Abstract
Background
Studies regarding frameless stereotactic brain biopsy mainly report high diagnostic yield (DY) as opposed to relatively low diagnostic accuracy. This discrepancy raises the question of the certainty and precision of obtained diagnoses. This article proposes a DY definition encompassing diagnostic certainty and precision according to the World Health Organization (WHO) central nervous system (CNS) tumour classification system. Furthermore, our eight-year experience with this procedure is reviewed and evaluated.
Methods
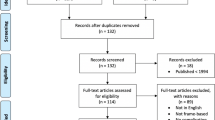
A consecutive series of 235 frameless biopsy procedures was reviewed. Criteria were set up for categorising obtained diagnoses. All cases were included in a predictive factor analysis of inconclusive biopsy and postoperative complications.
Results
According to our predefined DY criteria, the DY was 72.8 %. The inconclusive biopsy outcome measured 21.7 %; the non-diagnostic biopsy outcome was 5.5 %. The only predictive factor found for inconclusive biopsy procedures was age under 30. Predictive factors for postoperative complications, which were found statistically significant after multivariable analysis, were glucose level and intra-operative haemorrhage. The total morbidity rate was 8.5 %, including a mortality rate of 0.9 %.
Conclusions
Although frameless stereotactic brain biopsy procedures are considered to be relatively safe, the true DY is significantly less than previously reported, most probably due to the lack of standardised DY criteria. Based on our DY definition and subsequent DY findings, standardisation of DY criteria and definition is paramount for biopsy diagnosis interpretation.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Anaplastic astrocytoma
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DA:
-
Diagnostic accuracy
- DY:
-
Diagnostic yield
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma multiforme
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Air EL, Leach JL, Warnick RE, McPherson CM (2009) Comparing the risks of frameless stereotactic biopsy in eloquent and noneloquent regions of the brain: a retrospective review of 284 cases. J Neurosurg 111:820–824
Aker FV, Hakan T, Karadereler S, Erkan M (2005) Accuracy and diagnostic yield of stereotactic biopsy in the diagnosis of brain masses comparison of results of biopsy and resected surgical specimens. Neuropathology 25:207–213
Allouch H, Pfeifenbring S, Behnke-Mursch J, Halatsch ME, Mursch K (2013) Real-time ultrasound monitoring during intracranial needle biopsies: operative results and detection of complications in 100 cases. World Neurosurg. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2013.01.019
Barnett GH, Miller DW, Weisenberger J (1999) Frameless stereotaxy with scalp-applied fiducial markers for brain biopsy procedures: experience in 218 cases. J Neurosurg 91:569–576
Bekelis K, Radwan TA, Desai A, Roberts DW (2012) Frameless robotically targeted stereotactic brain biopsy: feasibility, diagnostic yield and safety. J Neurosurg 116:1002–1006
Brainard JA, Prayson RA, Barnett GH (1997) Frozen section evaluation of stereotactic brain biopsies: diagnostic yield at the stereotactic target position in 188 cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med 121:481–484
Capabianca P, Spaziante R, Caputi F, Pettinato G, Del Basso De Caro M, Carrabs G, de Divitiis E (1991) Accuracy of the analysis of multiple small fragments of glial tumors obtained by stereotactic biopsy. Acta Cytol 35(5):505–511
Chandrasoma PT, Smitch MM, Apuzzo ML (1989) Stereotactic biopsy in the diagnosis of brain masses comparison of results of biopsy and resected surgical specimen. Neurosurgery 24(2):160–165
Chen CC, Hsu PW, Erich Wu TW, Lee ST, Chang CN, Wei KC, Chuang CC, Wu CT, Lui TN, Hsu YH, Lin TK, Lee SC, Huang YC (2009) Stereotactic brain biopsy: single center retrospective analysis of complications. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 111:835–839
