Abstract
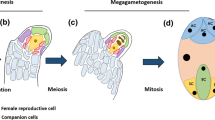
The endosporic male gametophyte of the water fern, Marsilea vestita, provides a unique opportunity to study the mechanisms that control cell fate determination during a burst of rapid development. In this review, we show how the spatial and temporal control of development in this simple gametophyte involves several distinct modes of RNA processing that allow the translation of specific mRNAs at distinct stages during gametogenesis. During the early part of development, nine successive cell division cycles occur in precise planes within a closed volume to produce seven sterile cells and 32 spermatids. There is no cell movement in the gametophyte; so, cell position and size within the spore wall define cell fate. After the division cycles have been completed, the spermatids become sites for the de novo formation of basal bodies, for the assembly of a complex cytoskeleton, for nuclear and cell elongation, and for ciliogenesis. In contrast, the adjacent sterile cells exhibit none of these changes. The spermatids differentiate into multiciliated, corkscrew-shaped gametes that resemble no other cells in the entire plant. Development is controlled post-transcriptionally. The transcripts stored in the microspore are released (unmasked) in the gametophyte at different times during development. At the start of these studies, we identified several key mRNAs that undergo translation at specific stages of gametophyte development. We developed RNA silencing protocols that enabled us to block the translation of these proteins and thereby establish their necessity and sufficiency for the completion of specific stages of gametogenesis. In addition, RNAi enabled us to identify additional proteins that are essential for other phases of development. Since the distributions of mRNAs and the proteins they encode are not identical in the gametophyte, transcript processing is apparently important in allowing translation to occur under strict temporal and spatial control. Transcript polyadenylation occurs in the spermatogenous cells in ways that match the translation of specific mRNAs. We have found that the exon junction complex plays key roles in transcript regulation and modifications that underlie cell specification in the gametophyte. We have recently become interested in the mechanisms that control the unmasking of the stored transcripts and have linked the synthesis and redistribution of spermidine in the gametophyte to the control of mRNA release from storage during early development and later to basal body formation, cytoskeletal assembly, and nuclear and cell elongation in the differentiating spermatids.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaldi PP, Felicetti L, Campioni N (1977) Flow of informational RNA from cytoplasmic poly(A)-containing particles to polyribosomes in Artemia salina cysts at early stages of development. Dev Biol 59:49–61
Andersen CBF, Ballut L, Johansen JS, Chamieh H, Nielsen KH, Olivera CLP, Pedersen JS, Seraphin B, LeHir H, Andersen GR (2006) Structure of the exon junction core complex with a trapped DEAD-box ATPase bound to RNA. Science 313:1968–1972
Ballut L, Marchadier B, Baguet A, Tomasetto C, Seraphin B, LeHir H (2005) The exon junction core complex is locked onto RNA by inhibition of eIF4AIII ATPase activity. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:861–869
Baron AT, Greenwood T, Bazinet C, Salisbury JL (1992) Centrin is a component of the pericentriolar lattice. Biol Cell 76:383–388
Bode J, Willmitzer L, Opatz K (1977) On the competition between protamines and histones: studies directed towards the understanding of spermiogenesis. Eur J Biochem 72:393–403
Bono F, Ebert J, Unterholzner L, Guttler T, Izaurralde E, Conti E (2004) Molecular insights into the interaction of PYM with the Mago-Y14 core of the exon junction complex. EMBO Rep 5:304–310
Boscher JM, Labouesse M (2000) RNA interference: genetic wand and genetic watchdog. Nat Cell Biol 2:E31–E36
