Abstract
Purpose
To determine the correlation of the difference between postoperative lumbar lordosis (LL) and ideal LL with the sagittal vertical axis (SVA) at the final follow-up in patients with adult spinal deformity (ASD).
Methods
Fifty-one patients with degenerative lumbar kyphosis (DLK) (mean age 66.5 years) who underwent surgical correction with a minimum 2-year follow-up were evaluated. Based on the difference between postoperative LL and ideal LL using the Korean version of Legaye’s formula, we divided the 51 patients into two groups: overcorrection (degree of postoperative LL > ideal LL) and undercorrection (degree of postoperative LL < ideal LL).
Results
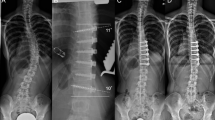
Our clinical series of patients comprised 24 in the overcorrection and 27 in the undercorrection group. No significant differences were found in preoperative pelvic incidence (PI 52.6° vs. 57.3°), sacral slope (SS 23.3° vs. 18.3°), LL (−6.9° vs. −2.3°), thoracic kyphosis (TK 4.7° vs. 4.9°) and SVA (140 vs. 139 mm) except pelvic tilt (PT 29.4° vs. 39.0°), between the two groups. All the patients in the overcorrection group and 16 in the undercorrection group achieved postoperative optimal sagittal balance based on SVA ≤ 50 mm. In addition, significant differences in PT (10.5° vs. 26.7°), SS (42.1° vs. 30.6°), LL (−64.3° vs. −37.1°), TK (22.6° vs. 15.8°), and SVA (−1 vs. 41 mm) between the two groups were observed postoperatively. Furthermore, four patients (16.7 %) in the overcorrection group and eight (50 %) in the undercorrection group had sagittal decompensation at the final follow-up. Our results showed that the difference between postoperative LL and ideal LL had a significant correlation with postoperative and final follow-up SVA in our clinical series.
Conclusion
Overcorrection of LL is an effective treatment modality to maintain optimal sagittal alignment in patients with DLK; this suggests that it should be considered in preoperative planning for patients with ASD with sagittal imbalance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farcy JP, Schwab FJ (1997) Management of flatback and related kyphotic decompensation syndromes. Spine 22:2452–2457
Jackson RP, McManus AC (1994) Radiographic analysis of sagittal plane alignment and balance in standing volunteers and patients with low back pain matched for age, sex, and size. A prospective controlled clinical study. Spine 19:1611–1618
Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Hecquet J, Marty C (1998) Pelvic incidence: a fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur Spine J 7:99–103
Lindh M (1989) Biomechanics of the lumbar spine. In: Nordin M, Frankel VH (eds) Philadelphia
Farfan HF, Huberdeau RM, Dubow HI (1972) Lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration: the influence of geometrical features on the pattern of disc degeneration—a post mortem study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 54:492–510
Bernhardt M, Bridwell KH (1989) Segmental analysis of the sagittal plane alignment of the normal thoracic and lumbar spines and thoracolumbar junction. Spine 14:717–721
Keller TS, Colloca CJ, Harrison DE, Moore RJ, Gunzburg R (2007) Muscular contributions to dynamic dorsoventral lumbar spine stiffness. Eur Spine J 16:245–254
Goel VK, Kong W, Han JS, Weinstein JN, Gilbertson LG (1993) A combined finite element and optimization investigation of lumbar spine mechanics with and without muscles. Spine 18:1531–1541
Lee JH, Kim KT, Suk KS, Lee SH, Jeong BO, Kim JS, Eoh JH, Kim YJ (2010) Analysis of spinopelvic parameters in lumbar degenerative kyphosis: correlation with spinal stenosis and spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:E1386–E1391. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181e88be6
Takemitsu Y, Harada Y, Iwahara T, Miyamoto M, Miyatake Y (1988) Lumbar degenerative kyphosis. Clinical, radiological and epidemiological studies. Spine 13:1317–1326
Jeon CH, Kim DJ, Kim SK, Lee HM, Park HJ (2006) Validation in the cross-cultural adaptation of the Korean version of the oswestry disability index. J Korean Med Sci 21:1092–1097
Cho KJ, Suk SI, Park SR, Kim JH, Kang SB, Kim HS, Oh SJ (2010) Risk factors of sagittal decompensation after long posterior instrumentation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Spine 35:1595–1601. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181bdad89
Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Rhim S, Cheh G (2006) Sagittal thoracic decompensation following long adult lumbar spinal instrumentation and fusion to L5 or S1: causes, prevalence, and risk factor analysis. Spine 31:2359–2366
Videbaek TS, Bunger CE, Henriksen M, Neils E, Christensen FB (2011) Sagittal spinal balance after lumbar spinal fusion: the impact of anterior column support results from a randomized clinical trial with an eight- to thirteen-year radiographic follow-up. Spine 36:183–191. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181cc8fce
Booth KC, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Baldus CR, Blanke KM (1999) Complications and predictive factors for the successful treatment of flatback deformity (fixed sagittal imbalance). Spine 24:1712–1720
Lee CS, Lee CK, Kim YT, Hong YM, Yoo JH (2001) Dynamic sagittal imbalance of the spine in degenerative flat back: significance of pelvic tilt in surgical treatment. Spine 26:2029–2035
Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G (2005) Sagittal plane alignment of the spine and gravity: a radiological and clinical evaluation. Acta Orthop Belg 71:213–220