Dammers R, Haitsma IK, Schouten JW, Kros JM, Avezaat CJ, Vincent AJ (2008) Safety and efficacy of frameless and frame-based intracranial biopsy techniques. Acta Neurochir 150:23–29
Dammers R, Schouten JW, Haitsma IK, Vincent AJPE, Kros JM, Dirven CMF (2010) Towards improving the safety and diagnostic yield of stereotactic biopsy in a single centre. Acta Neurochir 152(11):1915–1921
Dorward NL, Paleologos TS, Alberti O, Thomas DG (2002) The advantages of frameless stereotactic biopsy over frame-based biopsy. Br J Neurosurg 16:110–118
Field M, Witham TF, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2001) Comprehensive assessment of hemorrhage risks and outcomes after stereotactic brain biopsy. J Neurosurg 94(4):545–551
Frati A, Pichierri A, Bastianello S, Raco A, Santoro A, Esposito V, Giangaspero F, Salvati M (2011) Frameless stereotactic cerebral biopsy: our experience in 296 cases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 89:234–245
Fritsch MJ, Leber MJ, Gossett L, Lulu BA, Hamilton AJ (1998) Stereotactic biopsy of intracranial brain lesions. High diagnostic yield without increased complications: 65 consecutive biopsies with early postoperative CT scans. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 71:36–42
Gempt J, Buchman N, Ryang YM, Krieg S, Kretuzer J, Meyer B, Ringel F (2012) Frameless image-guided stereotaxy with real-time visual feedback for brain biopsy. Acta Neurochir 154:1663–1667
Germano IM, Queenan JV (1998) Clinical experience with intracranial brain needle biopsy using frameless surgical navigation. Comput Aided Surg 3:33–39
Gralla J, Nimsky C, Buchfelder M, Fahlbusch R, Ganslandt O (2003) Frameless stereotactic brain biopsy procedures using the Stealth Station: indications, accuracy and results. Zentralbl Neurochir 64:166–170
Greenlee RT, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA (2000) Cancer statistics, 2000. CA Cancer J Clin 50(1):7–33
Jackson RJ, Fuller GN, Abi-Said D, Lang FF, Gokaslan ZL, Shi WM, Wildrick DM, Sawaya R (2001) Limitations of stereotactic biopsy in the initial management of gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 3:193–200
Jain D, Sharma MC, Sarkar C, Gupta D, Singh M, Mahapatra AK (2006) Comparative analysis of diagnostic accuracy of different brain biopsy procedures. Neurol India 54(4):394–398
Jain D, Sharma MC, Sarkar C, Gupta D, Mahapatra AK (2006) Correlation of diagnostic yield of stereotactic brain biopsy with number of biopsy bits and site of the lesion. Brain Tumor Pathol 23(2):71–75
Khan MK, Hunter GK, Vogelbaum M, Suh JH, Chao ST (2009) Evidence-based adjuvant therapy for gliomas: current concepts and newer developments. Indian J Cancer 46(2):96–107
Kim JE, Kim DG, Paek SH, Jung HW (2003) Stereotactic biopsy for intracranial lesions: reliability and its impact on the planning of treatment. Acta Neurochir 145:547–554
Lefranc M, Monet P, Desenclos C, Peltier J, Fichten A, Toussaint P, Sevestre H, Deramond H, Le Gars D (2012) Perfusion MRI as a neurosurgical tool for improved targeting in stereotactic tumor biopsies. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 90(4):240–247
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK (eds) (2007) World Health Organization classification of tumours of the central nervous system. IARC, Lyon. ISBN 92-832-2430-2
McGirt MJ, Woodworth GF, Coon BSAL, Frazier JM, Amundson E, Garonzik I, Olivi A, Weingart JD (2005) Independent predictors of morbidity after image-guided stereotactic brain biopsy: a risk assessment of 270 cases. J Neurosurg 102:897–901
McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. New York: McGraw-Hill companies (2002) Diagnostic yield http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/diagnostic+yield. Accessed 4 Feb 2014
Mineo JF, Bordron A, Baroncini M, Ramirez C, Maurage CA, Bond S, Dam-Hieu P (2007) Prognosis factors of survival time in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: a multivariate analysis of 340 pathients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 149(3):245–252