Boswell RE, Prout ME, Steichen JC (1991) Mutations in a newly identified Drosophila melanogaster gene, mago nashi, disrupt germ cell formation and result in the formation of mirror-image symmetrical double abdomen embryos. Development 113:373–384
Brown RC, Carothers ZB (1986) Comparative studies of spermatogenesis in the Bryopsida. II. Blepharoplast morphology in Archidium tenerrinum Mitt. The Bryrologist 89:42–48
Carothers ZB (1973) Studies of spermatogenesis in the Hepaticae. IV. On the blepharoplast of Blasia. Am J Bot 60:819–828
Carothers ZB (1975) Comparative studies on spermatogenesis in bryophytes. In: Duckett JG, Racey PA (eds). The biology of the male gamete. Biol J Linn Soc 7(Suppl 1):71–84
Carothers ZB, Kreitner GL (1967) Studies of spermatogenesis in the Hepaticae: I. Ultrastructure of the Vierergruppe in Marchantia. J Cell Biol 33:43–51
Carothers ZB, Rushing AE (1990) Blepharoplast morphology in Treubia tasmanica (Hepiticae: Treubiales). Bryologist 93:409–416
Carothers ZB, Robbins RR, Haas DL (1975) Some ultrastructural aspects of spermatogenesis in Lycopodium complanatum. Protoplasma 86:339–350
Chamberlain CJ (1898) The homology of the blepharoplast. Bot Gaz 26:431–435
Chamberlain CJ (1909) Spermatogenesis in Dioon edule. Bot Gaz 47:215–236
Chapman RL, Henk MC (1983) Ultrastructure of Cephaleuros virescens (Chroolepidaceae; Chlorophyta). IV. Absolute configuration analysis of the cruciate flagellar apparatus and multilayered structures in the pre- and post-release gametes. Amer J Bot 70:1340–1355
Cheng SC, Tarn WY, Tsao TY, Abelson J (1993) PRP19: a novel spliceosomal component. Mol Cell Biol 13:1876–1882
Comai L, Dietrich RA, Maslyar DJ, Baden CS, Harada JJ (1989) Coordinate expression of transcriptionally regulated isocitrase lyase and malate synthase genes in Brassica napus L. Plant Cell 1:293–300
Dammermann A, Muller-Reichert T, Pelletier L, Habermann B, Desai A, Oegema K (2004) Centriole assembly requires both centriolar and pericentriolar material proteins. Dev Cell 7:815–829
De Moor CH, Richter JD (1999) Cytoplasmic polyadenylation elements mediate masking and unmasking of cyclin B1 mRNA. EMBO J 18:2294–2303
Deeb F, van der Weele CM, Wolniak SM (2010) Spermidine is a morphogenetic determinant for cell fate specification in the male gametophyte of the water fern Marsilea vestita. Plant Cell 22:3678–3691
Degot S, Le Hir H, Alpy F, Kedinger V, Stoll I, Wendling C, Seraphin B, Rio M-C, Tomasetto C (2004) Association of the breast cancer protein MLN51 with the exon junction complex via its speckle localizer and RNA binding module. J Biol Chem 279:33702–33715
Dibbayawan T, Harper JDI, Elliot J, Gunning BES, Marc J (1995) A γ-tubulin that associates specifically with centrioles in HeLa cells and the basal body complex in Chlamydomonas. Cell Biol Int 19:559–567
Doxsey SJ, Stein P, Evans L, Calarco P, Kirschner M (1994) Pericentrin, a highly conserved protein of centrosomes involved in microtubule organization. Cell 76:639–650
Duckett JG (1973) An ultrastructural study of the differentiation of the spermatozoid of Equisetum. J Cell Sci 12:95–129
Dure L, Waters L (1965) Long-lived messenger RNA: evidence from cotton seed germination. Science 147:410–412
Dutcher SK, Trabuco EC (1998) The UNI3 gene is required for assembly of basal bodies of Chlamydomonas and encodes delta-tubulin, a new member of the tubulin superfamily. Mol Biol Cell 9:1293–1308
Erickson HP (2000) γ-Tubulin nucleation: template or protofilament? Nat Cell Biol 2:E93–E96
Fire A (1999) RNA-triggered gene silencing. Trends Genet 15:358–363
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC (1998) Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 391:806–811
Fox CA, Sheets MD, Wickens MP (1989) Poly(A) addition during maturation of frog oocytes: distinct nuclear and cytoplasmic activities and regulation by the sequence UUUUUAU. Genes Dev 3:2151–2162
Gehring NH, Neu-Yilik G, Schell T, Hentze MW, Kulozik AE (2003) Y14 and hUpf3b form an NMD-activating complex. Mol Cell 11:939–949
Geimer S, Melkonian M (2005) Centrin scaffold in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii revealed by immunoelectron microscopy. Eukaryot Cell 4:1253–1263
