Abstract
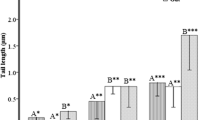
Ephestia kuehniella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) is cosmopolitan pest of stored products. The effect of strong magnetic fields (MFs) on DNA damage and oxidative stress on larvae stage of E. kuehniella was assessed. Antioxidant enzyme systems, which include superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione S-transferase (GST), and malondialdehyde (MDA), the end product of lipid peroxidation as a result of strong MF intoxication that might occur in the larvae tissue, were evaluated. A simple technique of single-cell gel electrophoresis (DNA comet assay) enabled a quick detection of MF treatment on larvae. The larvae were exposed in a 1.4-Tesla (T) MF from a DC power supply at 50 Hz for different time periods (3, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h). MFs caused increasing DNA damage and demonstrated using the comet assay with its parameters including tail DNA%, tail length and tail moment. DNA damage at increasing exposure times were significantly larger than the control group (p < 0.05). These parameters were detected using BS 200 ProP with image analysis software. SOD, CAT, GPx, and GST activities decreased and MDA level increased in the MF-treated group in larvae tissue compared to control group for increasing exposure times at 1.4 T (p < 0.05). In our investigation, we showed that MFs caused oxidative stress and proved to be DNA damage as revealed by the comet assay. MFs may be used to determine potential toxic effects as a control agent against E. kuehniella larvae.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Ahmed M (2001) Disinfestation of stored grains, pulses, dried fruits and nuts, and other dried foods. In: Molins RA (ed) Food irradiation: principles and applications. Wiley, New York, p 77
Azizoglu U, Yilmaz S, Karaborklu S, Ayvaz A (2011) Ovicidal activity of microwave and UV radiations on Mediterranean flour moth Ephestia kuehniella Zeller, 1879 (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Turk Entomol Derg 35(3):437–446
Buyukuslu N, Çelik O, Atak C (2006) The effect of magnetic field on the activity of superoxide dismutase. J Cell Mol Biol 5:57–62
Cerda H, Delincee H, Haine H, Rupp H (1997) The DNA “comet assay” as a rapid screening technique to control irradiated food. Mutat Res 375:161–181
Cheung CCC, Zheng GJ, Li AMY, Richardson BJ, Lam PKS (2001) Relationships between tissue concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and antioxidative responses of marine mussels, Perna viridis. Aquat Toxicol 52:189–203
Delincee H (1996) Introduction to DNA methods for identification of irradiated foods. In: McMurray CH, Stewart EM, Gray R, Pearce J (eds) Detection methods for irradiated foods current status. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 345–348
Denegre JM, Valles JM, Lin K, Jordan WB (1998) Cleavage planes in frog eggs altered by strong magnetic fields. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14729–14732
Dini L, Abbro L (2005) Bioeffects of moderate-intensity static magnetic fields on cell cultures. Micron 36:195–217
Dogan D, Can C, Kocyigit A, Dikilitas M, Taskin A, Bilinc H (2011) Dimethoate-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in Oncorhynchus mykiss. Chemosphere 84(1):39–46
El-Ashry MY, Ibrahim MA, Ali EA (2008) The Influence of 50 Hz magnetic field on liver oxidative. Suez Canal Univ Med J 11(1):53–58
Erel Y, Yazici N, Ozvatan S, Ercin D, Cetinkaya N (2009) Detection of irradiated quail meat by using DNA comet assay and evaluation of comets by image analysis. Radiat Phys Chem 78:776–781
Esterbauer H, Zollner H, Schaur RJ (1990) Aldehydes formed by lipid peroxidation: mechanisms of formation, occurrence, and determination. In: Vigo-Pelfrey C (ed) Membrane lipid oxidation. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 239–268
Freitas AMB, Landgraf FJG, Nyvlt J, Giulietti M (1999) Influence of magnetic field in the kinetics of crystallization of diamagnetic and paramagnetic inorganic salts. Cryst Res Technol 34(10):1239–1244
García O, Romero I, González JE, Mandia T (2007) Measurement of DNA damage on silver stained comets using free Internet software. Mutat Res 627:186–190
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione-S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hansen LS, Jensen KMV (2002) Effect of temperature on parasitism and host-feeding of Trichogramma turkestanica (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) on Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Econ Entomol 95(1):50–56
Hasan M, Todoriki S, Miyanoshita A, Imamura T (2008) Detection of gamma radiation-induced DNA damage in maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) assessed using the comet assay. Int J Radiat Bio 84:815–820
Hassan F (1978) Erythrocyte pathophysiology of ribo flavine deficiency, Ph.D. Thesis, London, Faculty of Medicine, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
Hong FT (1995) Magnetic field effects on biomolecules, cells, and living organisms. Biosystems 36:187–229
Hyršl P, Buyukguzel E, Buyukguzel K (2007) The effects of boric acid-induced oxidative stress on antioxidant enzymes and survivorship in Galleria mellonella. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 66:23–31
Icen E, Armutcu F, Buyukguzel K, Gurel A (2005) Biochemical stress indicators of greater wax moth exposure to organophosphorus insecticides. J Econ Entomol 98(2):358–366
Imamura T, Miyanoshita A, Todoriki S, Hayashi T (2004a) Usability of a soft-electron (low-energy electron) machine for disinfestation of grains contaminated with insect pests. Radiat Phys Chem 71:213–215
