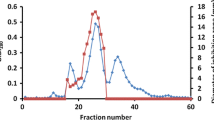
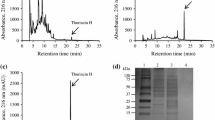
Abstract
Bacillus subtilis H27, an isolate from a commercial cheonggukjang product, inhibited Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 19111 and Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579. Antimicrobial activity of culture supernatant was completely destroyed by proteinase K treatment, indicating the proteinaceous nature of the inhibitory substance. The bacteriocin, Bac H27, was most stable at pH 7 and stable between pH 3-6 and 8-9 but inactive at pH 10 and above. The activity reduced to 50% after 15 min at 80°C. Brain heart infusion (BHI) was the best medium for the Bac H27 activity (160 AU/mL). Bac H27 was purified by ammonium sulfate precipitation followed by Q-Sepharose and Sephadex G-75 column chromatographies. Its size was estimated to be 4.9 kDa by Tricine SDSPAGE. Partially purified Bac H27 killed L. monocytogenes ATCC 19111 when added into L. monocytogenes culture. Bac H27 could be useful as a novel food grade preservative inhibiting B. cereus and L. monocytogenes, 2 important food pathogens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eom SM, Jung BY, Oh HI. Changes in chemical components of cheonggukjang prepared with germinated soybean during fermentation. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 52: 133–141 (2009)
Lee JJ, Kim AR, Lee H, Kim CH, Chang HC, Lee MY. Effects of soybean, cheonggukjang, and doenjang on serum cholesterol level and weight reduction in rats fed a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet. Korean J. Food Preserv. 18: 226–235 (2011)
Stein T. Bacillus subtilis antibiotics: Structures, syntheses, and specific functions. Mol. Microbiol. 56: 845–857 (2005)
Klein C, Kaletta C, Schnell N, Entian KD. Analysis of genes involved in biosynthesis of the lantibiotic subtilin. Appl. Environ. Microb. 58: 132–142 (1992)
Sutyak KE, Wirawan RE, Aroutcheva AA, Chikindas ML. Isolation of the Bacillus subtilis antimicrobial peptide subtilosin from the dairy product-derived Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 104: 1067–1074 (2007)
Oman TJ, Boettcher JM, Wang H, Okalibe XN, van der Donk WA. Sublancin is not a lantibiotic but an S-linked glycopeptides. Nat. Chem. Biol. 7: 78–80 (2011)
Kindoli S, Lee HA, Kim JH. Properties of Bac W42, a bacteriocin produced by Bacillus subtilis W42 isolated from cheonggukjang. J. Microbiol. Biotechn. 22: 1092–1100 (2012)
Hoover DG, Harlander SK. Screening methods for detecting bacteriocin activity. pp 23–39. In: Bacteriocins of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Hoover DG, Steenson LR (eds). Academic Press, San Diego, CA, USA (1993)
Daeschel MA. Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. pp. 57–79. In: Food Biopreservatives of Microbial Origin. Ray B, Daeschel MA (eds). CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, FL, USA (1992)
Kwon GH, Lee HA, Park JY, Kim JS, Lim J, Park CS, Kwon DY, Kim YS, Kim JH. Development of a RAPD-PCR method for identification of Bacillus species isolated from cheonggukjang. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 129: 282–287 (2009)
Martínez MA, Delgado OD, Breccia JD, Baigorí MD, Siñeriz F. Revision of the taxonomic position of the xylanolytic Bacillus sp. MIR32 reidentified as Bacillus halodurans and plasmid-mediated transformation of B. halodurans. Extremophiles 6: 391–395 (2002)
Bradford MM. Rapid and sensitive methods for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254 (1976)
Schägger H, von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of protein in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal. Biochem. 166: 368–379 (1987)
Nicolas GG, LaPointe G, Lavoie CM. Production, purification, sequencing, and activity spectra of mutacins D-123.1 and F-59.1. BMC Microbiol. 11: 69 (2011)
Kayalvizhi N, Gunasekaran P. Production and characterization of a low-molecular-weight bacteriocin from Bacillus licheniformis MKU3. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 47: 600–607 (2008)
Cherif A, Chehimi S, Limem F, Hansen BM, Hendriksen NB, Daffonchio D, Boudabous A. Detection and characterization of the novel bacteriocin entomocin 9, and safety evaluation of its producer, Bacillus thuringiensis ssp. entomocidus HD9. J. Appl. Microbiol. 95: 990–1000 (2003)
Bizani D, Brandelli A. Characterization of a bacteriocin produced by a newly isolated Bacillus sp. strain 8A. J. Appl. Microbiol. 93: 512–519 (2002)
Kwon GH, Lee HA, Kim JH. A bacteriocin of 5-kDa in size secreted by Bacillus subtilis 168. Korean J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38: 163–167 (2010)
Lee KH, Jun DK, Kim SW, Paik HD. Partial characterization of polyfermenticin SCD, a newly identified bacteriocin of Bacillus polyfermenticus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 32: 146–151 (2001)
Kamoun F, Mejdoub H, Aouissaoui H, Reinbolt J, Hammami A, Jaoua S. Purification, amino acid sequence and characterization of Bacthuricin F4, a new bacteriocin produced by Bacillus thuringiensis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 98: 881–888 (2005)
Tabbene O, Slimene IB, Bouabdallah F, Mangoni ML, Urdaci MC, Limam F. Production of anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus activity from Bacillus subtilis sp. strain B38 newly isolated from soil. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 157: 407–419 (2009)
Korenblum E, von der Weid I, Santos ALS, Rosado AS, Sebastián GV, Coutinho CMLM, Magalhâes FCM, de Paiva MM, Seldin L. Production of antimicrobial substances by Bacillus subtilis LFE-1, B. firmus H2O-1 399, and B. licheniformis T6-5 isolated from an oil reservoir in Brazil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 98: 667–675 (2005)
Babasaki K, Takao T, Shimonishi Y, Kurahashi K. Subtilosin A, a new antibiotic peptide produced by Bacillus subtilis 168: Isolation, structural analysis, and biogenesis. J. Biochem. 98: 585–603 (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kindoli, S., Lee, H.A., Heo, K. et al. Properties of a bacteriocin from Bacillus subtilis H27 isolated from Cheonggukjang . Food Sci Biotechnol 21, 1745–1751 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-012-0232-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-012-0232-9