Abstract
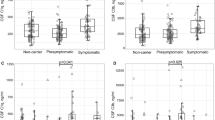
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is strongly associated with loss of synapses. The complement system has been shown to be involved in synaptic elimination. Several studies point to an association between AD and the complement system. The purpose of this study was to examine the association of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of complement components 3 and 4 (C3 and C4, respectively), and complement receptor 1 (CR1) with AD in 43 patients with AD plus dementia, 42 patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) who progressed to AD during follow-up (MCI-AD), 42 patients with stable MCI and 44 controls. Complement levels were also applied in a multivariate model to determine if they provided any added value to the core AD biomarkers Aβ42, T-tau and P-tau. We found elevated CSF levels of C3 and C4 in AD compared with MCI without progression to AD, and elevated CSF levels of CR1 in MCI-AD and AD when these groups were merged. These results provide support for aberrant complement regulation as a part in the AD process, but the changes are not diagnostically useful.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreasen N, Hesse C, Davidsson P, Minthon L, Wallin A, Winblad B, Vanderstichele H, Vanmechelen E, Blennow K (1999) Cerebrospinal fluid beta-amyloid(1–42) in Alzheimer disease: differences between early- and late-onset Alzheimer disease and stability during the course of disease. Arch Neurol 56(6):673–680
Bergamaschini L, Donarini C, Gobbo G, Parnetti L, Gallai V (2001) Activation of complement and contact system in Alzheimer’s disease. Mech Ageing Dev 122(16):1971–1983
Blennow K, Wallin A, Agren H, Spenger C, Siegfried J, Vanmechelen E (1995) Tau protein in cerebrospinal fluid: a biochemical marker for axonal degeneration in Alzheimer disease? Mol Chem Neuropathol 26(3):231–245. doi:10.1007/BF02815140
Blennow K, Hampel H, Weiner M, Zetterberg H (2010) Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma biomarkers in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6(3):131–144. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2010.4
Bylesjö M, Rantalainen M, Cloarec O, Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Trygg J (2006) OPLS discriminant analysis: combining the strengths of PLS-DA and SIMCA classification. J Chemom 20(8–10):341–351. doi:10.1002/cem.1006
Charbel Issa P, Chong NV, Scholl HP (2006) The significance of the complement system for the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration: current evidence and translation into clinical application. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie) 249(2):163–174. doi:10.1007/s00417-010-1568-6
Chu Y, Jin X, Parada I, Pesic A, Stevens B, Barres B, Prince DA (2010) Enhanced synaptic connectivity and epilepsy in C1q knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(17):7975–7980. doi:10.1073/pnas.0913449107
Davis AE 3rd, Mejia P, Lu F (2008) Biological activities of C1 inhibitor. Mol Immunol 45(16):4057–4063. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2008.06.028
Eikelenboom P, Veerhuis R (1996) The role of complement and activated microglia in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 17:673–680
Eikelenboom P, Hack CE, Kamphorst W, Rozemuller JM (1992) Distribution pattern and functional state of complement proteins and alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in cerebral beta/A4 deposits in Alzheimer’s disease. Res Immunol 143:617–620