Oghaki H, Kleihues P (2005) Epidemiology and etiology of gliomas. Acta Neuropathol 109(1):93–108
Owen CM, Linskey ME (2009) Frame-based stereotaxy in a frameless era: current capabilities, relative role, and the positive- and negative predictive values of blood through the needle. J Neurooncol 93:139–149
Reitheimer T, Lopez WO, Doostkam S, Machein MR, Pinsker MO, Trippel M, Nikkhah G (2013) Intraindividual comparison of histopathological diagnosis obtained by stereotactic serial biopsy to open surgical resection specimen in patients with intracranial tumours. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115(10):1955–1960
Sawin PD, Hitchon PW, Follett KA, Torner JC (1998) Computed imaging-assisted stereotactic brain biopsy: a risk analysis of 225 consecutive cases. Surg Neurol 49:640–649
Schulder M, Spiro D (2011) Intraoperative MRI for stereotactic biopsy. In: Pamir MN, Seifert V, Kiris T (eds) Intraoperative imaging. Acta Neurochir Suppl 109:81–87
Shastri-Hurst N, Tsegave M, Robson DK, Lowe JS, Macarthur DC (2006) Stereotactic brain biopsy: an audit of sampling reliability in a clinical case series. Br J Neurosurg 20(4):222–226
Shooman D, Belli A, Grundy PL (2010) Image-guided stereotactic biopsy without intraoperative neuropathological examination. J Neurosurg 113:170–178
Smith JS, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Barbaro NM, McDermott MW (2005) Frame-based stereotactic biopsy remains an important diagnostic tool with distinct advantages over frameless stereotactic biopsy. J Neurooncol 73:173–179
Widhalm G, Minchev G, Woehrer A, Preusser M, Kiesel B, Furtner J, Mert A, Di Ieva A, Tomanek B, Prayer D, Marosi C, Heinfellner JA, Knosp E, Wolfsberger S (2012) Strong 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced fluorescence is a novel intraoperative marker for representative tissue samples in stereotactic brain tumor biopsies. Neurosurg Rev 35:381–391
Willems PWA, Noordmans HJ, Ramos LMP, Taphoorn MJB, Berkelbach van der Sprenkel JW, Viergever MA, Tulleken CA (2003) Clinical evaluation of stereotactic brain biopsies with an MKM-mounted instrument holder. Acta Neurochir 145:889–897
Woodworth GF, McGirt MJ, Samdani A, Garonzik I, Olivi A, Weingart JD (2006) Frameless image-guided stereotactic brain biopsy procedure: diagnostic yield, surgical morbidity, and comparison with the frame-based technique. J Neurosurg 104:233–237
Woerdeman PA, Willems PW, Noordmans HJ, Tulleken CA, van der Sprenkel JW (2007) Application accuracy in frameless image-guided neurosurgery: a comparison study of three patient-to-image registration methods. J Neurosurg 106(6):1012–1016
Zoeller GK, Benveniste RJ, Landy H, Morcos JJ, Jagid J (2009) Outcome and management strategies after nondiagnostic stereotactic biopsies of brain lesions. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 87(3):174–181
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mrs. A. Hamersma, head of Trialbureau of Radiology, for retrieving archived imaging data.
Conflicts of interest
With the submission of this manuscript I would like to state that the authors report no conflicts of interest concerning the materials and methods used or the findings specified in this paper. Furthermore, the authors declare that this study was performed in accordance with the research ethical guidelines.
Presentation at a conference
This study has not been presented at a conference.
Clinical trial registration number
A clinical trial registration number was not required since the study was conducted with retrospectively obtained data from patient medical files.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khatab, S., Spliet, W. & Woerdeman, P.A. Frameless image-guided stereotactic brain biopsies: emphasis on diagnostic yield. Acta Neurochir 156, 1441–1450 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2145-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2145-2