Gifford EM Jr, Lin J (1975) Light microscope and ultrastructural studies of the male gametophyte in Ginkgo biloba: the spermatogenous cell. Am J Bot 62:974–981
Glab N, Lavidl B, Quin LX, Trehin C, Bergounioux C, Meijer L (1994) Olomoucine, an inhibitor of the cdc2/cdk2 kinases activity, blocks plant cells at the G1 to S and G2 to M cell cycle transitions. FEBS Lett 353:207–211
Gorgoni B, Gray NK (2004) The roles of cytoplasmic poly(A)-binding proteins in regulating gene expression: a developmental perspective. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 3:125–141
Grosfeld H, Littauer UZ (1975) Cryptic form of mRNA in dormant Artemia salina cysts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 67:176–181
Gross PR, Cousineau GH (1963) Effects of actinomycin D on macromolecule synthesis and early development in sea urchin eggs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 18:321–326
Gross PR, Cousineau GH (1964) Macromolecule synthesis and the influence of actinomycin on early development. Exp Cell Res 33:368–395
Hart PE, Wolniak SM (1998) Spermiogenesis in Marsilea vestita: a temporal correlation between centrin expression and blepharoplast differentiation. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 41:39–48
Hart PE, Wolniak SM (1999) Molecular cloning of a centrin homolog from Marsilea vestita and evidence for its translational control during spermiogenesis. Biochem Cell Biol 77:101–108
Harvey EB (1936) Parthenogenetic merogony or cleavage, without nuclei in Arbacia punctulata. Biol Bull 71:101–121
Harvey EB (1940) A comparison of the development of nucleate and non-nucleate eggs of Arbacia punctulata. Biol Bull 79:166–187
Hepler PK (1976) The blepharoplast of Marsilea: its de novo formation and spindle association. J Cell Sci 21:361–390
Hoffman JC, Vaughn KC (1995) Using the developing spermatogenous cells of Ceratopteris to unlock the mysteries of the plant cytoskeleton. Int J Plant Sci 156:346–358
Hoffman JC, Vaughn KC, Joshi HC (1994) Structural and immunocytochemical characterization of microtubule organizing centers in pteridophyte spermatogenous cells. Protoplasma 179:46–60
Hughes DW, Galau GA (1989) Temporally modular gene expression during cotyledon development. Genes Dev 3:358–369
Hughes DW, Galau GA (1991) Developmental and environmental induction of Lea and LeaA mRNAs and the postabscission program during embryo culture. Plant Cell 3:605–618
Hyams JS, Borisy GG (1978) Isolated flagellar apparatus of Chlamydomonas: characterization of forward swimming and alteration of waveform and reversal of motion by calcium ions in vitro. J Cell Sci 33:235–253
Hyams JS, Vondy KP, Luba A, Bell PR (1983) Structural and macromolecular events associated with basal body morphogenesis in Marsilea. J Submicros Cytol 15:133–138
Kataoka N, Diem MD, Kim VK, Yong J, Dreyfuss G (2001) Magoh, a human homolog of Drosophila mago nashi protein, is a component of the splicing-dependent exon–exon junction complex. EMBO J 20:6424–6433
Kaur-Sawhney R, Tiburcio AF, Atlabells T, Galston AW (2003) Polyamines in plants: an overview. J Cell Mol Biol 2:1–12
Kim VN, Yong J, Kataoka N, Abel L, Diem MD, Dreyfuss G (2001) The Y14 protein communicates to the cytoplasm the position of exon–exon junctions. EMBO J 20:2062–2068
Kimura M, Nambara E (2010) Stored and neosynthesized mRNA in Arabidopsis seeds: effects of cycloheximide and controlled deterioration treatment on the resumption of transcription during imbibition. Plant Mol Biol 73:119–129
Klink VP, Wolniak SM (2001) Centrin is necessary for the formation of the motile apparatus in spermatids of Marsilea. Mol Biol Cell 12:761–776
Klink VP, Wolniak SM (2003) Changes in the abundance and distribution of conserved centrosomal, cytoskeletal and ciliary proteins during spermiogenesis in Marsilea vestita. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 56:57–73
Klotz C, deLoubresse NG, Ruiz F, Beisson J (1997) Genetic evidence for a role of centin-associated proteins in the organization and dynamics of the infraciliary lattice in Paramecium. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 38:172–186
