Abstract
Background
While the dose of allopurinol is limited in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), information is lacking concerning the efficacy, safety, and maintenance dose of febuxostat in Chinese patients with hyperuricemia and with CKD stages 3–5.
Methods
A single center, prospective cohort study was conducted in patients with CKD stages 3–5 and with hyperuricemia who had not yet begun to undergo renal replacement therapy. We enrolled 208 patients who were newly treated with febuxostat (n = 112) or allopurinol (n = 96) in this study. The efficacy of febuxostat was determined by the proportion of patients with serum uric acid (sUA) < 360 µmol/L at the end of the study and changes of renal function.
Results
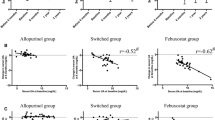
The target of sUA < 360 µmol/L was reached by 96.4% of participants in the febuxostat group and 37.5% in the allopurinol group at 6 months. The eGFR in the febuxostat group showed an increase from 28.45 to 30.65 mL/min/1.73 m2 at 6 months, while in the allopurinol group, the eGFR decreased from 28.06 to 24.39 mL/min/1.73 m2. Linear regression analysis showed that the reduction in sUA was significantly associated with an increase in eGFR and decrease in proteinuria. We found that 83.0% of the patients could remain with sUA < 360 µmol/L at a maintenance dose of febuxostat 20 mg/day.
Conclusion
Febuxostat had superior urate-lowering efficacy to that of allopurinol in Chinese Han patients with hyperuricemia with CKD stages 3–5, and the reduction in sUA levels was associated with a slower progression of renal function.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edwards NL. The role of hyperuricemia and gout in kidney and cardiovascular disease. Cleve Clin J Med. 2008;75:13–6.
Kuriyama S, Maruyama Y, Nishio S, Takahashi Y, Kidoguchi S, Kobayashi C, Takahashi D, Sugano N, Hosoya T, Yokoo T. Serum uric acid and the incidence of CKD and hypertension. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2015;19(6):1127–34.
Johnson RJ, Kang DH, Feig D, Kivlighn S, Kanellis J, Watanabe S, Tuttle KR, Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Herrera-Acosta J, Mazzali M. Is there a pathogenetic role for uric acid in hypertension and cardiovascular and renal disease? Hypertension. 2003;41(6):1183–90.
Tsuji T, Ohishi K, Takeda A, Goto D, Sato T, Ohashi N, Fujigaki Y, Kato A, Yasuda H. The impact of serum uric acid reduction on renal function and blood pressure in chronic kidney disease patients with hyperuricemia. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2018; 1–9.
Stamp LK, O’Donnell JL, Zhang M, James J, Frampton C, Barclay ML, Chapman PT. Using allopurinol above the dose based on creatinine clearance is effective and safe in patients with chronic gout, including those with renal impairment. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;63(2):412–21.
Grabowski BA, Khosravan R, Vernillet L, Mulford DJ. Metabolism and excretion of [14C] febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, in healthy male subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;51(2):189–201.
Hira D, Chisaki Y, Noda S, Araki H, Uzu T, Maegawa H, Yano Y, Morita SY, Terada T. Population pharmacokinetics and therapeutic efficacy of febuxostat in patients with severe renal impairment. Pharmacology. 2015;96(1–2):90–8.
Burns CM, Wortmann RL. Gout therapeutics: new drugs for an old disease. Lancet. 2011;377(9760):165–77.
Shibagaki Y, Ohno I, Hosoya T, Kimura K. Safety, efficacy and renal effect of febuxostat in patients with moderate-to-severe kidney dysfunction. Hypertens Res. 2014;37(10):919–25.
Liao Y, Liao W, Liu J, Xu G, Zeng R. Assessment of the CKD-EPI equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate in adults from a Chinese CKD population. J Int Med Res. 2011;39(6):2273–80.
Schumacher HR Jr, Becker MA, Wortmann RL, Macdonald PA, Hunt B, Streit J, Lademacher C, Joseph-Ridge N. Effects of febuxostat versus allopurinol and placebo in reducing serum urate in subjects with hyperuricemia and gout: a 28-week, phase III, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(11):1540–8.
