Abstract
Purpose
Most morphometric studies on lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis (DS) have focused solely on the L4–L5 slipped level, neglecting the shape of the entire lumbar segments. The purpose of this study was to present a morphometric analysis of the entire lumbar IVDs and VBs in DS.
Methods
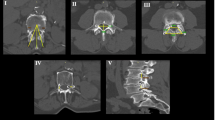
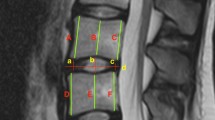
Out of 500 lumbar CTs, the first 100 CTs, 50 with DS at L4 and 50 age- and sex-matched control CTs, were randomly selected. All lumbar IVD and VB heights, widths, lengths and sagittal wedging as well as lumbar lordosis (LL) and sacral inclination (SI) were measured and relevant ratios calculated. The prevalence of lumbar vertebral osteophyte was also measured.
Results
A total of 6700 measurements were taken. Age, height, weight and BMI had no effect on all parameters. Compared with controls, in females with DS, the majority of IVDs were flatter, with increased kyphotic wedging at L1–L2 (Δ1.3°) and L2–L3 (Δ1.8°), turning to lordotic wedging at L3–L4 (Δ5.9°), and decreased lordotic wedging at L4–L5 (Δ2.7°) and L5–S1 (Δ5.3°). The posterior IVD/VB ratio of all lumbar levels, middle IVD/VB ratio of L3–S1 and anterior IVD/VB ratio of L4–S1 were smaller. In males with DS, the L2–L3 IVD manifested more kyphotic wedging (Δ3.8°), the L4 VB wedging was more lordotic (Δ2.4°) and all L4–L5 IVD/VB ratios and L3–L4 middle and posterior IVD/VB ratios were smaller.
Conclusions
Individuals with DS have a more generalized degenerative disc disease on all lumbar vertebral levels, characterized by decreased disc space heights and kyphotic posture of the upper lumbar segments, occurring more predominantly in females than in males with DS.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Markwalder M (1993) Surgical management of neurogenic claudication in 100 patients with lumbar spinal stenosis due to degenerative spondylolisthesis. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 120:136–142
Drury T, Ames SE, Costi K et al (2009) Degenerative spondylolisthesis in patients with neurogenic claudication effects functional performance and self-reported quality of life. Spine 34:2812–2817
Hasegewa K, Kitahara K, Hara T et al (2009) Biomechanical evaluation of segmental instability in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 18:465–470
Hasegawa K, Shimoda H, Kitahara K et al (2011) What are the reliable radiological indicators of lumbar segmental instability? J Bone Joint Surg Br 93:650–657
Jacobsen S, Sonne-Holm S, Rovsing H et al (2007) Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: an epidemiological perspective: the Copenhagen Osteoarthritis Study. Spine 32:120–125
Iguchi T, Wakami T, Kurihara A, et al 9 (2002) Lumbar multilevel degenerative spondylolisthesis: radiological evaluation and factors related to anterolisthesis and retrolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech 15:93–99
Imada K, Matsui H, Tsuji H (1995) Oophorectomy predisposes to degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77:126–130
Hosoe H, Ohmori K (2008) Degenerative lumbosacral spondylolisthesis: possible factors which predispose the fifth lumbar vertebra to slip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:356–359
Barrey C, Jund J, Perrin G et al (2007) Spinopelvic alignment of patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Neurosurgery 61:981–986
Legaye J, Duval-Beaupère G, Hecquet J et al (1998) Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J 7:99–103
Roussouly P, Pinheiro-Franco J (2011) Sagittal parameters of the spine: biomechanical approach. Eur Spine J 20:578–585
Been E, Ling L, Hunter D et al (2011) Geometry of the vertebral bodies and the intervertebral discs in lumbar segments adjacent to spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: pilot study. Eur Spine J 20:1159–1165
Chen I, Wei T (1976) Disc height and lumbar index as independent predictors of degenerative spondylolisthesis in middle-aged women with low back pain. Spine 34:1402–1409
Berlemann U, Jeszenszky DJ, Buhler DW et al (1999) The role of lumbar lordosis, vertebral end-plate inclination, disc height, and facet orientation in degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord 12:68–73
Funao H, Tsuji T, Hosogane N et al (2012) Comparative study of spinopelvic sagittal alignment between patients with and without degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 21:2181–2187
Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Wedge JH, Yong-Hing K et al (1978) Pathology and pathogenesis of lumbar spondylosis and stenosis. Spine 3:319–328
Kalichman L, Kim DH, Li L et al (2009) Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: prevalence and association with low back pain in the adult community-based population. Spine 34:199–205
Sanderson P, Fraser R (1996) The influence of pregnancy on the development of degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 78:951–954
Farfan HF (1980) The pathological anatomy of degenerative spondylolisthesis: a cadaver study. Spine 5:412–418
