Abstract
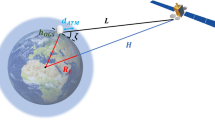
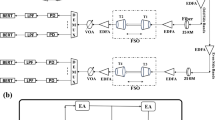
In spite of the tremendous technical advancement of available components, the major limitation of free-space laser communication (lasercom) performance is due to the atmosphere, because a portion of the atmospheric path always includes turbulence and multiple scattering effects. Starting from a fundamental understanding of the laser communications system under diverse weather conditions, this chapter provides a comprehensive treatment of the evaluation of parameters needed for analyzing system performance. The significance of higher-order statistics of probability density functions of irradiance fluctuations due to turbulence to performance analysis is explained. Starting from link analysis, the necessary expressions relating link margin, bit-error-rate, signal-to-noise-ratio, and probability of fade statistics are presented. Results for laboratory-simulated atmospheric turbulence and multiple scattering are presented. Example numerical results for simulations of lasercom systems operating under various atmospheric conditions are presented for various scenarios such as uplink-downlink (e.g., between ground and satellite, aircraft or UAV) and horizontal (terrestrial) link. Both turbulence and multiple scattering effects have been included in the analysis with both on-off keying and pulse-position modulation schemes. Statistical estimation and computation of communication parameters presented in this chapter will be useful in designing and optimizing lasercom systems that are reliable under all weather conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.K. Killinger, J.H. Churnside, and L.S. Rothman, Atmospheric Optics, OSA Handbook of Optics, edited by M. Bass (1995), Chapter 44.
E.J. McCartney, Optics of the Atmosphere (Wiley, New York, 1969).
I.I. Kim, B. McArthur, and E. Korevaar, Comparison of laser beam propagation at 785 nm and 1550 nm in fog and haze for optical wireless communications, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 4214, p. 26-37, Optical Wireless Communications III, edited by Eric J. Korevaar (2000).
Brian R. Strickland, Michael J. Lavan, Eric Woodbridge, and Victor Chan, Effects of fog on the bit-error rate of a free-space laser communication system, Appl. Opt., 38, 424-431 (1999).
S.G. Lambert and W.L. Casey, Laser Communications in Space (Artech, Boston, 1995).
R.H. Kingston, Optical Sources, detectors, and Systems: Fundamentals and Applications (Academic, San Diego, 1995).
W.S. Ross, W.P. Jaeger, J. Nakai, T.T. Nguyen and J.H. Shapiro, Atmospheric Optical Propagation--an Integrated Approach, Opt. Eng., 21, 775 (1982).
A.K. Majumdar, Laboratory-Simulation Experiment for Optical Communication through Low-Visibility Atmosphere using a diode laser, IEEE J. Quantum Electron., QE-20, 919 (1984).
R.W. Svorec, Parametric Performance Analysis of Spaceborne Laser Communication Systems, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 295, 66 (1981).
A.K. Majumdar, Optical Communication between aircraft in low-visibility atmosphere using a diode laser, Appl. Opt., 24 (21), 3659-3665 (1985).
Alan J. MacGovern, David A. Nahrstedt, and Michael M. Johnson, Atmospheric propagation for tactical directed energy application, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 4034, pp. 128-139, Laser Weapons Technology, Todd D. Steiner, Paul H. Merritt, Eds. (2000).
V.I. Tatarskii, The Effects of the Turbulent Atmosphere on Wave Propagation (translated from Russian by IPST) (Available from the U.S. Dept. of Commerce, NTIS, Springfield, VA 22151), 1971.
Larry C. Andrews, Ronald L. Phillips, and Cynthia Y. Hopen, Laser Beam Scintillation with Applications, SPIE Press, Bellingham, Washington (2001).
Jennifer C. Ricklin, Stephane Bucaille, and Frederic M. Davidson, Performance loss factors for optical communication through clear air turbulence, Proc. SPIE, 5160, 1-12 (2003).
J.C. Ricklin and F. M. Dadidson, Atmospheric turbulence effects on a partially coherent Gaussian beam: implications for free-space laser communications, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 19(9), 1794-1803 (2002).
Arun K. Majumdar, Higher-order skewness and excess coefficients of some probability distributions applicable to optical propagation phenomena, J. Opt. Soc. Am., 69 (1), 199-202 (1979).
Arun K. Majumdar, Uniqueness of statistics derived from moments of irradiance fluctuations in atmospheric optical propagation, Opt. Commun., 50 (1),1-7 (1984).
Arun K. Majumdar, Higher-order statistics of laser-irradiance fluctuations due to turbulence, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 1, 1067-1074 (1984).
Arun K. Majumdar and Hideya Gamo, Statistical measurements of irradiance fluctuations of a multipass laser beam propagated through laboratory-simulated atmospheric turbulence, Appl. Opt., 21 (12), 2229-2235 (1982).
Hideya Gamo and Arun K. Majumdar, Atmospheric turbulence chamber for optical transmission experiment: characterization by thermal method, Appl. Opt., 17 (23), 3755-3761 (1978).
Arun K. Majumdar, John A. DiUbaldo, and Alenka Brown-VanHoozer, Laboratory Simulation of Atmospheric Turbulence for Laser propagation: design and characterization, Proc. SPIE. Vol. 3432 (1998).
M.A. Al-Habash, L.C. Andrews and R. L. Phillips, Mathematical model for the irradiance probability density function of a laser beam propagating through turbulent media, Opt. Eng., 40 (8), 1554-1562 (2001).
