Abstract
Background
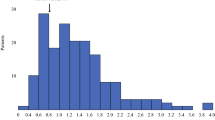
In patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer treated by concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT), baseline malnutrition and its progression have been shown to be associated with a poor outcome. We conducted this study to determine the variation in four blood test parameters including serum albumin level (ALB), creatinine (Cre), hemoglobin (Hb) and platelet (Plt) during CCRT for stage III esophageal cancer patients and its effect on patients’ outcome.
Methods
One hundred eighty-three patients diagnosed with stage III esophageal cancer were retrospectively investigated. In addition to known prognostic factors, baseline level of the four blood test parameters and their variation at day 105 (ΔALB, ΔCre, ΔHb and ΔPlt, respectively) were analyzed.
Results
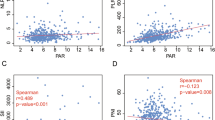
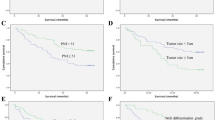
The median observation period for patients who survived was 57.2 months, and the 5-year overall survival rate was 35.6% (95% CI 34.2–36.9%). In multivariate analyses, baseline ALB (≥ 3.6 g/dL), higher ΔALB (≥ + 0.3 g/dL) were independent predictors for overall survival (p = 0.001 and < 0.001, respectively), in addition to other clinical factors including T stage and overall treatment time (OTT). For disease-free survival, ΔALB was only a predictor in hematological parameters (p = 0.001) in addition to T stage and OTT. No hematological and clinical parameters had significant correlation with local control in multivariate analysis. Furthermore, ΔALB showed significant correlation with OS and DFS in log-rank test (p = 0.002 and 0.002, respectively).
Conclusions
Our results suggest improvement in ALB after treatment might be a favorable prognostic factor in esophageal cancer patients treated by CCRT.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper J, Guo M, Herskovic A, et al. Chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced esophageal cancer: long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized trial (RTOG 85-01). JAMA. 1999;281:1623–7.
Minsky BD, Pajak TF, Ginsberg RJ, et al. INT 0123 (Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 94-05) phase III trial of combined-modality therapy for esophageal cancer: high-dose versus standard-dose radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1167–74.
Tougeron D, Fiore D, Thureau S, et al. Safety and outcome of definitive chemoradiotherapy in elderly patients with oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;99:1586–92.
Umezawa R, Jingu K, Matsushita H, et al. Long-term results of chemoradiotherapy for stage II-III thoracic esophageal cancer in a single institution after 2000 -with a focus on comparison of three protocols-. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:813.
Fiore D, Lecleire S, Pop D, et al. Baseline nutritional status is predictive of response to treatment and survival in patients treated by definitive chemoradiotherapy for a locally advanced esophageal cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:2557–63.
Clavier JB, Antoni D, Atlani D, et al. Baseline nutritional status is prognostic factor after definitive radiochemotherapy for esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 2014;27:560–7.
Cox S, Powell C, Carter B, et al. Role of nutritional status and intervention in oesophageal cancer treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy: outcomes from SCOPE1. Br J Cancer. 2016;115:172–7.
Fiore A, Lecleire S, Gangloff A, et al. Impact of nutritional parameter variations during definitive chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced oesophageal cancer. Dig Liver Dis. 2014;46:270–5.
Goh SL, Silva RP, Dhital K, et al. Is low serum albumin associated with postoperative complications in patients undergoing oesophagectomy for oesophageal malignancies? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015;20:107–13.
Chang PH, Yeh KY, Huang JS, et al. Pretreatment performance status and nutrition are associated with early mortality of locally advanced head and neck cancer patients undergoing concurrent chemoradiation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;270:1909–15.
Riccardi D, Allen K. Nutritional management of patients with esophageal and esophagogastric junction cancer. Cancer Control. 1999;6:64–72.
Hamai Y, Hihara J, Emi M, et al. Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors for thoracic esophageal cancer with clinical evidence of adjacent organ invasion. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:3495–502.
Gupta D, Lis C. Pretreatment serum albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: a systematic review of the epidemiological literature. Nutr J. 2010;9:69.
Wang CY, Hsieh MJ, Chiu YC, et al. Higher serum C-reactive protein concentration and hypoalbuminemia are poor prognostic indicators in patients with esophageal cancer undergoing radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92:270–5.
Cong MH, Li SL, Cheng GW, et al. An interdisciplinary nutrition support team improves clinical and hospitalized outcomes of esophageal cancer patients with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128:3003–7.
Fietkau R, Lewitzki V, Kuhnt T, et al. A disease-specific enteral nutrition formula improves nutritional status and functional performance in patients with head and neck and esophageal cancer undergoing chemoradiotherapy: results of a randomized, controlled, multicenter trial. Cancer. 2013;119:3343–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the study. The institutional review board approved this retrospective study (2014-1-543).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takeda, K., Umezawa, R., Takahashi, N. et al. Impact of change in serum albumin level during and after chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer. Esophagus 15, 190–197 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-018-0612-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-018-0612-1