Finehout EJ, Franck Z, Lee KH (2005) Complement protein isoforms in CSF as possible biomarkers for neurodegenerative disease. Dis Markers 21(2):93–101
Haga S, Ikeda K, Sato M, Ishii T (1993) Synthetic Alzheimer amyloid beta/A4 peptides enhance production of complement C3 component by cultured microglial cells. Brain Res 601:88–94
Hansson O, Zetterberg H, Buchhave P, Londos E, Blennow K, Minthon L (2006) Association between CSF biomarkers and incipient Alzheimer’s disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment: a follow-up study. Lancet Neurol 5(3):228–234. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70355-6
Harold D, Abraham R, Hollingworth P, Sims R, Gerrish A, Hamshere ML, Pahwa JS, Moskvina V, Dowzell K, Williams A, Jones N, Thomas C, Stretton A, Morgan AR, Lovestone S, Powell J, Proitsi P, Lupton MK, Brayne C, Rubinsztein DC, Gill M, Lawlor B, Lynch A, Morgan K, Brown KS, Passmore PA, Craig D, McGuinness B, Todd S, Holmes C, Mann D, Smith AD, Love S, Kehoe PG, Hardy J, Mead S, Fox N, Rossor M, Collinge J, Maier W, Jessen F, Schurmann B, van den Bussche H, Heuser I, Kornhuber J, Wiltfang J, Dichgans M, Frolich L, Hampel H, Hull M, Rujescu D, Goate AM, Kauwe JS, Cruchaga C, Nowotny P, Morris JC, Mayo K, Sleegers K, Bettens K, Engelborghs S, De Deyn PP, Van Broeckhoven C, Livingston G, Bass NJ, Gurling H, McQuillin A, Gwilliam R, Deloukas P, Al-Chalabi A, Shaw CE, Tsolaki M, Singleton AB, Guerreiro R, Muhleisen TW, Nothen MM, Moebus S, Jockel KH, Klopp N, Wichmann HE, Carrasquillo MM, Pankratz VS, Younkin SG, Holmans PA, O’Donovan M, Owen MJ, Williams J (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41(10):1088–1093. doi:10.1038/ng.440
Hsieh H, Boehm J, Sato C, Iwatsubo T, Tomita T, Sisodia S, Malinow R (2006) AMPAR removal underlies Abeta-induced synaptic depression and dendritic spine loss. Neuron 52(5):831–843. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2006.10.035
Kaarniranta K, Salminen A, Haapasalo A, Soininen H, Hiltunen M (2011) Age-related macular degeneration (AMD): Alzheimer’s disease in the eye? J Alzheimer’s Dis 24(4):615–631. doi:10.3233/JAD-2011-101908
Kamenetz F, Tomita T, Hsieh H, Seabrook G, Borchelt D, Iwatsubo T, Sisodia S, Malinow R (2003) APP processing and synaptic function. Neuron 37(6):925–937
Kirby E, Bandelow S, Hogervorst E (2010) Visual impairment in Alzheimer’s disease: a critical review. J Alzheimer’s Dis 21(1):15–34. doi:10.3233/JAD-2010-080785
Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G, Campion D, Sleegers K, Hiltunen M, Combarros O, Zelenika D, Bullido MJ, Tavernier B, Letenneur L, Bettens K, Berr C, Pasquier F, Fievet N, Barberger-Gateau P, Engelborghs S, De Deyn P, Mateo I, Franck A, Helisalmi S, Porcellini E, Hanon O, de Pancorbo MM, Lendon C, Dufouil C, Jaillard C, Leveillard T, Alvarez V, Bosco P, Mancuso M, Panza F, Nacmias B, Bossu P, Piccardi P, Annoni G, Seripa D, Galimberti D, Hannequin D, Licastro F, Soininen H, Ritchie K, Blanche H, Dartigues JF, Tzourio C, Gut I, Van Broeckhoven C, Alperovitch A, Lathrop M, Amouyel P (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41(10):1094–1099. doi:10.1038/ng.439
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34(7):939–944
Mulder C, Schoonenboom SN, Wahlund LO, Scheltens P, van Kamp GJ, Veerhuis R, Hack CE, Blomberg M, Schutgens RB, Eikelenboom P (2002) CSF markers related to pathogenetic mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 109(12):1491–1498. doi:10.1007/s00702-002-0763-y
