Abstract
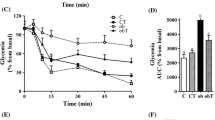
Taurine (Tau) is involved in beta (β)-cell function and insulin action regulation. Here, we verified the possible preventive effect of Tau in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity and glucose intolerance and in the disruption of pancreatic β-cell morpho-physiology. Weaning Swiss mice were distributed into four groups: mice fed on HFD diet (36 % of saturated fat, HFD group); HTAU, mice fed on HFD diet and supplemented with 5 % Tau; control (CTL); and CTAU. After 19 weeks of diet and Tau treatments, glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and islet morpho-physiology were evaluated. HFD mice presented higher body weight and fat depots, and were hyperglycemic, hyperinsulinemic, glucose intolerant and insulin resistant. Their pancreatic islets secreted high levels of insulin in the presence of increasing glucose concentrations and 30 mM K+. Tau supplementation improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity with a higher ratio of Akt phosphorylated (pAkt) related to Akt total protein content (pAkt/Akt) following insulin administration in the liver without altering body weight and fat deposition in HTAU mice. Isolated islets from HTAU mice released insulin similarly to CTL islets. HFD intake induced islet hypertrophy, increased β-cell/islet area and islet and β-cell mass content in the pancreas. Tau prevented islet and β-cell/islet area, and islet and β-cell mass alterations induced by HFD. The total insulin content in HFD islets was higher than that of CTL islets, and was not altered in HTAU islets. In conclusion, for the first time, we showed that Tau enhances liver Akt activation and prevents β-cell compensatory morpho-functional adaptations induced by HFD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahren B, Pacini G (2002) Insufficient islet compensation to insulin resistance vs. reduced glucose effectiveness in glucose-intolerant mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283(4):E738–E744
Anuradha CV, Balakrishnan SD (1999) Taurine attenuates hypertension and improves insulin sensitivity in the fructose-fed rat, an animal model of insulin resistance. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 77(10):749–754
Arany E, Strutt B, Romanus P, Remacle C, Reusens B, Hill DJ (2004) Taurine supplement in early life altered islet morphology, decreased insulitis and delayed the onset of diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice. Diabetologia 47(10):1831–1837
Araujo EP, De Souza CT, Ueno M, Cintra DE, Bertolo MB, Carvalheira JB, Saad MJ, Velloso LA (2007) Infliximab restores glucose homeostasis in an animal model of diet-induced obesity and diabetes. Endocrinology 148(12):5991–5997
Batista TM, Ribeiro RA, Amaral AG, de Oliveira CA, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2012) Taurine supplementation restores glucose and carbachol-induced insulin secretion in islets from low-protein diet rats: involvement of Ach-M3R, Synt 1 and SNAP-25 proteins. J Nutr Biochem 23(3): 306–312
Bernardis LL, Patterson BD (1968) Correlation between ‘Lee index’ and carcass fat content in weanling and adult female rats with hypothalamic lesions. J Endocrinol 40(4):527–528
Carneiro EM, Latorraca MQ, Araujo E, Beltra M, Oliveras MJ, Navarro M, Berna G, Bedoya FJ, Velloso LA, Soria B, Martin F (2009) Taurine supplementation modulates glucose homeostasis and islet function. J Nutr Biochem 20(7):503–511
Carvalho CP, Martins JC, da Cunha DA, Boschero AC, Collares-Buzato CB (2006) Histomorphology and ultrastructure of pancreatic islet tissue during in vivo maturation of rat pancreas. Ann Anat 188(3):221–234
Chang KJ (2000) Effect of taurine and beta-alanine on morphological changes of pancreas in streptozotocin-induced rats. Adv Exp Med Biol 483:571–577
Cnop M, Welsh N, Jonas JC, Jorns A, Lenzen S, Eizirik DL (2005) Mechanisms of pancreatic beta-cell death in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: many differences, few similarities. Diabetes 54(Suppl 2):S97–S107
Colivicchi MA, Raimondi L, Bianchi L, Tipton KF, Pirisino R, Della Corte L (2004) Taurine prevents streptozotocin impairment of hormone-stimulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 495(2–3):209–215
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sil PC (2011) Taurine suppresses doxorubicin-triggered oxidative stress and cardiac apoptosis in rat via up-regulation of PI3-K/Akt and inhibition of p53, p38-JNK. Biochem Pharmacol 81(7):891–909
De Souza CT, Araujo EP, Stoppiglia LF, Pauli JR, Ropelle E, Rocco SA, Marin RM, Franchini KG, Carvalheira JB, Saad MJ, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM, Velloso LA (2007) Inhibition of UCP2 expression reverses diet-induced diabetes mellitus by effects on both insulin secretion and action. FASEB J 21(4):1153–1163
Di Leo MA, Santini SA, Silveri NG, Giardina B, Franconi F, Ghirlanda G (2004) Long-term taurine supplementation reduces mortality rate in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Amino Acids 27(2):187–191
Elghazi L, Balcazar N, Bernal-Mizrachi E (2006) Emerging role of protein kinase B/Akt signaling in pancreatic beta-cell mass and function. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38(2):157–163
Franconi F, Bennardini F, Mattana A, Miceli M, Ciuti M, Mian M, Gironi A, Anichini R, Seghieri G (1995) Plasma and platelet taurine are reduced in subjects with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: effects of taurine supplementation. Am J Clin Nutr 61(5):1115–1119
Gomez-Perez Y, Gianotti M, Proenza AM, Llado I (2011) Age-related decline of skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity in rats: effect of sex and muscle type. Rejuvenation Res 14(2):153–161
