Abstract
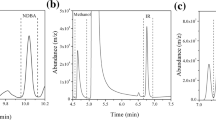
Nitrosamines which have been detected in various latex products are carcinogens. The method for determination of volatile nitrosamines in latex products was developed using a combination of headspace solid phase micro-extraction (HS-SPME) and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS). A carboxen/polydimethylsiloxane (CAR/PDMS) fiber was used for HS-SPME involving the following variables: (1) agitation conditions, (2) extraction temperature (3) extraction time, and (4) salt concentration. The instrument performances of three detection systems including GC combined thermal energy analyzer, nitrogen chemiluminescence detector and MS were evaluated. The agitation conditions including magnetic stirring and ultrasonication were investigated by the comparison of extraction efficiency of HS-SPME for nitrosamines. Obtained optimal detection conditions of nitrosamines were HS-SPME at 45 °C for 60 min assisted with magnetic stirring and saturated NaCl followed by GC–MS. To evaluate this method performance, the commercial products including eleven latex products (gloves, balloons and condoms) and four liquid silicone nipples were analyzed with the method. The results revealed that the method is suitable for simple and effective determination of nitrosamines in latex products. The advantage of this HS-SPME–GC–MS method is simple treatment, fast analysis, adequate sensitivity and without organic solvent.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
IARC (1987) International agency for research on cancer, IARC monographs. Lyon, France
Fiddler W, Pensabene JW, Kimoto WI (1985) Investigation of volatile nitrosamines in disposable protective gloves. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J 46(8):463–465
Gloria MB (1991) Levels of volatile N-nitrosamines in baby bottle rubber nipples commercialized in Belo Horiaonte, Mina Gerais, Brazil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 47(1):120–125
Pensabene JW, Fiddler W, Gates RA, Foster JM (1995) Nitrosamine formation and penetration in hams processed in elastic rubber nettings: N-nitrosodibutylamine and N-nitrosodibenzylamine. Agric Food Chem 43:1919–1922
Biaudet H, Mouillet L, Debry G (1997) Migration of nitrosamines from condoms to physiological secretions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:847–853
Altkofer W, Braune S, Ellendt K, Kettl-Grömminger M, Steiner G (2005) Migration of nitrosamines from rubber products are balloons and condoms harmful to the human health. Mol Nutr Food Res 49:235–238
Feng D, Wang HP, Cheng XL, Wang JD, Ning LF, Zhou QF, Zhou Y, Yang QL (2009) Detection and toxicity assessment of nitrosamines migration from latex gloves in the Chinese Market. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212:533–540
Feng D, Zhou QF, Cheng XL, Wang JD, Yang QL (2010) Analysis of nitrosamines migration from condoms in the Chinese Market using a proper migration experiment. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84:373–377
Spiegelhalder B, Preussmann R (1983) Occupational nitrosamine exposures. I. Rubber and tyre industry. Carcinogenesis 4:1147–1152
EN 12868 (1999) Child use and care articles—Methods for determining the release of N-nitrosamines and N-nitrosatable substances from elastomer or rubber teats and soothers. European Committee for Standardization
ISO/CD (29941) (2008) Condoms—determination of nitrosamines migrating from nature rubber latex condoms into various mediad. International Standard Organization
AOAC Official Method 987.05. (1984) Nitrosamines in baby bottle rubber nipples (gas chromatographic method). Association of Official Analytical Chemists
Reche F, Garrigós MC, Marín ML, Cantó A, Jiménez A (2002) Optimization of parameters for the supercritical fluid extraction in the determination of N-nitrosamines in rubbers. J Chromarogr A 963:419–426
Reche F, Garrigós MC, Marín ML, Jiménez A (2002) Determination of N-nitrosamines in latex by sequential supercritical fluid extraction and derivatization. J Chromarogr A 976:301–307
Incavo JA, Schafer MA (2006) Simplified method for the determination of N-nitrosamines in rubber vulcanizates. Anal Chim Acta 557:256–261
Wang X, Gao YH, Xu XJ, Zhao JF, Song GX, Hu YM (2011) Derivatization method for determination of nitrosamines by GC–MS. Chromatographia 73:321–327
Andrade R, Reyes FGR, Rath S (2005) A method for the determination of volatile N-nitrosamines in food by HS-SPME–GC–TEA. Food Chem 91:173–179
Grebel JE, Young CC, Suffet IH (2006) Solid-phase microextraction of N-nitrosamines. J Chromatogr A 1117:11–18
Ventanas S, Martin D, Estévez M, Ruiz J (2006) Analysis of volatile nitrosamines from a model system using SPME-DED at different temperatures and times of extraction. Food Chem 99(4):842–850
Ventanas S, Ruiz J (2006) On-site analysis of volatile nitrosamines in food model systems by solid-phase microextraction coupled to a direct extraction device. Talanta 70:1017–1023
Llop A, Borrull F, Pocurull E (2010) Fully automated determination of N-nitrosamines in environmental waters by headspace solid-phase microextraction followed by GC–MS–MS. J Sep Sci 33:3692–3700
Wercinski SAS, Pawliszyn J (1999) Solid-phase microextraction theory. In: Wercinski SAS (ed) Solid-phase microextraction. A practical guide. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–26
Alpendurada MF (2000) Solid-phase microextraction: a promising technique for sample preparation in environmental analysis. J Chromatog A 889(1):3–14
Lee JH, Diono R, Kim GY, Min DB (2003) Optimization of solid phase microextraction analysis for the headspace volatile compounds of Parmesan cheese. J Agric Food Chem 51:1136–1140
Lee JH, Kand JH, Min DB (2003) Optimization of solid-phase microextraction for the analysis of the headspace volatile compounds in kimchi, a traditional Korean fermented vegetable product. J Food Sci 68(3):844–848
Vas G, Vékey K (2004) Solid-phase microextraction: a powerful sample preparation tool prior to mass spectrometric analysis. J Mass Spectrom 39:233–254
Rial-Otero R, Gaspar EM, Moura I, Capelo JL (2007) Gas chromatography mass spectrometry determination of acaricides from honey after a new fast ultrasonic-based solid phase micro-extraction sample treatment. Talanta 71:1906–1914
Santos HM, Capelo JL (2007) Trends in ultrasonic-based equipment for analytical sample treatment. Talanta 73:795–802
Commission Directive 93/11/EEC. (1993) The release of N-nitrosamines and N-nitrosatable substances from elastomer or rubber teats and soothers. Official Journal of the European Communities No. L 93/37
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their appreciation of the financial support obtained from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 20876011, 20806006 and 20636010), National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, Grant No. 2007CB714304, 2011CB200905), National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 program, Grant No. 2007AA100404, 2007AA10Z360).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, D., Liu, L., Zhao, L. et al. Determination of Volatile Nitrosamines in Latex Products by HS-SPME–GC–MS. Chromatographia 74, 817–825 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-011-2148-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-011-2148-6