Kreitner GL (1977) Transformation of the nucleus in Marchantia spermatids: morphogenesis. Am J Bot 64:464–475
Kreitner GL, Carothers ZB (1976) Studies of spermatogenesis in the Hepaticae. V. Blepharoplast development in Marchantia polymorpha. Am J Bot 63:545–557
Kuligowski J, Ferrand M, Chenou E (1991) Stored mRNA in early embryos of a fern Marsilea vestita: a paternal and maternal origin. Mol Reprod Dev 30:27–33. doi:10.1002/mrd.1080300104
Lamond AI, Spector DL (2003) Nuclear speckles: a model for nuclear organelles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:605–612
Lau C-K, Dlem MD, Dreyfuss G, Van Duyne GD (2003) Structure of the Y14-Magoh core of the exon junction complex. Curr Biol 13:933–941
LeHir H, Izaurralde E, Maquat LE, Moore MJ (2000) The spliceosome deposits multiple proteins 20–24 nucleotides upstream of mRNA exon–exon junctions. EMBO J 19:6860–6869
LeHir H, Gatfield D, Braun IC, Forler D, Izaurralde E (2001a) The protein Mago provides a link between splicing and mRNA localization. EMBO Rep 2:1119–1124
LeHir H, Gatfield D, Izaurralde E, Moore MJ (2001b) The exon–exon junction complex provides a binding platform for factors involved in mRNA export and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. EMBO J 20:4987–4997
Leidel S, Delattre M, Cerutti L, Baumer K, Gonczy P (2005) SAS-6 defines a protein family required for centrosome duplication in C. elegans and in human cells. Nat Cell Biol 7:115–125
Levy YY, Lai EY, Remillard SP, Heintzelman MB, Fulton C (1996) Centrin is a conserved protein that forms diverse associations with centrioles and MTOCs in Naegleria and other organisms. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 33:298–323
Levy YY, Lai EY, Remillard SP, Fulton C (1998) Centrin is synthesized and assembled into basal bodies during Naegleria differentiation. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 40:249–260
Li Y, Wang FH, Knox RB (1989) Ultrastructural analysis of the flagellar apparatus in sperm cells of Ginkgo biloba. Protoplasma 14:57–63
Lopez-Smith R, Renzaglia KS (2008) Sperm cell architecture, insemination, and fertilization in the model fern, Ceratopteris richardii. Sex Plant Reprod 21:153–167
Luders J, Patel UK, Stearns T (2006) GCP-WD is a γ-tubulin targeting factor required for centrosomal and chromatin-mediated microtubule nucleation. Nat Cell Biol 8:137–147
Luo M, Reed R (1999) Splicing is required for rapid and efficient mRNA export in metazoans. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 96:14937–14942
Malatesta M, Zancanaro C, Martin TE, Chan EK, Amalric F, Luhrmann R, Vogel P, Fakan S (1994) Cytochemical and immunocytochemical characterization of nuclear bodies during hibernation. Eur J Cell Biol 65:82–93
Malatesta M, Cardinali A, Battistelli S, Zancanaro C, Martin TE, Fakan S, Gazzanelli G (1999) Nuclear bodies are usual constituents in tissue of hibernating dormice. Anat Rec 254:389–395
Maquat LE, Carmichael GG (2001) Quality control of mRNA function. Cell 104:173–176
Marc J, Gunning BES (1986) Immunofluorescent localization of cytoskeletal tubulin and actin during spermatogenesis in Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn. Protoplasma 134:163–177
Marshall WF, Rosenbaum JL (2000) How centrioles work: lessons from green yeast. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:119–125
Martin OC, Gunawardane RN, Iwamatsu A, Zheng Y (1998) Xgrip109: a γ-tubulin-associated protein with an essential role in γ-tubulin ring complex (γTuRC) assembly and centrosome function. J Cell Biol 141:675–687
McGrew LL, Dworkin-Rastl E, Dworkin MB, Richter JD (1989) Poly(A) elongation during Xenopus oocyte maturation is required for translational recruitment and is mediated by a short sequence element. Genes Dev 3:803–815
Meier L (1996) Chemical inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases. Trends Cell Biol 6:393–397
Melkonian M, Schulze D, McFadden GI, Robenek H (1988) A polyclonal antibody (anticentrin) distinguishes between two types of fibrous flagellar roots in green algae. Protoplasma 144:56–61
