Abstract
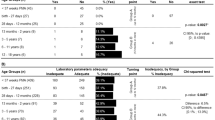
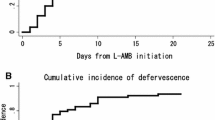
High-dose (5–7 mg/kg/day) liposomal amphotericin B was evaluated prospectively during the period 1995–2001 in 41 episodes of systemic candidiasis occurring in 37 neonates (36 of the 37 were premature infants with very low birth weights). Median age at the onset of systemic candidiasis was 17 days. Candida spp. were isolated from blood in all patients and from urine, skin abscesses and peritoneal fluid in 6, 5 and 1 neonates, respectively. Candidiasis was due to Candida parapsilosis in 17 cases, Candida albicans in 15 cases, Candida tropicalis in 5 cases, Candida guilliermondii in 2 cases, Candida glabrata in 2 cases and an unidentified Candida sp. in 1 case. Twenty-eight, five and eight infants received 7, 6–6.5 and 5 mg/kg/day, respectively. Median duration of therapy was 18 days; median cumulative dose was 94 mg/kg. Fungal eradication was achieved in 39 of 41 (95%) episodes; median duration of therapy until fungal eradication was 8.7±4.5 days. Fungal eradication was achieved after 10.9±4.8 days in patients who had received previous antifungal therapy compared to 8.2±4.3 days in those treated with liposomal amphotericin B as first-line therapy. One patient died due to systemic candidiasis on day 12 of therapy. High-dose liposomal amphotericin B was effective and safe in the treatment of neonatal candidiasis. Fungal eradication was more rapid in patients treated early with high doses and in patients who received high-dose liposomal amphotericin B as first-line therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van den Anker JN, van Popele NM, Sauer PJJ (1995) Antifungal agents in neonatal systemic candidiasis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 39:1391–1397
Rowen JL, Tate JM (1998) Management of neonatal candidiasis. Pediatr Infect Dis J 17:1007–1011
Deray G (2002). Amphotericin B nephrotoxicity. J Antimicrob Chemother 49 [Suppl S1]:37–41
Baley JE, Kliegman RM, Fanaroff AA (1984) Disseminated fungal infections in very low-birth-weight infants: therapeutic toxicity. Pediatrics 73:153–157
Koren G, Lau A, Klein J, Golas C, Bologna-Campeanu M, Soldin S, MacLeod SM, Prober C (1988) Pharmacokinetics and adverse events of amphotericin B in infants and children. J Pediatr 113:559–563
Kingo ARM, Smyth JA, Waisman D (1997) Lack of evidence of amphotericin toxicity in very low birth weight infants treated for systemic candidiasis. Pediatr Infect Dis J 16:1002–1003
Kossoff EH, Buescher ES, Karlowicz MG (1998) Candidemia in a neonatal intensive care unit: trends during fifteen years and clinical features of 111 cases. Pediatr Infect Dis J 17:504–508
Friedman S, Richardson SE, Jacobs SE, O'Brien K (2000) Systemic Candida infection in extremely low birth weight infants: short-term morbidity and long-term neurodevelopmental outcome. Pediatr Infect Dis J 19:499–504
Huttova M, Hartmanova I, Kralinsky K, Filka J, Uher J, Kurak J, Krizan S, Krcmery V Jr (1998) Candida fungemia in neonates treated with fluconazole: report of forty cases, including eight with meningitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J 17:1012–1015
Huang YC, Lin TY, Lien RI, Chou YH, Kuo CY, Yang PH, Hsieh WS (2000) Fluconazole therapy in neonatal candidemia. Am J Perinatol 17:411–415
Walsh TJ, Seibel NL, Arndt C, Harris RE, Dinubile MJ, Reboli A, Hiemenz J, Chanock SJ (1999) Amphotericin B lipid complex in pediatric patients with invasive fungal infections. Pediatr Infect Dis J 18:702–708
Adler-Shohat F, Waskin H, Lieberman JM (2001) Amphotericin B lipid complex for neonatal invasive candidiasis. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 84:F131–133
Hann IM, Prentice HG (2001) Lipid-based amphotericin B: a review of the last 10 years of use. Int J Antimicrob Agents 17:161–169
Lackner H, Schwinger W, Urban C, Muller W, Ritschl E, Reiterer F, Kutttnig-Haim M, Urlesberger B, Hauer C (1992) Liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome) for treatment of disseminated fungal infections in two infants of very low birth weight. Pediatrics 89:1259–1261
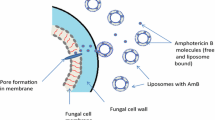
Adler-Moore JP, Proffitt RT (1993) Development, characterization, efficacy and mode of action of AmBisome, a unilamellar liposomal formulation of amphotericin B. J Liposome Res 3:429–450
Jarlov JO, Born P, Bruun B (1995) Candida albicans meningitis in a 27 weeks premature infant treated with liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome). Scand J Infect Dis 27:419–420
Evdoridou J, Roilides E, Bibashi E, Kremenoupoulos G (1997) Multifocal osteoarthritis due to Candida albicans in a neonate: serum level monitoring of liposomal amphotericin B and literature review. Infection 25:112–116
Al Arishi H, Frayha HH, Kalloghlian A, Alaiyan SA (1997) Liposomal amphotericin B in neonates with invasive candidiasis. Am J Perinatol 14:573–576
Scarcella A, Pasquariello MB, Giugliano B, Vendemmia M, de Lucia A (1998) Liposomal amphotericin B treatment for neonatal fungal infections. Pediatr Infect Dis J 17:146–148
Weitkamp JH, Poets CF, Sievers R, Musswessels E, Groneck P, Thomas P, Bartmann P (1998) Candida infection in very low birth-weight infants: outcome and nephrotoxicity of treatment with liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome). Infection 26:11–15
Juster-Reicher A, Leibovitz E, Linder N, Amitay M, Flidel-Rimon O, Even-Tov S, Mogilner B, Barzilai A (2000) Liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome) in the treatment of neonatal candidiasis in very low birth weight infants. Infection 28:223–226
Russo R, Nigro LC, Minniti S, Montineri A, Gradoni L, Caldeira L, Davidson RN (1996) Visceral leishmaniasis in HIV-infected patients: treatment with high-dose liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome). J Infect 32:133–137
Thakur CP (2001) A single high-dose treatment of kala-azar with AmBisome (amphotericin B lipid complex): a pilot study. Int J Antimicrob Agents 17:67–70
Walsh TJ, Goodman JL, Pappas P, Bekersky I, Buell DN, Roden M, Barrett J, Anaissie E (2001) Safety, tolerance, and pharmacokinetics of high-dose liposomal amphotericin B (AmBisome) in patients infected with Aspergillus species and other filamentous fungi: maximum tolerated dose study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:3487–3496
Chapman RL, Faix RG (2000) Persistently positive cultures and outcome in invasive neonatal candidiasis. Pediatr Infect Dis J 19:822–827
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juster-Reicher, A., Flidel-Rimon, O., Amitay, M. et al. High-Dose Liposomal Amphotericin B in the Therapy of Systemic Candidiasis in Neonates. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 22, 603–607 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-003-0993-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-003-0993-4