Abstract
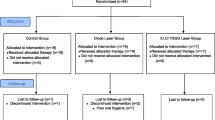
The aim of this controlled, parallel design clinical study was to evaluate the effectiveness of an Er:YAG (erbium-doped:yttrium, aluminum, and garnet) laser for nonsurgical treatment of periimplantitis lesions. Twenty patients, each of whom displayed at least one implant with (a) moderate and (b) advanced periimplantitis (n=40 implants; IMZ, ITI, Spline Twist, ZL-Duraplant, Camlog), were randomly instrumented nonsurgically using either (1) an Er:YAG laser (100 mJ/pulse, 10 Hz) device (LAS) or (2) mechanical debridement using plastic curettes and antiseptic therapy with chlorhexidine digluconate (0.2%) (C). The following clinical parameters were measured at baseline, 3, 6, and 12 months after treatment: plaque index, bleeding on probing (BOP), probing depth, gingival recession, and clinical attachment level (CAL). Mean BOP improved significantly in both groups at 3, 6, and 12 months (a− lesions: P<0.001 and b− lesions: P<0.01, respectively). After 3 and 6 months, the mean reduction of BOP was significantly higher in the LAS group when compared to the C group (a− and b− lesions: P<0.01 and P<0.05, respectively). At 3 and 6 months, both groups revealed significant CAL gains at a− and b− lesions (P<0.01, respectively). In both groups, however, the mean CAL at a− and b− lesions was not significantly different from the respective baseline values at 12 months (P>0.05, respectively). Although treatment of periimplantitis lesions with LAS resulted in a significantly higher BOP reduction than C, its effectiveness seemed to be limited to a period of 6 months, particularly at b− lesions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrektsson T, Isidor F (1994) Consensus report of session IV. In: Lang NP, Karring T (eds) Proceedings of the first European workshop on periodontology. Quintessence, London, pp 365–369
Aoki A, Ando Y, Watanabe H, Ishikawa I (1994) In vitro studies on laser scaling of subgingival calculus with an erbium:YAG laser. J Periodontol 65:1097–1106
Augthun M, Tinschert J, Huber A (1998) In vitro studies on the effect of cleaning methods on different implant surfaces. J Periodontol 69:857–864
Bach G, Neckel C, Mall C, Krekeler G (2000) Conventional versus laser-assisted therapy of periimplantitis: a five-year comparative study. Implant Dent 9:247–251
Badersten A, Nilveus R, Egelberg J (1990) Scores of plaque, bleeding, suppuration and probing depth to predict probing attachment loss. 5 years of observation following nonsurgical periodontal therapy. J Clin Periodontol 17:102–107
Becker W, Becker BE, Newman MG, Nyman S (1990) Clinical and microbiologic findings that may contribute to dental implant failure. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 5:31–38
Claffey N, Egelberg J (1995) Clinical indicators of probing attachment loss following initial periodontal treatment in advanced periodontitis patients. J Clin Periodontol 22:690–696
Cortellini P, Paolo G, Prato P, Tonetti MS (1996) Long-term stability of clinical attachment following guided tissue regeneration and conventional therapy. J Clin Periodontol 23:106–111
Deppe H, Horch HH, Henke J, Donath K (2001) Per-implant care of ailing implants with the carbon dioxide laser. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 16:659–667
Eberhard J, Ehlers H, Falk W, Acil Y, Albers HK, Jepsen S (2003) Efficacy of subgingival calculus removal with Er:YAG laser compared to mechanical debridement: an in situ study. J Clin Periodontol 30:511–518
Ericsson I, Lindhe J (1993) Probing depth at implants and teeth. An experimental study in the dog. J Clin Periodontol 20:623–627
Folwaczny M, Mehl A, Aggstaller H, Hickel R (2002) Antimicrobial effects of 2.94 μm Er:YAG laser radiation on root surfaces: an in vitro study. J Clin Periodontol 29:73–78