Imamura T, Todoriki S, Sota N, Nakakita H, Ikenaga I, Hayashi T (2004b) Effect of “soft-electron” (low-energy electron) treatment on three stored-product insect pests. J Stored Prod Res 40(2):169–177
Isik I, Celik I (2008) Acute effects of methyl parathion and diazinon as inducers for oxidative stress on certain biomarkers in various tissues of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Pestic Biochem Phys 92:38–42
Jones DS, Macfadden BJ (1982) Induced magnetization in the monarch butterfly, Danaus plexippus (Insecta: Lepidoptera). J Exp Biol 96:1–9
Kameya H, Miyanoshita A, Imamura T, Todoriki S (2012) Assessment of gamma ray-induced DNA damage in Lasioderma serricorne using the comet assay. Radiat Phys Chem 81(3):316–321
Koo HN, Yoon SH, Shin YH, Yoon C, Woo JS, Kim GH (2011) Effect of electron beam irradiation on developmental stages of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J Asia Pac Entomol 14(3):243–247
Kwon JH, Kwon YJ, Byun MW, Kim KS (2004) Competitiveness of gamma irradiation with fumigation for chestnuts associated with quarantine and quality security. Radiat Phys Chem 71:43–46
Livingstone DR (2001) Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar Pollut Bull 42:656–666
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
Modesto KA, Martinez CB (2010) Effects of roundup transorb on fish: hematology, antioxidant defenses and acetylcholinesterase activity. Chemosphere 81:781–787
Monteiro DA, Almeida JA, Rantin FT, Kalinin AL (2006) Oxidative stress biomarkers in the freshwater characid fish, Brycon cephalus, exposed to organophosphorus insecticide Folisuper 600 (methyl parathion). Comp Biochem Phys 143:141–149
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1987) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Med 70:158–165
Pan H (1996) The effect of a 7 T magnetic field on the egg hatching of Heliothis virescens. Magn Reson Imaging 14(6):673–677
Pandir D, Sahingoz R, Ercan FS (2013) Effects of magnetic field on different stages of Mediterranean flour moth Ephestia kuehniella and its preference by Trichogramma embryophagum females. Biocontrol Sci Techn. Manuscript ID CBST-2013-0109 (in press)
Ramirez E, Monteagudo JL, García-Gracia M, Delgado JM (1983) Oviposition and development of Drosophila modified by magnetic fields. Bioelectromagnetics 4:315–326
Riley PA (1994) Free radicals in biology: oxidative stress and the effects of ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 65:27–33
Rojas E, Lopez MC, Valverde M (1999) Single cell gel electrophoresis assay: methodology and applications. J Chromatogr Biomed 722:225–254
Rosen AD (2003) Mechanism of action of moderate-intensity static magnetic fields on biological systems. Cell Biochem Biophys 39:163–173
Rothkamm SB, Rothkamm K, Folkard M, Patel G, Hone P, Lloyd D, Ainsbury L, Prise KM (2009) DNA and chromosomal damage in response to intermittent extremely low-frequency magnetic fields. Mutat Res Gennet Toxicol Environ 672(2):82–89
Sabo J, Mirossa L, Horovcak L, Sarissky M, Mirossay A, Mojzis J (2002) Effects of static magnetic field on human leukemic cell line HL-60. Bioelectrochemistry 56:227–231
Shafey TM, Aljumaah RS, Swillam SA, Al-Mufarrej SI, Al-Abdullatif AA, Ghannam MM (2011) Effects of short term exposure of eggs to magnetic field before incubation on hatchability and post-hatch performance of meat chickens. Saudi J Biol Sci 18(4):381–386
Shen W, Zhao XP, Wang O, Niu BO, Liu Y, He LH, Weng HB, Meng ZQ, Chen YY (2011) Genotoxicity evaluation of low doses of avermectin to hemocytes of silkworm (Bombyx mori) and response of gene expression to DNA damage. Pestic Biochem Phys 101(3):159–164
Starick NT, Longstaff BC, Condon B (2005) The influence of fluctuating low-level magnetic fields on the fecundity and behaviour of Rhyzoperta dominica (F.). J Stored Prod Res 41:255–270
Temur’jants N, Shekhotkin A, Kamynina I, Nasilevich V (1996) Effect of weak alternating magnetic fields on infarction rhythms or rat blood leukocytes functional activity. Biofizika 41:930–933
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for the in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicity testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221
Todoriki S, Hasan M, Miyanoshita A, Imamura T, Hayashi T (2006) Assessment of electronbeam-induced DNA damage in larvae of chestnut weevil, Curculio sikkimensis (Heller) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) using comet assay. Radiat Phys Chem 75:292–296
Todorovic D, Mircic D, Ilijin L, Mrdakovic M, Vlahovic M, Prolic Z, Mataruga VP (2012) Effect of magnetic fields on antioxidative defense and fitness-related traits of Baculum extradentatum (Insecta: Phasmatodea). Bioelectromagnetics 33(3):265–273
Tuncbilek AS, Canpolat U, Ayvaz A (2009) Effects of gamma radiation on suitability of stored cereal pest eggs and the reproductive capability of the egg parasitoid Trichogramma evanescens (Trichogrammatidae: Hymenoptera). Biocontrol Sci Technol 19:179–191
Valles JM (2002) Model of magnetic field-induced mitotic apparatus reorientation in frog eggs. Biophys J 82:1260–1265
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Bozok University Science and Technology Application and Research Center for supplying the Hall Effects System and Mrs. Sevcan Oztemiz (Adana Plant Protection Research Institute) for supplying the Ephestia kuehniella used in the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C.G. Athanassiou.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandir, D., Sahingoz, R. Magnetic field-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in Mediterranean flour moth Ephestia kuehniella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) larvae. J Pest Sci 87, 79–87 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-013-0521-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-013-0521-y