M. Nakagami, The m distribution—a general formula of intensity distribution of rapid fading, in Statistical Methods in Radio Wave Propagation, edited by W.C. Hoffman, 3-36 (Pergamon, New York, 1960).
Robert K. Tyson, Bit-error-rate for free-space adaptive optics laser communication, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 19 (40), 753-758 (2002).
Sherman Karp, Robert M. Gagliardi, Steven E. Moran and Larry B. Stotts, Optical Channels (Plenum Press, New York, 1988).
H.T. Yura and W.G. McKinley, Optical Scintillation Statistics for IR ground-to-space laser communication systems, Appl. Opt., 22 (21), 3353-3358 (1983).
H.G. Salfren, Effect of atmospheric turbulence on the bit error probability of a space to ground neaf infrared laser communications link using binary pulse position modulation and an avalanche photodiode detector, NASA Technical Memorandum 100699, Scientific and Technical Information Branch, 1987.
R.M. Gagliardi and S. Karp, M-ary Poisson detection and optical communication, IEEE Trans. Commun. Tech., COM-17, 208-216 (1969).
Robert M. Gagliardi and Sherman Karp, Optical Communications (Robert E. Krieger Publishing Company, Malabar, Florida, 1988).
Arun K. Majumdar and William C. Brown, Atmospheric Turbulence effecys on the Performance of Multi-Gigabit Downlink PPM Laser Communications, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 1218, 568-584, Free-Space Laser Communication Technologies II (1990).
Fotios Panagiotis Kourouniotis, Atmospheric Turbulence and Multiple Scattering effects on the Bit Error Rate of the Optical Receiver for PPM MultiGigabit Laser Communications, Master of Science Thesis, University of Colorado (1991).
J.H. Churnside and R. J. Hill, Probability density of irradiance scintillations for strong path-integrated refractive turbulence, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 4 (4), 727-733 (1987).
Akira Ishimaru, Wave Propagation and Scattering in Random Media, Vol.2 (Academic Press, 1978).
Shin Tsy Hong, I. Sreenivasiah, and Akira. Ishimaru, Plane Wave Pulse Propagatioin Through Random Media, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagation, AP-25, 6 (1997).
T.M. Shay, D.A. Hazzard, J. MacCannell, G. Lee, C.D. Garrett, J. A. Payne, N. Dahlstrom and S. Horan, First Experimental Demonstration of Full-Duplex optical Communications on a Single Laser Beam, AIAA 15th Annual AIAA/Utah State University Small Satellite Conference, August 13-16, 2001.
TGerardo G. Ortiz, Shinhak Lee, Steve Monacos, Malcom Wright and Abhijit Biswas, Design and development of a robust ATP subsystem for the Altair UAV-to-Ground Lasercomm 2.5 Gbps Demonstration, In Free-Space Laser Communication Technologies XV, G. Stephen Mecherle, Editor, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 4975 (2003).
J.M. Kahn and J. R. Barry, Wireless infrared communications, Proc. IEEE. 85 (3), 265-298 (1997).
G.W. Marsh and J. M. Kahn, Performance evaluation of experimental 50-Mbpss diffuse infrared wireless link using on-off keying with decision-feedback equalization, IEEE Trans. Commun., 44 (11), 1496-1504 (1996).
A.P. Tang and J. M. Kahn, Wireless infared communication links using multi-beam transmitter and imaging receivers, Proc. IEEE Intl. Conf. Commun., pp. 180-186 (1996).
Koorosh Akhavan, Mohsen Kavehrad and Svetla Jivkova, High-speed power-efficient indoor wireless infrared communication using code combining-Part I, IEEE Trans. Commun., 50 (7), 1098-1109 (2002).
Lijun Jiang, George Chung Kit Chen, Ye Yang, New Wei Lee, Allen Yeo and Hongga Li, Light-emitting-diode-based eide-field-of-view transceiver for indoor optical infrared wireless communication, Opt. Eng., 43 (4), 918-923 (2004).
Soo Hee Khoo, Wenwei Zhang, Grahame E. Faulkner, Dominic C. O'Brien and David J. Edwards, Receiver angle diversity design for high-speed diffuse indoor wireless communications, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 4530, 116-124, Optical Wireless Communication IV, edited by Eric J. Korevaar (2001).
Neil Savage, Linking with light, IEEE Spectrum, 39 (8), 32-35 (2002).
Sadik Esener and Philippe Marchand, Present and future needs of free-space optical interconnects, internet website: http://ipdps.eece.unm.edu/2000/wocs/18001109.pdf
Arun K. Majumdar and George H. Fortescue, Wide-beam atmospheric optical communication for aircraft application using semiconductor diodes, Appl. Opt., 22 (16), 2495-2504 (1983).
Isaac I. Kim, Harel Hakakha, Prasanna Adhikari, Eric Korevaar and Arun K. Majumdar, Scintillation reduction using multiple transmitters, in Free-Space Laser Communications Technologies IX, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 2990, 1997.
M. Jeganathan, K.E. Wilson, and J.R. Lesh, Preliminary analysis of fluctuations in the received Uplink-Beacon-Power data obtained from the GOLD experiments, JPL's TDA Progress Report 42-124, 20-32 (1996).
V. Vilnrotter, C.W. La, M. Srinivasan, R. Mukai, and K. Andrews, An optical array receiver for deep-space communication through atmospheric turbulence, JPL Publication: IPN Progress Report, Report 42-154, 1-21 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majumdar, A. Free-space laser communication performance in the atmospheric channel. J Optic Comm Rep 2, 345–396 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10297-005-0054-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10297-005-0054-0