Rosenberg N (1975) Degenerative spondylolisthesis: Predisposing factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am 57:467–474
Cinotti G, Postacchini F, Fassari F et al (1997) Predisposing factors in degenerative spondylolisthesis. A radiographic and CT study. Int Orthop 21:337–342
Belfi L, Ortiz A, Katz D (2006) Computed tomography evaluation of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in asymptomatic patients. Spine 15:E907–E910
Saint-Louis L (2001) Lumbar spinal stenosis assessment with computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and myelography. Clin Orthop Relat Res 384:122–136
Paul C, Hansen A (1982) computed tomography in spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 6:62–71
Schuller S, Charles Y, Steib J (2011) Sagittal spinopelvic alignment and body mass index in patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 20:713–719
Chen IR, Wei TS (2009) Disc height and lumbar index as independent predictors of degenerative spondylolisthesis in middle-aged women with low back pain. Spine 34:1402–1409
Galbsura F, Schmidt H, Neidliniger-Wilke C et al (2011) The effect of degenerative morphological changes of the intervertebral disc on the lumbar spine biomechanics: a poroelastic finite element investigation. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 14:729–739
Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Berthonnaud E et al (2005) Classification of the normal variation in the sagittal alignment of the human lumbar spine and pelvis in the standing position. Spine 30:346–353
Korez R, Likar B, Pernus F et al (2014) Parametric modeling of the intervertebral disc space in 3D: application to CT images of the lumbar spine. Comput Med Imaging Graph 38:596–605
Merckaert S, Pierzchala K, Kulik G et al (2015) Influence of anatomical variations on lumbar foraminal stenosis pathogenesis. Eur Spine J 24:313–318
Smorgick Y, Mirovsky Y, Fischgrund JS et al (2014) Radiographic predisposing factors for degenerative spondylolisthesis. Orthopedics 37:260–264
Maatta JH, Kraatari M, Wolber L et al (2014) Vertebral endplate change as a feature of intervertebral disc degeneration: a heritability study. Eur Spine J 23:1856–1862
Miao J, Wang S, Park WM et al (2013) Segmental spinal canal volume in patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine J 13:706–712
Dai L (2001) Orientation and tropism of lumbar facet joints in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Int Orthop 25:40–42
Toyone T, Moriya H, Kitahara H, Takahashi K, Yamagata M, Murakami M, Takahashi Y (1993) Assessment of segmental spinal instability using magnetic resonance imaging. In: Yonenobu K, Ono Y, Takemitsu Y (eds) Lumbar fusion and stabilization. Springer- Verlag, Tokyo, pp 35–44
Masharawi Y, Alperovitch-Najenson D, Steinberg N et al (2007) Lumbar facet orientation in spondylolysis: a skeletal study. Spine 6:176–180
Masharawi Y, Peleg S, Nili S et al (2007) Lumbar facet anatomy changes in spondylolysis: a comparative skeletal study. Eur Spine J 16:993–997
Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Morizono Y et al (1990) Natural history of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Pathogenesis and natural course of the slippage. Spine 15:1204–1210
Newman P (1955) Spondylolisthesis, its cause and effect. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 16:305–323
Love T, Fagan A, Fraser R (1999) Degenerative spondylolisthesis developmental or acquired. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81:670–674
Boden S, Riew K, Yamaguchi K et al (1996) Orientation of the lumbar facet joints: association with degenerative disc disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am 78:403–411
Sato K, Wakamatsu E, Yoshizumi A et al (1989) The configuration of the laminas and facet joints in degenerative spondylolisthesis: a clinicoradiologic study. Spine 14:1265–1271
Kalichman L, Suri P, Guermazi A et al (2009) Facet orientation and tropism: associations with facet joint osteoarthritis and degeneratives. Spine 34:E579–E585
Haruki F, Takashi T, Naobumi H et al (2012) Comparative study of spinopelvic sagittal alignment between patients with and without degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 21:2181–2187
Grobler L, Robertson P, Novotny J et al (1993) Etiology of spondylolisthesis. Assessment of the role played by lumbar facet joint morphology. Spine 18:80–91
Anekstein Y, Floman Y, Smorgick Y et al (2015) Seven years follow-up for total lumbar facet joint replacement (TOPS) in the management of lumbar spinal stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 24:2306–2314
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
The authors thank Mrs. Phyllis Curchack Kornspan for her editorial assistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abu-Leil, S., Floman, Y., Bronstein, Y. et al. A morphometric analysis of all lumbar intervertebral discs and vertebral bodies in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 25, 2535–2545 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4673-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4673-3