Micklem DR, Dasgurpta R, Elliott H, Gergely F, Davidson C, Brand A, Gonzalez-Reyes A, St Johnston D (1997) The mago nashi gene is required for the polarisation of the oocyte and the formation of perpendicular axes in Drosophila. Curr Biol 7:468–478
Middendorp S, Kuntziger T, Abraham Y, Holmes S, Bordes N, Paintrand M, Paoletti A, Bornens M (2000) A role for centrin 3 in centrosome reproduction. J Cell Biol 148:405–415
Mizukami I, Gall J (1966) Centriole replication. II. Sperm formation in the fern, Marsilea and the cycad, Zamia. J Cell Biol 29:97–111
Mohr SE, Dillon ST, Boswell RE (2001) The RNA-binding protein Tsunagi interacts with Mago Nashi to establish polarity and localize oskar mRNA during Drosophila oogenesis. Genes Dev 15:2886–2899
Montgomery MK, Fire A (1998) Double-stranded RNA as a mediator in sequence-specific genetic silencing and co-suppression. Trends Genet 14:255–258
Moritz M, Braunfeld MB, Guenebaut V, Heuser J, Agard DA (2000) Structure of the γ-tubulin ring complex: a template for microtubule nucleation. Nat Cell Biol 2:365–370
Murata T, Sonobe S, Baskin TI, Hyodo S, Hasezawa S, Nagata T, Horio T, Hasebe M (2005) Microtubule-dependent microtubule nucleation based on recruitment of γ-tubulin in higher plants. Nat Cell Biol 7:961–968
Muthukrishnan S, Filipowicz W, Sierra JM, Both GW, Shatkin AJ, Ochoa S (1975) mRNA methylation and protein synthesis in extracts from embryos of brine shrimp, Artemia salina. J Biol Chem 250:9336–9341
Myles DG, Hepler PK (1977) Spermiogenesis in the fern Marsilea: microtubules, nuclear shaping and cytomorphogenesis. J Cell Sci 23:57–83
Myles DG, Hepler PK (1982) Shaping of the sperm nucleus in Marsilea: a distinction between factors responsible for shape generation and shape determination. Dev Biol 90:238–252
Myles DG, Southworth D, Hepler PK (1978) Cell surface topography during Marsilea spermiogenesis: flagellar reorientation and membrane particle arrays. Protoplasma 93:405–417
Nakabayashi K, Okamoto M, Koshiba T, Kamiya Y, Nambara E (2005) Genome-wide profiling of stored mRNA in Arabidopsis thaliana seed germination: epigenetic and genetic regulation of transcription in seed. Plant J 41:697–709
Newmark PA, Boswell RE (1994) The mago nashi locus encodes an essential product required for germ plasm assembly in Drosophila. Development 120:1303–1313
Newmark PA, Mohr SE, Gong L, Boswell RE (1997) Mago nashi mediates the posterior follicle cell-to-oocyte signal to organize axis formation in Drosophila. Development 124:3197–3207
Ngo J, Tshudi C, Gull K, Ullu E (1998) Double-stranded RNA induces mRNA degradation in Trypanosoma brucei. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 95:14687–14692
Norstog K (1974) Fine structure of the spermatozoid of Zamia: the vieregruppe. Am J Bot 61:449–456
Nott A, Le Hir H, Moore MJ (2004) Splicing enhances translation in mammalian cells: an additional function of the exon junction complex. Genes Dev 18:210–222
O'Connell KF, Caron C, Kopish KR, Hurd DD, Kemphues KJ, Li Y, White J (2001) The C. elegans zyg-1 gene encodes a regulator of centrosome duplication with distinct maternal and paternal roles in the embryo. Cell 105:547–558
Palacios IM, St. Johnston D (2002) Kinesin light chain-independent function of the Kinesin heavy chain in cytoplasmic streaming and posterior localisation in the Drosophila oocyte. Development 129:5473–5485
Palacios IM, Gatfield D St, Johnston D, Izaurralde E (2004) An eIF4AIII-containing complex required for mRNA localization and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Nature 427:753–757
Paoletti A, Moudjou M, Paintrand M, Salisbury J, Bornens M (1996) Most of the centrin in animal cells is not centrosome-associated and centrosomal centrin is confined to the distal lumen of centrioles. J Cell Sci 109:3089–3102
Paolillo DJ Jr (1965) On the androcyte of Polytrichum, with special reference to the Dreiergruppe and the limosphere (Nebenkern). Can J Bot 43:669–676
Paolillo DJ Jr, Kreitner GL, Reighard J (1968) Spermatogenesis in Polytrichum junperinum. I. The origin of the apical body and elongation of the nucleus. Planta 78:226–247 (Berl)