Naj AC, Jun G, Beecham GW, Wang LS, Vardarajan BN, Buros J, Gallins PJ, Buxbaum JD, Jarvik GP, Crane PK, Larson EB, Bird TD, Boeve BF, Graff-Radford NR, De Jager PL, Evans D, Schneider JA, Carrasquillo MM, Ertekin-Taner N, Younkin SG, Cruchaga C, Kauwe JS, Nowotny P, Kramer P, Hardy J, Huentelman MJ, Myers AJ, Barmada MM, Demirci FY, Baldwin CT, Green RC, Rogaeva E, St George-Hyslop P, Arnold SE, Barber R, Beach T, Bigio EH, Bowen JD, Boxer A, Burke JR, Cairns NJ, Carlson CS, Carney RM, Carroll SL, Chui HC, Clark DG, Corneveaux J, Cotman CW, Cummings JL, DeCarli C, DeKosky ST, Diaz-Arrastia R, Dick M, Dickson DW, Ellis WG, Faber KM, Fallon KB, Farlow MR, Ferris S, Frosch MP, Galasko DR, Ganguli M, Gearing M, Geschwind DH, Ghetti B, Gilbert JR, Gilman S, Giordani B, Glass JD, Growdon JH, Hamilton RL, Harrell LE, Head E, Honig LS, Hulette CM, Hyman BT, Jicha GA, Jin LW, Johnson N, Karlawish J, Karydas A, Kaye JA, Kim R, Koo EH, Kowall NW, Lah JJ, Levey AI, Lieberman AP, Lopez OL, Mack WJ, Marson DC, Martiniuk F, Mash DC, Masliah E, McCormick WC, McCurry SM, McDavid AN, McKee AC, Mesulam M, Miller BL, Miller CA, Miller JW, Parisi JE, Perl DP, Peskind E, Petersen RC, Poon WW, Quinn JF, Rajbhandary RA, Raskind M, Reisberg B, Ringman JM, Roberson ED, Rosenberg RN, Sano M, Schneider LS, Seeley W, Shelanski ML, Slifer MA, Smith CD, Sonnen JA, Spina S, Stern RA, Tanzi RE, Trojanowski JQ, Troncoso JC, Van Deerlin VM, Vinters HV, Vonsattel JP, Weintraub S, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Williamson J, Woltjer RL, Cantwell LB, Dombroski BA, Beekly D, Lunetta KL, Martin ER, Kamboh MI, Saykin AJ, Reiman EM, Bennett DA, Morris JC, Montine TJ, Goate AM, Blacker D, Tsuang DW, Hakonarson H, Kukull WA, Foroud TM, Haines JL, Mayeux R, Pericak-Vance MA, Farrer LA, Schellenberg GD (2011) Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 43(5):436–441. doi:10.1038/ng.801
Rosen AM, Stevens B (2010) The role of the classical complement cascade in synapse loss during development and glaucoma. Adv Exp Med Biol 703:75–93. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-5635-4_6
Sarma JV, Ward PA (2011) The complement system. Cell Tissue Res 343(1):227–235. doi:10.1007/s00441-010-1034-0
Scheff SW, Price DA (2003) Synaptic pathology in Alzheimer’s disease: a review of ultrastructural studies. Neurobiol Aging 24(8):1029–1046
Seshadri S, Fitzpatrick AL, Ikram MA, DeStefano AL, Gudnason V, Boada M, Bis JC, Smith AV, Carassquillo MM, Lambert JC, Harold D, Schrijvers EM, Ramirez-Lorca R, Debette S, Longstreth WT Jr, Janssens AC, Pankratz VS, Dartigues JF, Hollingworth P, Aspelund T, Hernandez I, Beiser A, Kuller LH, Koudstaal PJ, Dickson DW, Tzourio C, Abraham R, Antunez C, Du Y, Rotter JI, Aulchenko YS, Harris TB, Petersen RC, Berr C, Owen MJ, Lopez-Arrieta J, Varadarajan BN, Becker JT, Rivadeneira F, Nalls MA, Graff-Radford NR, Campion D, Auerbach S, Rice K, Hofman A, Jonsson PV, Schmidt H, Lathrop M, Mosley TH, Au R, Psaty BM, Uitterlinden AG, Farrer LA, Lumley T, Ruiz A, Williams J, Amouyel P, Younkin SG, Wolf PA, Launer LJ, Lopez OL, van Duijn CM, Breteler MM (2010) Genome-wide analysis of genetic loci associated with Alzheimer disease. J Am Med Assoc 303(18):1832–1840. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.574
Shankar GM, Bloodgood BL, Townsend M, Walsh DM, Selkoe DJ, Sabatini BL (2007) Natural oligomers of the Alzheimer amyloid-beta protein induce reversible synapse loss by modulating an NMDA-type glutamate receptor-dependent signaling pathway. J Neurosci 27(11):2866–2875. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4970-06.2007
