Abstract
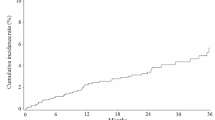
This large-scale postmarketing surveillance of raloxifene (60 mg/day) was conducted to assess the safety and effectiveness of raloxifene for long-term use in postmenopausal Japanese women with osteoporosis. The baseline examination included 6,967 women (mean age, 70.4 years). Participants completed observation after 6, 12, 24, and 36 months of therapy. Adverse drug reactions (ADR) were reported in 776 participants (11.14 %), with a total of 87 serious ADR cases occurring in 76 participants (1.09 %). The most frequently reported ADRs were edema peripheral (45/6,967, 0.65 %) and venous thromboembolism (11/6,967, 0.16 %). Of the 6,967 participants, 2,784 were included in the effectiveness analysis. Lumbar spine bone mineral density (BMD) increased significantly (p < 0.001, paired t test) compared with baseline at 6, 12, 24, and 36 months (2.51 %, 2.85 %, 4.76 %, and 3.51 %, respectively). Significant decreases in serum and urinary cross-linked amino-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (NTX) and urinary deoxypyridinoline levels from baseline were observed at 3 months, followed by a significant decrease of serum bone alkaline phosphatase at 6 months [p < 0.001 for all comparisons except serum NTX (p = 0.011), Wilcoxon signed-rank test]. Early reductions in the biochemical markers of bone turnover (BTM) observed at 3 months with raloxifene treatment correlated negatively with subsequent increases in lumbar spine BMD at 1 year (r = −0.347, p = 0.008). The incidence of any new clinical fractures within 3 years was 1.18 % (82/6,967 participants). In summary, no new signals in safety were observed in the daily use of raloxifene. Moreover, the effectiveness profile of raloxifene was confirmed in practical use by this large-scale, long-term, postmarketing surveillance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Committee of Japanese guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis (2006) Life Science Publishing, Basel
Ettinger B, Black DM, Mitlak BH, Knickerbocker RK, Nickelsen T, Genant HK, Christiansen C, Delmas PD, Zanchetta JR, Stakkestad J, Glüer CC, Krueger K, Cohen FJ, Eckert S, Ensrud KE, Avioli LV, Lips P, Cummings SR (1999) Reduction of vertebral fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis treated with raloxifene: results from a 3-year randomized clinical trial. Multiple Outcomes of Raloxifene Evaluation (MORE) Investigators. JAMA 18:637–645
Nakamura T, Liu JL, Morii H, Huang QR, Zhu HM, Qu Y, Hamaya E, Thiebaud D (2006) Effect of raloxifene on clinical fractures in Asian women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab 24:414–418
Morii H, Ohashi Y, Taketani Y, Fukunaga M, Nakamura T, Itabashi A, Sarkar S, Harper K (2003) Effect of raloxifene on bone mineral density and biochemical markers of bone turnover in Japanese postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Osteoporosis Int 14:793–800
Osteoporosis Diagnostic Criteria Review Committee: Japanese Society for Bone and Mineral Research, (2001) Diagnostic criteria for primary osteoporosis: year 2000 revision. J Bone Miner Metab 19:331–337
Evista® [US Package Insert 1/2011]. Indianapolis, IN: Eli Lilly and Company; 2011. http://pi.lilly.com/us/evista-pi.pdf. Accessed 4th Nov 2011
Kayser J, Ettinger B, Pressman A (2001) Postmenopausal hormonal support: discontinuation of raloxifene versus estrogen. Menopause 8:328–332
Barrett-Connor E, Mosca L, Collins P, Geiger MJ, Grady D, Kornitzer M, McNabb M, Wenger N (2006) Effects of raloxifene on cardiovascular events and breast cancer in postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med 355:125–137
Mosca L, Barrett-Connor E, Wenger NK, Collins P, Grady D, Kornitzer M, Moscarelli E, Paul S, Wright TJ, Helterbrand JD, Anderson PW (2001) Design and methods of the Raloxifene Use for The Heart (RUTH) study. Am J Cardiol 88:392–395
Uebayashi J (1995) Current medical practice of the treatment of deep thrombophlebitis and pulmonary embolism in special institutions in Japan. Research report in 1995 by the Ministry of Health and Welfare-sponsored Research Group of Blood Coagulation Abnormalities, pp 55–58
Urushihara H, Kikuchi N, Yamada M, Yoshiki F, Miyauchi A (2009) Raloxifene and stroke risks in Japanese postmenopausal women with osteoporosis on post marketing surveillance. Menopause 16:971–977
Martino S, Disch D, Dowsett SA, Keech CA, Mershon J (2005) Safety assessment of raloxifene over eight years in a clinical trial setting. Curr Med Res Opin 21:1441–1452
Goldstein SR, Duvernoy CS, Calaf J, Adachi JD, Mershon JL, Dowsett S, Agnusdei D, Stuenkel C (2009) Raloxifene use in clinical practice: efficacy and safety. Menopause 16:413–421
Cosman F, Baz-Hecht M, Cushman M, Vardy MD, Cruz JD, Nieves JW, Zion M, Lindsay R (2005) Short-term effects of estrogen tamoxifen and raloxifene on hemostasis: a randomized-controlled study and review of the literature. Thromb Res 116:1–13
Nishizawa Y, Nakamura T, Shiraki M, Ohta H, Fukunaga H, Dowsett SA, Agnusdei D, Stuenkel CA (2006) Metabolic bone markers after treatment of raloxifene chloride for menopausal osteoporosis women (preliminary report). Osteoporosis Jpn 14:231–235
Qu Y, Wong M, Thiebaud D, Stock JL (2005) The effect of raloxifene therapy on the risk of new clinical vertebral fractures at three and six months: a secondary analysis of the MORE trial. Curr Med Res Opin 21:1955–1959
Liu JL, Zhu HM, Huang QR, Zhang ZL, Li HL, Qin YJ, Zhang Y, Wei DL, Lu JH, Liu H, Chen XP, Liu YJ, Ekangaki A, Zheng YM, Diez-Perez A, Harper K (2004) Effects of raloxifene hydrochloride on bone mineral density, bone metabolism and serum lipids in Chinese postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: a multi-center, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Chin Med J 117:1029–1035
Seeman E, Crans GG, Diez-Perez AA, Pinette KV, Delmas PD (2006) Anti-vertebral fracture efficacy of raloxifene: a meta-analysis. Osteoporosis Int 17:313–316
Delmas PD, Genant HK, Crans GG, Stock JL, Wong M, Siris E, Adachi JD (2003) Severity of prevalent vertebral fractures and the risk of subsequent vertebral and nonvertebral fractures: results from the MORE trial. Bone (NY) 33:522–532
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the efforts of the investigators who participated in the surveillance and thank the contributors to manuscript preparation and editing (Laura Bean Warner, Pamela Boltz, and Todd Cravens of PharmaNet/i3). This study was supported by Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan) and Eli Lilly Japan K.K. (Kobe, Japan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Iikuni, N., Hamaya, E., Nihojima, S. et al. Safety and effectiveness profile of raloxifene in long-term, prospective, postmarketing surveillance. J Bone Miner Metab 30, 674–682 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-012-0365-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-012-0365-1