Paris J, Phillippe M (1988) Poly(A) metabolism and polysomal recruitment of maternal mRNAs during early Xenopus development. Dev Biol 140:221–224
Pennell RI, Hyams JS, Bell PR (1986) The blepharoplast of Marsilea: a structure concerned with basal body assembly lacking tubulin. Eur J Cell Biol 40:238–241
Pennell RI, Vondy K, Bell PR, Hyams JS (1988) Composition and function of the blepharoplast of Marsilea vestita. Eur J Cell Biol 46:51–60
Pfeffer W (1884) Locomotorische Richtungsbewegungen durch chemische Reize. Unters Bot Inst Tubingen 1:363–482
Proweller A, Butler S (1994) Efficient translation of poly(A)-deficient mRNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev 8:2629–2640
Rafiq M, Suen CKM, Choudhury N, Joannou CL, White KN, Evans RW (1997) Expression of recombinant human ceruloplasmin—an absolute requirement for splicing signals in the expression cassette. FEBS 407:132–136
Renzaglia KS, Carothers ZB (1986) Ultrastructural studies of spermatogenesis in the Anthocerotales. IV. The blepharoplast and mid-stage spermatid of Notothylas. J Hattori Bot Lab 60:97–104
Renzaglia KS, Garbary DJ (2001) Motile gametes of land plants: diversity, development and evolution. Crit Rev Plant Sci 20:107–213
Robert D (1977) Le noyau du spermnatozoide du Selaginella kraussiana: etude cytochemique en microscopie electronique. J Ultrastruct Res 58:178–195
Rosenthal ET, Tansey TR, Ruderman JV, Gottesman M (1983) Sequence-specific adenylation and deadenylations accompany changes in the translation of maternal messenger RNA after fertilization of Spisula oocytes. J Mol Biol 166:309–327
Ruiz F, Beisson J, Rossier J, Dupuis-Williams P (1999) Basal body duplication in Paramecium requires γ-tubulin. Curr Biol 9:43–46
Ryu WS, Mertz JE (1989) Simian virus 40 late transcripts lacking excisable intervening sequences are defective in both stability in the nucleus and transport to the cytoplasm. J Virol 63:4386–4394
Salisbury JL (1983) Contractile flagellar roots: the role of calcium. J Submicros Cytol 15:105–110
Salisbury JL (1995) Centrin, centrosomes, and mitotic spindle poles. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7:39–45
Salisbury JL (2007) A mechanistic view on the evolutionary origin for centrin-based control of centriole duplication. J Cell Physiol 213:420–428
Schumacher J, Ashcroft N, Donovan PJ, Golden A (1998a) A highly conserved centrosomal kinase, AIR-1, is required for accurate cell cycle progression and segregation of developmental factors in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Development 125:4391–4402
Schumacher J, Golden A, Donovan PJ (1998b) AIR-2: an Aurora/Ipl1-related protein kinase associated with chromosomes and midbody microtubules is required for polar body extrusion and cytokinesis in C. elegans embryos. J Cell Biol 143:1635–1646
Sharp LW (1912) Spermatogenesis in Equisetum. Bot Gaz 54:89–119
Sharp LW (1914) Spermatogenesis in Marsilia. Bot Gaz 58:419–431
Shibuya T, Tange TØ, Sonenberg N, Moore MJ (2004) eIF4AIII binds spliced mRNA in the exon junction complex and is essential for nonsense-mediated decay. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:346–351
Shin M, Larsson L-I, Fujiwara K (2007) Polyamines in spermatocytes and residual bodies of rat testis. Biochem Cell Biol 127:649–655
Slevin MK, Gourronc F, Hartley RS (2007) ElrA binding to the 3′UTR of cyclin E1 mRNA requires polyadenylation elements. Nucleic Acids Res 35:2167–2176. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm084
Spector DL, Lamond AI (2011) Nuclear speckles. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a000646
Tabor CW, Tabor H (1984) Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem 53:749–790
Taillon BE, Adler SA, Suhan JP, Jarvik JW (1992) Mutational analysis of centrin: an EF-hand protein associated with three distinct contractile fibers in the basal body apparatus of Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol 119:1613–1624
Tange TØ, Nott A, Moore MJ (2004) The ever-increasing complexities of the exon junction complex. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16:279–284