Smyth MD, Cribbs DH, Tenner AJ, Shankle WR, Dick M, Kesslak JP, Cotman CW (1994) Decreased levels of C1q in cerebrospinal fluid of living Alzheimer patients correlate with disease state. Neurobiol Aging 15(5):609–614
Spitzer RL, Williams JBW, American Psychiatric Association (1987) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-III-R, 3rd edn. Cambridge University, Cambridge
Stevens B, Allen NJ, Vazquez LE, Howell GR, Christopherson KS, Nouri N, Micheva KD, Mehalow AK, Huberman AD, Stafford B, Sher A, Litke AM, Lambris JD, Smith SJ, John SW, Barres BA (2007) The classical complement cascade mediates CNS synapse elimination. Cell 131(6):1164–1178. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.036
Tibbling G, Link H, Ohman S (1977) Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. I. Establishment of reference values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 37(5):385–390
Vanmechelen E, Vanderstichele H, Davidsson P, Van Kerschaver E, Van Der Perre B, Sjogren M, Andreasen N, Blennow K (2000) Quantification of tau phosphorylated at threonine 181 in human cerebrospinal fluid: a sandwich ELISA with a synthetic phosphopeptide for standardization. Neurosci Lett 285(1):49–52
Wang Y, Hancock AM, Bradner J, Chung KA, Quinn JF, Peskind ER, Galasko D, Jankovic J, Zabetian CP, Kim HM, Leverenz JB, Montine TJ, Ginghina C, Edwards KL, Snapinn KW, Goldstein DS, Shi M, Zhang J (2011) Complement 3 and factor h in human cerebrospinal fluid in Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple-system atrophy. Am J Pathol 178(4):1509–1516. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.01.006
Winblad B, Palmer K, Kivipelto M, Jelic V, Fratiglioni L, Wahlund LO, Nordberg A, Backman L, Albert M, Almkvist O, Arai H, Basun H, Blennow K, de Leon M, DeCarli C, Erkinjuntti T, Giacobini E, Graff C, Hardy J, Jack C, Jorm A, Ritchie K, van Duijn C, Visser P, Petersen RC (2004) Mild cognitive impairment–beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. J Intern Med 256(3):240–246. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01380.x
Yasojima K, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1999a) Complement regulators C1 inhibitor and CD59 do not significantly inhibit complement activation in Alzheimer disease. Brain Res 833(2):297–301
Yasojima K, Schwab C, McGeer EG, McGeer PL (1999b) Up-regulated production and activation of the complement system in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Am J Pathol 154(3):927–936. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65340-0
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Åsa Källén, Monica Christiansson, Dzemila Secic and Sara Hullberg for skillful technical assistance, and Doctor Rochelle Ackerley for helpful comments on the manuscript. This study was supported by grants from the Sahlgrenska Academy, the Swedish Research Council (K2010-63P-21562-01-4, K2011-61X-20401-05-6, K2011-62X-21857-01-6, K2011-62X-21710-01-1, K2010-62X-12600-13-3), the Söderberg Foundation, Alzheimer’s Association, Gun and Bertil Stohne’s Foundation, Stiftelsen för Gamla Tjänarinnor, The Swedish Alzheimer Foundation, ALF funding for medical training and research and Swedish State Support for Clinical Research. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daborg, J., Andreasson, U., Pekna, M. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of complement proteins C3, C4 and CR1 in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 119, 789–797 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0797-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0797-8