Abstract
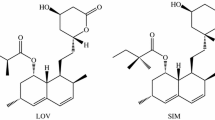
In this study, stability of statin drugs in different conditions, such as various pH, diverse solvents ratio, presence of UV, and sunlight have been investigated. Results suggest strong dependence of statins upon pH, potential environmental persistence towards sun light, and UV light degradation via singlet excited state obtained by excitation into the π–π* band. In acidic conditions interconversion between lactone and hydroxy acid forms in aqueous solutions at room temperature is retarded, while for the same sun-exposed samples are accelerated. Longer exposures lead to the degradation processes. Statin interconversion in water is much lower than in acetonitrile.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Halling-Sørensen B, Jørgensen SE, Holten Lützhøft HC, Nors Nielsen S, Lanzky PF, Ingerslev F (1998) Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—a review. Chemosphere 36:357–393. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00354-8
Hernando MD, Aguera A, Fernandez-Alba R (2007) LC–MS analysis and environmental risk of lipid regulators. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1269–1285. doi:10.1007/s00216-006-0781-y
Hwang LS, Yang D-J (2006) Study on the conversion of three natural statins from lactone forms to their corresponding hydroxy acid forms and their determination in Pu-Erh tea. J Chromatogr A 1119:277–284. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.12.031
Jørgensen SE, Halling-Sùrensen B (2000) Drugs in the environment. Chemosphere 40:691–699. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00438-5
Loffler D, Joss A, Zabczynski S, Gobel A, Hoffmann B, McArdell CS, Ternes TA, Thomsen A, Siergrist H (2006) Biological degradation of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater treatment: Proposing a classification scheme. Water Res 40:1686–1696. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.02.014
Metcalfe CD, Miao XS (2003) Determination of cholesterol-lovering statin drugs in aqueous samples using liquid chromatography–electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 998:133–141. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(03)00645-9
Miao XS, Koenig BG, Metcalfe CD (2002) Analysis of acidic drugs in the effluents of sewage treatment plants using liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 952:139–147. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(02)00088-2
Petrovic M, Barcelo D (2007) LC–MS for identifying photodegradation products of pharmaceuticals in the environment. Trends Analyt Chem 26:1076–1085. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2007.02.010
Petrovic M, Hernando MD, Diaz-Cruz MS, Barcelo D (2005) Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of pharmaceutical residues in the environmental samples: a review. J Chromatogr A 1067:1–14. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2004.10.110
Ternes T, Joss A, Keller E, Alder AC, Gobel A, McArdell CS, Siegrist H (2005) Removal of pharmaceuticals and fragrances in biological wastewater treatment. Water Res 39:3139–3152. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.05.031
Wang H, Wu Y, Zhao Z (2001) Fragmentation study of simvastatin and lovastatin using electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 36:58–70
Zuccato E, Castiglioni S, Bagnati R, Calamari D, Fanelli R (2005) A multiresidue analytical method using solid-phase extraction and high-pressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry to measure pharmaceuticals of different therapeutic classes in urban wastewaters. J Chromatogr A 1092:206–215. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.07.012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piecha, M., Sarakha, M., Trebše, P. et al. Stability studies of cholesterol lowering statin drugs in aqueous samples using HPLC and LC–MS. Environ Chem Lett 8, 185–191 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-009-0207-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-009-0207-0