Becker MA, Schumacher HR, Espinoza LR, Wells AF, MacDonald P, Lloyd E, Lademacher C. The urate-lowering efficacy and safety of febuxostat in the treatment of the hyperuricemia of gout: the CONFIRMS trial. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(2):R63.
Sezai A, Soma M, Nakata K, Osaka S, Ishii Y, Yaoita H, Hata H, Shiono M. Comparison of febuxostat and allopurinol for hyperuricemia in cardiac surgery patients with chronic kidney disease (NU-FLASH trial for CKD). J Cardiol. 2015;66(4):298–303.
Ficarra BJ. Significance of hyperuricemia in surgery: an introduction to current observations. Am J Surg. 1947;73(3):363–4.
Saag KG, Whelton A, Becker MA, MacDonald P, Hunt B, Gunawardhana L. Impact of febuxostat on renal function in gout patients with moderate-to-severe renal impairment. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(8):2035–43.
Filiopoulos V, Hadjiyannakos D, Vlassopoulos D. New insights into uric acid effects on the progression and prognosis of chronic kidney disease. Ren Fail. 2012;34(4):510–20.
Corry DB, Eslami P, Yamamoto K, Nyby MD, Makino H, Tuck ML. Uric acid stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and oxidative stress via the vascular rennin-angiotensin system. J Hypertens. 2008;26(2):269–75.
Ma L, Wei L, Chen H, Zhang Z, Yu Q, Ji Z, Jiang L. Influence of urate-lowering therapies on renal handling of uric acid. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35(1):133–41.
Tanaka K, Nakayama M, Kanno M, Kimura H, Watanabe K, Tani Y, Hayashi Y, Asahi K, Terawaki H, Watanabe T. Renoprotective effects of febuxostat in hyperuricemic patients with chronic kidney disease: a parallel-group, randomized, controlled trial. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2015;19(6):1044–53.
Sánchez-Lozada LG, Tapia E, Soto V, Avila-Casado C, Franco M, Wessale JL, Zhao L, Johnson RJ. Effect of febuxostat on the progression of renal disease in 5/6 nephrectomy rats with and without hyperuricemia. Nephron Physiol. 2008;108(4):p69–78.
Omori H, Kawada N, Inoue K, Ueda Y, Yamamoto R, Matsui I, Kaimori J, Takabatake Y, Moriyama T, Isaka Y, Rakugi H. Use of xanthine oxidase inhibitor febuxostat inhibits renal interstitial inflammation and fibrosis in unilateral ureteral obstructive nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012;16(4):549–56.
Sanchez-Lozada LG, Tapia E, Santamaria J, Avila-Casado C, Soto V, Nepomuceno T, Rodríguez-Iturbe B, Johnson RJ, Herrera-Acosta J. Mild hyperuricemia induces vasoconstriction and maintains glomerular hypertension in normal and remnant kidney rats. Kidney Int. 2005;67(1):237–47.
Sezai A, Soma M, Nakata K, Hata M, Yoshitake I, Wakui S, Hata H, Shiono M. Comparison of febuxostat and allopurinol for hyperuricemia in cardiac surgery patients (NU-FLASH Trial). Circ J. 2013;77(8):2043–9.
Becker MA Jr, Wortmann SH, MacDonald RL, Eustace PA, Palo D, Streit WA, Joseph-Ridge JN. Febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with hyperuricemia and gout. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(23):2450–61.
Becker MA Jr, Wortmann SH, MacDonald RL, Palo PA, Eustace WA, Vernillet D, Joseph-Ridge JN. Febuxostat, a novel nonpurine selective inhibitor of xanthine oxidase: a twenty-eight-day, multicenter, phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response clinical trial examining safety and efficacy in patients with gout. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(3):916–23.
Funding
The study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program) (81770679, 81470973) and Shandong Science and Technology Development Program (2010G0020222).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any original studies with human participants by any of the authors.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Wang, H., Ma, R. et al. The urate-lowering efficacy and safety of febuxostat versus allopurinol in Chinese patients with asymptomatic hyperuricemia and with chronic kidney disease stages 3–5. Clin Exp Nephrol 23, 362–370 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-018-1652-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-018-1652-5