Fox SC, Moriarty JD, Kusy RP (1990) The effects of scaling a titanium implant surface with metal and plastic instruments: an in vitro study. J Periodontol 61:485–490
Heitz-Mayfield LJ, Lang NP (2004) Antimicrobial treatment of peri-implant diseases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 19:128–139 (Suppl)
Karring ES, Stavropoulos A, Ellegaard B, Karring T (2005) Treatment of peri-implantitis by the Vector system. Clin Oral Implants Res 16:288–293
Kato T, Kusakari H, Hoshino E (1998) Bactericidal efficacy of carbon dioxide laser against bacteria-contaminated titanium implant and subsequent cellular adhesion to irradiated area. Lasers Surg Med 23:299–309
Kreisler M, Al Haj H, Götz H, Duschner H, d’Hoedt B (2002) Effect of simulated CO(2) and GaAlAs laser surface decontamination on temperature changes in Ti-plasma sprayed dental implants. Lasers Surg Med 30:233–239
Kreisler M, Götz H, Duschner H (2002) Effect of Nd:YAG, Ho:YAG, Er:YAG, CO2, and GaAIAs laser irradiation on surface properties of endosseous dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 17:202–211
Kreisler M, Kohnen W, Marinello C, Gotz H, Duschner H, Jansen B, d’Hoedt B (2002) Bactericidal effect of the Er:YAG laser on dental implant surfaces: an in vitro study. J Periodontol 73:1292–1298
Kreisler M, Kohnen W, Christoffers AB, Gotz H, Jansen B, Duschner H, d’Hoedt B (2005) In vitro evaluation of the biocompatibility of contaminated implant surfaces treated with an Er: YAG laser and an air powder system. Clin Oral Implants Res 16:36–43
Lang NP, Wetzel AC, Stich H, Caffesse RG (1994) Histologic probe penetration in healthy and inflamed peri-implant tissues. Clin Oral Implants Res 5:191–201
Lavigne SE, Krust-Bray KS, Williams KB, Killoy WJ, Theisen F (1994) Effects of subgingival irrigation with chlorhexidine on the periodontal status of patients with HA-coated integral dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 9:156–162
Löe H (1967) The gingival index, the plaque index and the retention index systems. J Periodontol 38:610–616 (Suppl)
Luterbacher S, Mayfield L, Bragger U, Lang NP (2000) Diagnostic characteristics of clinical and microbiological tests for monitoring periodontal and peri-implant mucosal tissue conditions during supportive periodontal therapy (SPT). Clin Oral Implants Res 11:521–529
Matarasso S, Quaremba G, Coraggio F, Vaia E, Cafiero C, Lang NP (1996) Maintenance of implants: an in vitro study of titanium implant surface modifications, subsequent to the application of different peophylaxis procedures. Clin Oral Implants Res 7:64–72
Matsuyama T, Aoki A, Oda S, Yoneyama T, Ishikawa I (2003) Effects of the Er:YAG laser irradiation on titanium implant materials and contaminated implant abutment surfaces. J Clin Laser Med Surg 21:7–17
Mombelli A (2002) Microbiology and antimicrobial therapy of peri-implantitis. Periodontol 2000 28:177–189
Mombelli A, Lang NP (1992) Antimicrobial treatment of peri-implant infections. Clin Oral Implants Res 3:162–168
Mombelli A, Lang NP (1994) Microbial aspects of implant dentistry. Periodontol 2000 4:74–80
Persson LG, Berglundh T, Lindhe J, Sennerby L (2001) Re-osseointegration after treatment of peri-implantitis at different implant surfaces. An experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res 12:595–603
Porras R, Anderson GB, Caffesse R, Narendran S, Trejo PM (2002) Clinical response to 2 different therapeutic regimens to treat peri-implant mucositis. J Periodontol 73:1118–1125
Quirynen M, De Soete M, van Steenberghe D (2002) Infectious risks for oral implants: a review of the literature. Clin Oral Implants Res 13:1–19
Romanos GE, Everts H, Nentwig GH (2000) Effects of diode and Nd:YAG laser irradiation on titanium discs: a scanning electron microscope examination. J Periodontol 71:810–815