Vialle R, Levassor N, Rillardon L, Templier A, Skalli W, Guigui P (2005) Radiographic analysis of the sagittal alignment and balance of the spine in asymptomatic subjects. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:260–267
Schwab F, Lafage V, Patel A, Farcy JP (2009) Sagittal plane considerations and the pelvis in the adult patient. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:1828–1833. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a13c08 00007632-200908010-00013 [pii]
Rose PS, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Cronen GA, Mulconrey DS, Buchowski JM, Kim YJ (2009) Role of pelvic incidence, thoracic kyphosis, and patient factors on sagittal plane correction following pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Spine 34:785–791
Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Rhim S, Cheh G (2006) An analysis of sagittal spinal alignment following long adult lumbar instrumentation and fusion to L5 or S1: can we predict ideal lumbar lordosis? Spine 31:2343–2352
Boulay C, Tardieu C, Hecquet J, Benaim C, Mouilleseaux B, Marty C, Prat-Pradal D, Legaye J, Duval-Beaupere G, Pelissier J (2006) Sagittal alignment of spine and pelvis regulated by pelvic incidence: standard values and prediction of lordosis. Eur Spine J 15:415–422. doi:10.1007/s00586-005-0984-5
Lonner BS, Auerbach JD, Sponseller P, Rajadhyaksha AD, Newton PO (2010) Variations in pelvic and other sagittal spinal parameters as a function of race in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 35:E374–E377. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181bb4f96
Lee CS, Chung SS, Kang KC, Park SJ, Shin SK (2011) Normal patterns of sagittal alignment of the spine in young adults radiological analysis in a Korean population. Spine 36:E1648–E1654. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318216b0fd
Mac-Thiong JM, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, Guigui P (2011) Age- and sex-related variations in sagittal sacropelvic morphology and balance in asymptomatic adults. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):572–577. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1923-2
Zhu Z, Sha S, Liu Z, Sun X, Jiang L, Yan H, Qian B, Qiu Y (2014) Sagittal spinopelvic alignment in adolescent thoracic scoliosis secondary to Chiari I malformation: a comparison between the left and the right curves. Eur Spine J 23:226–233. doi:10.1007/s00586-013-2980-5
Lee CS, Chung SS, Park SJ, Kim DM, Shin SK (2014) Simple prediction method of lumbar lordosis for planning of lumbar corrective surgery: radiological analysis in a Korean population. Eur Spine J 23:192–197. doi:10.1007/s00586-013-2895-1
Lee CS, Chung SS, Shin SK, Park JC, Kang KJ (2009) Analysis of surgical correction in lumbar degenerative kyphosis. The 26th fall congress. The Korean Society of spine surgery
Jang JS, Lee SH, Min JH, Han KM (2007) Lumbar degenerative kyphosis: radiologic analysis and classifications. Spine 32:2694–2699
Horton WC, Brown CW, Bridwell KH, Glassman SD, Suk SI, Cha CW (2005) Is there an optimal patient stance for obtaining a lateral 36” radiograph? A critical comparison of three techniques. Spine 30:427–433
Glattes RC, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Kim YJ, Rinella A, Edwards C 2nd (2005) Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity following long instrumented posterior spinal fusion: incidence, outcomes, and risk factor analysis. Spine 30:1643–1649
Glassman SD, Berven S, Bridwell K, Horton W, Dimar JR (2005) Correlation of radiographic parameters and clinical symptoms in adult scoliosis. Spine 30:682–688
Ondra SL, Marzouk S, Koski T, Silva F, Salehi S (2006) Mathematical calculation of pedicle subtraction osteotomy size to allow precision correction of fixed sagittal deformity. Spine 31:E973–E979
Smith JS, Bess S, Shaffrey CI, Burton DC, Hart RA, Hostin R, Klineberg E (2012) Dynamic changes of the pelvis and spine are key to predicting postoperative sagittal alignment after pedicle subtraction osteotomy: a critical analysis of preoperative planning techniques. Spine 37:845–853. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31823b0892
Lafage V, Ames C, Schwab F, Klineberg E, Akbarnia B, Smith J, Boachie-Adjei O, Burton D, Hart R, Hostin R, Shaffrey C, Wood K, Bess S (2012) Changes in thoracic kyphosis negatively impact sagittal alignment after lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy: a comprehensive radiographic analysis. Spine 37:E180–E187. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318225b926
Blondel B, Schwab F, Bess S, Ames C, Mummaneni PV, Hart R, Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Burton D, Boachie-Adjei O, Lafage V (2013) Posterior global malalignment after osteotomy for sagittal plane deformity: it happens and here is why. Spine 38:E394–E401. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182872415
Gottfried ON, Daubs MD, Patel AA, Dailey AT, Brodke DS (2009) Spinopelvic parameters in postfusion flatback deformity patients. Spine J 9:639–647. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2009.04.008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JH., Kim, KT., Lee, SH. et al. Overcorrection of lumbar lordosis for adult spinal deformity with sagittal imbalance: comparison of radiographic outcomes between overcorrection and undercorrection. Eur Spine J 25, 2668–2675 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4441-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4441-4