Q, Heath JR (2009) Self-powered microfluidic chips for multiplexed protein assays from whole blood. Lab Chip 9:2016–2020. doi:10.1039/b821247c
Regehr KJ, Domenech M, Koepsel JT et al (2009) Biological implications of polydimethylsiloxane-based microfluidic cell culture. Lab Chip 9:2132–2139. doi:10.1039/b903043c
Shiraki Y, Tsuruta K, Morimoto J et al (2015) Preparation of molecule-responsive microsized hydrogels via photopolymerization for smart microchannel microvalves. Macromol Rapid Commun 36:515–519. doi:10.1002/marc.201400676
Tsao CW, DeVoe DL (2009) Bonding of thermoplastic polymer microfluidics. Microfluid Nanofluidics 6:1–16
Unger MA, Chou HP, Thorsen T et al (2000) Monolithic microfabricated valves and pumps by multilayer soft lithography. Science 288:113–116. doi:10.1126/science.288.5463.113
Waldbaur A, Rapp H, Länge K, Rapp BE (2011) Let there be chip—towards rapid prototyping of microfluidic devices: one-step manufacturing processes. Anal Methods 3:2681
Weibel DB, Kruithof M, Potenta S et al (2005) Torque-actuated valves for microfluidics. Anal Chem 77:4726–4733. doi:10.1021/ac048303p
Wu H, Wheeler A, Zare RN (2004) Chemical cytometry on a picoliter-scale integrated microfluidic chip. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:12809–12813. doi:10.1073/pnas.0405299101
Wu MH, Huang SB, Cui Z et al (2008) Development of perfusion-based micro 3-D cell culture platform and its application for high throughput drug testing. Sens Actuators B Chem 129:231–240. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2007.07.145
Wu W-I, Sask KN, Brash JL, Selvaganapathy PR (2012) Polyurethane-based microfluidic devices for blood contacting applications. Lab Chip 12:960–970. doi:10.1039/c2lc21075d
Yobas L, Tang K-C, Yong S-E, Kye-Zheng Ong E (2008) A disposable planar peristaltic pump for lab-on-a-chip. Lab Chip 8:660–662. doi:10.1039/b720024b
Zeng S, Li B, Su X et al (2009) Microvalve-actuated precise control of individual droplets in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 9:1340–1343. doi:10.1039/b821803j
Zhang W, Lin S, Wang C et al (2009) PMMA/PDMS valves and pumps for disposable microfluidics. Lab Chip 9:3088–3094. doi:10.1039/b907254c
Zhang X, Chen Z, Huang Y (2015) A valve-less microfluidic peristaltic pumping method. Biomicrofluidics 9:014118. doi:10.1063/1.4907982
Zhu CH, Lu Y, Peng J et al (2012) Photothermally sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/graphene oxide nanocomposite hydrogels as remote light-controlled liquid microvalves. Adv Funct Mater 22:4017–4022. doi:10.1002/adfm.201201020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaegh, S.A.M., Wang, Z., Ng, S.H. et al. Plug-and-play microvalve and micropump for rapid integration with microfluidic chips. Microfluid Nanofluid 19, 557–564 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1582-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1582-4