Rühling A, Kocher T, Kreusch J, Plagmann HC (1994) Treatment of subgingival implant surfaces with Teflon-coated sonic and ultrasonic scaler tips and various implant curettes. An in vitro study. Clin Oral Implants Res 5:19–29
Schou S, Berglundh T, Lang NP (2004) Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 19:140–149 (Suppl)
Schwarz F, Rothamel D, Becker J (2003) Influence of an Er:YAG laser on the surface structure of titanium implants. Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnmed 113:660–671
Schwarz F, Rothamel D, Sculean A, Georg T, Scherbaum W, Becker J (2003) Effects of an Er:YAG laser and the Vector ultrasonic system on the biocompatibility of titanium implants in cultures of human osteoblast-like cells. Clin Oral Implants Res 14:784–792
Schwarz F, Sculean A, Berakdar M, Szathmari L, Georg T, Becker J (2003) In vivo and in vitro effects of an Er:YAG laser, a GaAlAs diode laser, and scaling and root planing on periodontally diseased root surfaces: a comparative histologic study. Lasers Surg Med 32:359–366
Schwarz F, Sculean A, Romanos G, Herten M, Horn N, Scherbaum W, Becker J (2005) Influence of different treatment approaches on the removal of early plaque biofilms and the viability of SAOS2 osteoblasts grown on titanium implants. Clin Oral Investig 9:111–117
Schwarz F, Sculean A, Rothamel D, Schwenzer K, Georg T, Becker J (2005) Clinical evaluation of an Er:YAG laser for nonsurgical treatment of peri-implantitis: a pilot study. Clin Oral Implants Res 16:44–52
Schwarz F, Bieling K, Venghaus S, Sculean A, Jepsen S, Becker J (2006) Influence of fluorescence-controlled Er:YAG laser radiation, the Vector system and hand instruments on periodontally diseased root surfaces in vivo. J Clin Periodontol 33:200–208
Schwarz F, Papanicolau P, Rothamel D, Beck B, Herten M, Becker J (2006) Influence of plaque biofilm removal on reestablishment of the biocompatibility of contaminated titanium surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A 774A:437–444
Sculean A, Schwarz F, Becker J (2005) Anti-infective therapy with an Er:YAG laser: influence on peri-implant healing. Expert Rev Med Devices 2:267–276
Sugi D, Fukuda M, Minoura S, Yamada Y, Tako J, Miwa K, Noguchi T, Nakashima K, Sobue T, Noguchi T (1998) Effects of irradiation of Er:YAG laser on quantity of endotoxin and microhardness of surface in exposed root after removal of calculus. Japanese Journal of Conservative Dentistry 41:1009–1017
Tonetti MS, Pini-Prato G, Cortellini P (1995) Effect of cigarette smoking on periodontal healing following GTR in infrabony defects. A preliminary retrospective study. J Clin Periodontol 22:229–234
Tucker D, Cobb CM, Rapley JW, Killoy WJ (1996) Morphologic changes following in vitro CO2 laser treatment of calculus-ladened root surfaces. Lasers Surg Med 18:150–156
Van de Velde E, Thielens P, Schautteet H, Vanclooster R (1991) Subcutaneous emphysema of the oral floor during cleaning of a bridge fixed on an IMZ implant. Case report. Rev Belge Med Dent 46:64–71
Weigel C, Brägger U, Hämmerle CH, Mombelli A, Lang NP (1995) Maintenance of new attachment 1 and 4 years following guided tissue regeneration (GTR). J Clin Periodontol 22:661–669
Yamaguchi H, Kobayashi K, Osada R, Sakuraba E, Nomura T, Arai T, Nakamura J (1997) Effects of irradiation of an erbium:YAG laser on root surfaces. J Periodontol 68:1151–1155
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the “Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Kieferchirurgie innerhalb der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Zahn-, Mund- und Kieferheilkunde”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarz, F., Bieling, K., Bonsmann, M. et al. Nonsurgical treatment of moderate and advanced periimplantitis lesions: a controlled clinical study. Clin Oral Invest 10, 279–288 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-006-0070-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-006-0070-3