Abstract
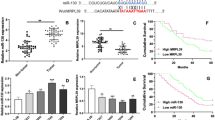
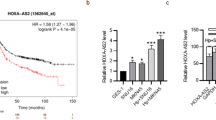
RAB GTPase 5A (RAB5A), a member of the Rab subfamily of small GTPases, acts as an oncogene and has been associated with various key cellular functions, including cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis and angiogenesis. Recently, it has been reported that the Rab5a gene is involved in the progression of cancer. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common and aggressive cancers, and it is usually associated with persistent hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections. Emerging evidence suggests that HBV alters microRNA (miRNA) expression profiles, but the mechanisms underlying this process have not yet been fully elucidated. Here, we examine how HBV affects the production of miR-101-1, which has been shown to be downregulated in HCC. We found that HBV could repress miR-101-3p by inhibiting its promoter activity. Downregulation of miR-101-3p promoted cancer cell growth and migration, and a specific miR-101-3p inhibitor was able to enhance proliferation and migration. Moreover, we identified Rab5a was one of the target genes of miR-101-3p in HBV-related HCC. Forced expression of miR-101-3p in liver cell lines resulted in a marked reduction of the expression of Rab5a at both the mRNA and protein level by directly targeting the 3′untranslated region of Rab5a. Overexpression of Rab5a resulted in a reversal of the suppression of proliferation and migration of SMMC-7721 cells mediated by miR-101-3p. Taken together, our data show that HBV can downregulate miR-101-3p expression by inhibiting its promoter activity and that downregulation of miR-101-3p promotes HCC cell proliferation and migration by targeting Rab5a. This provides new insights into the mechanisms of HBV-related HCC pathogenesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stefaniuk P, Cianciara J, Wiercinska-Drapalo A (2010) Present and future possibilities for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 16:418–424
McGlynn KA, London WT (2005) Epidemiology and natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 19:3–23
Li Y, Meng X, Feng H, Zhang G, Liu C, Li P (1999) Over-expression of the RAB5 gene in human lung adenocarcinoma cells with high metastatic potential. Chin Med Sci J 14(2):96–101
Li Y, Feng H, Chen Y (1999) RAB5A, a gene possibly related to metastasis of human carcinoma of the lung and stomach. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 21(3):178–181
Fukui K, Tamura S, Wada A, Kamada Y, Igura T, Kiso S, Hayashi N (2007) Expression of Rab5a in hepatocellular carcinoma: possible involvement in epidermal growth factor signaling. Hepatol Res 37(11):957–965
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Rigoutsos I (2009) New tricks for animal microRNAS: targeting of amino acid coding regions at conserved and nonconserved sites. Cancer Res 69:3245–3248
He XP, Shao Y, Li XL, Xu W, Chen GS, Sun HH, Xu HC, Xu X, Tang D, Zheng XF, Xue YP, Huang GC, Sun WH (2012) Downregulation of miR-101 in gastric cancer correlates with cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression and gastric tumor growth. FEBS J 279(22):4201–4212
Wang R, Wang HB, Hao CJ, Cui Y, Han XC, Hu Y, Li FF, Xia HF, Ma X (2012) MiR-101 is involved in human breast carcinogenesis by targeting Stathmin1. PloS One 7(10):e46173
Su H, Yang JR, Xu T, Huang J, Xu L, Yuan Y, Zhuang SM (2009) MicroRNA-101, down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer Res 69(3):1135–1142
Wei X, Xiang T, Ren G, Tan C, Liu R, Xu X, Wu Z (2013) miR-101 is down-regulated by the hepatitis B virus X protein and induces aberrant DNA methylation by targeting DNA methyltransferase 3A. Cell Signal 25(2):439–446
Liu Y, Zhao JJ, Wang CM, Li MY, Hang P, Wang L, Chen YQ, Zoulim F, Ma X, Xu DP (2009) Altered expression profiles of microRNAs in a stable hepatitis B virus-expressing cell line. Chin Med J 122:10–14
Ji F, Yang B, Peng X, Ding H, You H, Tien P (2011) Circulating microRNAs in hepatitis B virus-infected patients. J Viral Hepat 18(7):e242–e251