Tange TØ, Shibuya T, Jurica MS, Moore MJ (2005) Biochemical analysis of the EJC reveals two new factors and a stable tetrameric protein core. RNA 11:1869–1883
Tremblay K, Vigneault C, McGraw S, Sirard M-A (2005) Expression of cyclin B1 messenger RNA isoforms and initiation of cytoplasmic polyadenylation in the bovine oocyte. Biol Rep 72:1037–1044. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.104.034793
Tsai CW, Wolniak SM (2001) Cell cycle arrest allows centrin translation but not basal body formation during spermiogenesis in Marsilea. J Cell Sci 114:4265–4272
Tsai CW, van der Weele CM, Wolniak SM (2004) Differential segregation and modification of mRNA during spermiogenesis in Marsilea vestita. Dev Biol 269:319–330
van der Weele CM, Tsai CW, Wolniak SM (2007) Mago nashi is essential for spermatogenesis in Marsilea. Mol Biol Cell 18:3711–3722
Vassalli J, Huarte J, Belin D, Gubler P, Vassalli A, O’Connell ML, Parton LA, Rickles RJ, Strickland S (1989) Regulated polyadenylation controls mRNA translation during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Genes Dev 3:2163–2171
Vaughn KC, Renzaglia KS (2006) Structural and immunocytochemical characterization of the Ginkgo biloba L. sperm motility apparatus. Protoplasma 227:165–183
Vaughn KC, Sherman TD, Renzaglia KS (1993) A centrin homologue is a component of the multilayered structure in bryophytes and pteridophytes. Protoplasma 175:58–66
Webber HJ (1897) Notes on the fecundation of Zamia and the pollen tube apparatus of Ginkgo. Bot Gaz 24:225–235
Weich H, Grier B, Paschke T, Spang A, Grein K, Steinkotter J, Melkonian M, Scheibel E (1996) Characterization of green alga, yeast, and human centrins. J Biol Chem 271:22453–22461
Wiegand HL, Lu S, Cullen BR (2003) Exon junction complexes mediate the enhancing effect of splicing on mRNA expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:11327–11332
Wiese C, Zheng Y (2000) A new function for the g-tubulin ring complex as a microtubule minus-end cap. Nat Cell Biol 2:358–364
Wilkinson MF, Shyu A (2002) RNA surveillance by nuclear scanning? Nat Cell Biol 4:144–147
Wilusz CJ, Wormington M, Peltz SW (2001) The cap-to-tail guide to mRNA turnover. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:237–246
Wolniak SM, Cande WZ (1980) Physiological requirements for ciliary reactivation of bracken fern spermatozoids. J Cell Sci 43:195–207
Wolniak SM, Klink VP, Hart PE, Tsai CW (2000) Control of development and motility in the spermatozoids of lower plants. Grav Sp Biol Bull 13:85–93
Yatin M (2002) Polyamines in living organisms. J Cell Mol Biol 1:57–67
Young A, Dictenberg JB, Purohit A, Tuft R, Doxsey SJ (2000) Cytoplasmic dynein-mediated assembly of pericentrin and γ-tubulin onto centrosomes. Mol Biol Cell 11:2047–2056
Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp PA, Bartel DP (2000) RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 101:25–33
Zheng Y, Wong ML, Alberts B, Mitchison T (1995) Nucleation of microtubule assembly by a γ-tubulin-containing ring structure. Nature 378:578–583
Zhou Z, Luo M, Straesser K, Katahira J, Hurt E, Reed R (2000) The Protein Aly links pre-messenger-RNA splicing to nuclear export in metazoans. Nature 407:401–405
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the support for this project in the form of grants from NSF (MCB 0720486 and DBI 0842525). We are also grateful for the support from Maryland Agriculture Experiment Station for this project. Faten Deeb was partially supported by a USDA Food and Agricultural Sciences National Needs Graduate and Postdoctoral Fellowship Grant (#20053842015761) while this work was being performed.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolniak, S.M., van der Weele, C.M., Deeb, F. et al. Extremes in rapid cellular morphogenesis: post-transcriptional regulation of spermatogenesis in Marsilea vestita . Protoplasma 248, 457–473 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-011-0276-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-011-0276-3