Hansen SH (2001) The role of taurine in diabetes and the development of diabetic complications. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 17(5):330–346
Inuwa IM, El Mardi AS (2005) Correlation between volume fraction and volume-weighted mean volume, and between total number and total mass of islets in post-weaning and young Wistar rats. J Anat 206(2):185–192
Kahn SE, Prigeon RL, Schwartz RS, Fujimoto WY, Knopp RH, Brunzell JD, Porte D Jr (2001) Obesity, body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and islet beta-cell function as explanations for metabolic diversity. J Nutr 131(2):354S–360S
Kaniuk NA, Kiraly M, Bates H, Vranic M, Volchuk A, Brumell JH (2007) Ubiquitinated-protein aggregates form in pancreatic beta-cells during diabetes-induced oxidative stress and are regulated by autophagy. Diabetes 56(4):930–939
Lawrence M, Shao C, Duan L, McGlynn K, Cobb MH (2008) The protein kinases ERK1/2 and their roles in pancreatic beta cells. Acta Physiol (Oxford) 192(1):11–17
Li X, Monks B, Ge Q, Birnbaum MJ (2007) Akt/PKB regulates hepatic metabolism by directly inhibiting PGC-1alpha transcription coactivator. Nature 447(7147):1012–1016
Loizzo A, Carta S, Bennardini F, Coinu R, Loizzo S, Guarino I, Seghieri G, Ghirlanda G, Franconi F (2007) Neonatal taurine administration modifies metabolic programming in male mice. Early Hum Dev 83(10):693–696
Maturo J, Kulakowski EC (1988) Taurine binding to the purified insulin receptor. Biochem Pharmacol 37(19):3755–3760
Nakaya Y, Minami A, Harada N, Sakamoto S, Niwa Y, Ohnaka M (2000) Taurine improves insulin sensitivity in the Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rat, a model of spontaneous type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr 71(1):54–58
Nandhini AT, Anuradha CV (2002) Taurine modulates kallikrein activity and glucose metabolism in insulin resistant rats. Amino Acids 22(1):27–38
Nardelli TR, Ribeiro RA, Balbo SL, Vanzela EC, Carneiro EM, Boschero AC, Bonfleur ML (2011) Taurine prevents fat deposition and ameliorates plasma lipid profile in monosodium glutamate-obese rats. Amino Acids 41(4):901–908
Oprescu AI, Bikopoulos G, Naassan A, Allister EM, Tang C, Park E, Uchino H, Lewis GF, Fantus IG, Rozakis-Adcock M, Wheeler MB, Giacca A (2007) Free fatty acid-induced reduction in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion: evidence for a role of oxidative stress in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes 56(12):2927–2937
Persaud SJ, Muller D, Jones PM (2008) Insulin signalling in islets. Biochem Soc Trans 36(Pt 3):290–293
Ribeiro RA, Bonfleur ML, Amaral AG, Vanzela EC, Rocco SA, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2009) Taurine supplementation enhances nutrient-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic mice islets. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 25(4):370–379
Ribeiro RA, Vanzela EC, Oliveira CA, Bonfleur ML, Boschero AC, Carneiro EM (2010) Taurine supplementation: involvement of cholinergic/phospholipase C and protein kinase A pathways in potentiation of insulin secretion and Ca2+ handling in mouse pancreatic islets. Br J Nutr 104(8):1148–1155
Thomson JE, Jones EE, Eisen EJ (1994) Effect of spray-dried porcine plasma protein on feed intake, growth rate, and efficiency of gain in mice. J Anim Sci 72(10):2690–2695
Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Shozawa C, Sano K, Kamei Y, Kasaoka S, Hosokawa Y, Ezaki O (2006) Taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) deficiency creates a vicious circle promoting obesity. Endocrinology 147(7):3276–3284
Whiteman EL, Cho H, Birnbaum MJ (2002) Role of Akt/protein kinase B in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 13(10):444–451
Winzell MS, Magnusson C, Ahren B (2007) Temporal and dietary fat content-dependent islet adaptation to high-fat feeding-induced glucose intolerance in mice. Metabolism 56(1):122–128
Wu N, Lu Y, He B, Zhang Y, Lin J, Zhao S, Zhang W, Li Y, Han P (2010) Taurine prevents free fatty acid-induced hepatic insulin resistance in association with inhibiting JNK1 activation and improving insulin signaling in vivo. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 90(3):288–296
Xiao C, Giacca A, Lewis GF (2008) Oral taurine but not N-acetylcysteine ameliorates NEFA-induced impairment in insulin sensitivity and beta cell function in obese and overweight, non-diabetic men. Diabetologia 51(1):139–146
Zawalich WS, Zawalich KC (2000) A link between insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia: inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase augment glucose-induced insulin secretion from islets of lean, but not obese, rats. Endocrinology 141(9):3287–3295
Zawalich WS, Tesz GJ, Zawalich KC (2002) Inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase amplify insulin release from islets of lean but not obese mice. J Endocrinol 174(2):247–258
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ E-26/111.914/2011) and Conselho Nacional para o Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). We are grateful to LD Teixeira for animal care, E.C. Vanzela and J.C. Souza for technical assistance, T.M. Batista for help in data analysis and interpretation and Nicola Conran for editing the English. We also thank E.M. Risso and Prof. Dr. J.A. Farfán from the Laboratório de Fontes Protéicas (Faculdade de Engenharia de Alimentos, UNICAMP) for plasma Tau concentration determination.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeiro, R.A., Santos-Silva, J.C., Vettorazzi, J.F. et al. Taurine supplementation prevents morpho-physiological alterations in high-fat diet mice pancreatic β-cells. Amino Acids 43, 1791–1801 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1263-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1263-5