Xu X, Fan Z, Kang L, Han J, Jiang C, Zheng X, Zhu Z, Jiao H, Lin J, Jiang K, Ding L, Zhang H, Cheng L, Fu H, Song Y, Jiang Y, Liu J, Wang R, Du N, Ye Q (2013) Hepatitis B virus X protein represses miRNA-148a to enhance tumorigenesis. J Clin Investig 123(2):630–645
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Sprinzl MF, Oberwinkler H, Schaller H, Protzer U (2001) Transfer of hepatitis B virus genome by adenovirus vectors into cultured cells and mice: crossing the species barrier. J Virol 75(11):5108–5118
Luo J, Deng ZL, Luo X, Tang N, Song WX, Chen J, Sharff KA, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Kinzier KW, Vogeistein B, He TC (2007) A protocol for rapid generation of recombinant adenoviruses using the AdEasy system. Nat Protoc 2(5):1236–1247
Liu SS, Chen XM, Zheng HX, Shi SL, Li Y (2011) Knockdown of Rab5a expression decreases cancer cell motility and invasion through integrin-mediated signaling pathway. J Biomed Sci 18:58
Zhang ZZ, Liu X, Wang DQ, Teng MK, Niu LW, Huang AL, Liang Z (2011) Hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma at the miRNA level. World J Gastroenterol 17(28):3353–3358
Frankel LB, Wen J, Lees M, Høyer-Hansen M, Farkas T, Krogh A, Jäättelä M, Lund AH (2011) microRNA-101 is a potent inhibitor of autophagy. EMBO J 30(22):4628–4641
Huang J, Wang Y, Guo Y, Sun S (2010) Down-regulated microRNA-152 induces aberrant DNA methylation in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. Hepatology 52(1):60–70
Kong G, Zhang J, Zhang S, Shan C, Ye L, Zhang X (2011) Upregulated microRNA-29a by hepatitis B virus X protein enhances hepatoma cell migration by targeting PTEN in cell culture model. PLoS One 6(5):e19518
Yang L, Ma Z, Wang D, Zhao W, Chen L, Wang G (2010) MicroRNA-602 regulating tumor suppressive gene RASSF1A is over-expressed in hepatitis B virus-infected liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 9(10):803–808
Wei X, Tan C, Tang C, Ren G, Xiang T, Qiu Z, Liu R, Wu Z (2013) Epigenetic repression of miR-132 expression by the hepatitis B virus X protein in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Signal 25(5):1037–1043
Wu G, Yu F, Xiao Z, Xu K, Xu J, Tang W, Wang J, Song E (2011) Hepatitis B virus X protein downregulates expression of the miR-16 family in malignant hepatocytes in vitro. Br J Cancer 105(1):146–153
Fu X, Tan D, Hou Z, Hu Z, Liu G (2012) miR-338-3p is down-regulated by hepatitis B virus X and inhibits cell proliferation by targeting the 3′-UTR region of CyclinD1. Int J Mol Sci 13(7):8514–8539
Ling Y, Zhu J, Gao L, Liu Y, Zhu C, Li R, Wei L, Zhang C (2013) The silence of MUC2 mRNA induced by promoter hypermethylation associated with HBV in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Med Genet 14(1):14
Tian Y, Liu Y, Qu J, Li K, Qin D, Huang A, Tang H (2012) HBV regulated RhoC expression in HepG2.2.15 cells by enhancing its promoter activity. J Basic Microbiol 53(5):461–468
Chia WJ, Tang BL (2009) Emerging roles for Rab family GTPases in human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1795(2):110–116
Cheng KW, Lahad JP, Gray JW, Mills GB (2005) Emerging role of RAB GTPases in cancer and human disease. Cancer Res 65(7):2516–2519
Zahraour A, Touchot N, Chardin P, Tavitian A (1989) The Human Rab Gene5 encode a family of GTP-binding proteins related to yeast Ypt1 and SEC4 products involved in secretion. J Biol Chem 264(21):12394–12401
Zhao Z, Liu XF, Wu HC, Zou SB, Wang JY, Ni PH, Chen XH, Fan QS (2010) Rab5a overexpression promoting ovarian cancer cell proliferation may be associated with APPL1-related epidermal growth factor signaling pathway. Cancer Sci 101(6):1454–1462
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Nature Science Foundation of China (30771924) and Natural Science Foundation Project of CQ CSTC (2010BB5359).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Y. Sheng and J. Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, Y., Li, J., Zou, C. et al. Downregulation of miR-101-3p by hepatitis B virus promotes proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting Rab5a. Arch Virol 159, 2397–2410 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2084-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2084-5