Abstract
Background
To explore the potential application of placenta-specific PLAC1/Cancer Placenta (CP) 1 antigen for immunotherapy in CRC patients, further identification of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes from this antigen is necessary.
Methods
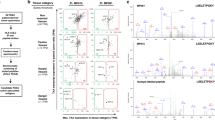
We assessed the protein expression of PLAC1/CP1 using a tissue chip and immunochemistry staining in CRC samples. Simultaneously, we predicted four PLAC1/CP1-derived HLA-A*0201-restricted peptides by using reverse immunology methods. Peptide-specific CD8+ T cell responses were assessed by an IFN-γ release ELISPOT assay. Effector CD8+ T cells lyse HLA-A*0201 CRC cell line SW620 was detected in a granzyme-B release ELISPOT cytotoxicity assay.
Results
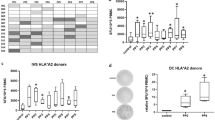
Our results indicated that PLAC1/CP1 was highly expressed in 56.7 % (55/97) of adenocarcinomas. PLAC1/CP1 protein expression was associated with CRC tumor differentiation, the tumor/node/metastasis stage, and lymph node metastasis. Two of four peptides showed high affinities in an HLA-A2 binding assay. In 66.7 % (6/9) of peripheral blood mononuclear cells of CRC samples with PLAC1/CP1 protein-positive expression, these two peptides, PLAC1/CP1 p41-50 (FMLNNDVCV) and PLAC1/CP1 p69-77 (HAYQFTYRV), were immunogenic in the induction of peptide-specific CD8+ T cell responses as assessed by an IFN-γ release ELISPOT assay. Furthermore, the generated effector CD8+ T cells could specifically lyse the PLAC1/CP1 HLA-A*0201 CRC cell line SW620 in a granzyme-B release ELISPOT cytotoxicity assay.
Conclusions
These results show that the PLAC1/CP1 antigen is a possible prognostic marker of CRC and that PLAC1/CP1 p41-50 and PLAC1/CP1 p69-77 are novel HLA-A*0201-restricted CD8+ T cell epitopes and potential targets for peptide-based immunotherapy in CRC patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Platsoucas CD, Fincke JE, Pappas J, Jung WJ, Heckel M, Schwarting R, et al. Immune responses to human tumors: development of tumor vaccines. Anticancer Res. 2003;23:1969–96.
Boon T, Coulie PG, Van den Eynde BJ, van der Bruggen P. Human T cell responses against melanoma. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:175–208.
Noguchi M, Kobayashi K, Suetsugu N, Tomiyasu K, Suekane S, Yamada A, et al. Induction of cellular and humoral immune responses to tumor cells and peptides in HLA-A24 positive hormone-refractory prostate cancer patients by peptide vaccination. Prostate. 2003;57:80–92.
Uemura H, Fujimoto K, Tanaka M, Yoshikawa M, Hirao Y, Uejima S, et al. A phase I trial of vaccination of CA9-derived peptides for HLA-A24-positive patients with cytokine-refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:1768–75.
Yajima N, Yamanaka R, Mine T, Tsuchiya N, Homma J, Sano M, et al. Immunologic evaluation of personalized peptide vaccination for patients with advanced malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:5900–11.
Scanlan MJ, Gure AO, Jungbluth AA, Old LJ, Chen YT. Cancer/testis antigens: an expanding family of targets for cancer immunotherapy. Immunol Rev. 2002;188:22–32.
Chen Q, Jackson H, Parente P, Luke T, Rizkalla M, Tai TY, et al. Immunodominant CD4+ responses identified in a patient vaccinated with full-length NY-ESO-1 formulated with ISCOMATRIX adjuvant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:9363–8.
Davis ID, Chen W, Jackson H, Parente P, Shackleton M, Hopkins W, et al. Recombinant NY-ESO-1 protein with ISCOMATRIX adjuvant induces broad integrated antibody and CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell responses in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:10697–702.
Van Baren N, Bonnet MC, Dréno B, Khammari A, Dorval T, Piperno-Neumann S, et al. Tumoral and immunologic response after vaccination of melanoma patients with an ALVAC virus encoding MAGE antigens recognized by T cells. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:9008–21.
Scanlan MJ, Simpson AJ, Old LJ. The cancer/testis genes: review, standardization, and commentary. Cancer Immunity. 2004;4:1.
Nagorsen D, Thiel E. Clinical and immunologic responses to active specific cancer vaccines in human colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:3064–9.
Liu FF, Dong XY, Pang XW, Xing Q, Wang HC, Zhang HG, et al. The specific immune response to tumor antigen CP1 and its correlation with improved survival in colon cancer patients. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:998–1006.
Mizukoshi E, Nakamoto Y, Marukawa Y, Arai K, Yamashita T, Tsuji H, et al. Cytotoxic T cell responses to human telomerase reverse transcriptase in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2006;43:1284–94.
Jackman SM, Kong X, Fant ME. Plac1 (placenta-specific 1) is essential for normal placental and embryonic development. Mol Reprod Dev. 2012;79:564–72.
Liu W, Zhai M, Wu Z, Qi Y, Wu Y, Dai C, et al. Identification of a novel HLA-A2-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope from cancer-testis antigen PLAC1 in breast cancer. Amino Acids. 2012;42:2257–65.
Koslowske M, Sahin U, Mitnacht-Kraus R, Seitz G, Huber C, Türeci O. A placenta specific gene ectopically activated in many human cancers is essentially involved in malignant cell processes. Cancer Res. 2007;67:9528–34.
Maeurer MJ, Martin D, Elder E, Storkus WJ, Lotze MT. Detection of naturally processed and HLA-A1-presented melanoma T-cell epitopes defined by CD8 (+) T-cells’ release of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor but not by cytolysis. Clin Cancer Res. 1996;2:87–95.
Nakatsuka K, Sugiyama H, Nakagawa Y, Takahashi H. Purification of antigenic peptide from murine hepatoma cells recognized by Class-I major histocompatibility complex molecule-restricted cytotoxic T-lymphocytes induced with B7-1-gene-transfected hepatoma cells. J Hepatol. 1999;30:1119–29.
Brichard V, Van Pel A, Wölfel T, Wölfel C, De Plaen E, Lethé B, et al. The tyrosinase gene codes for an antigen recognized by autologous cytolytic T lymphocytes on HLA-A2 melanomas. J Exp Med. 1993;178:489–95.
Kawakami Y, Eliyahu S, Delgado CH, Robbins PF, Rivoltini L, Topalian SL, et al. Cloning of the gene coding for a shared human melanoma antigen recognized by autologous T cells infiltrating into tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:3515–9.
Beattie T, Kaul R, Rostron T, Dong T, Easterbrook P, Jaoko W, et al. Screening for HIV-specific T-cell responses using overlapping 15-mer peptide pools or optimized epitopes. AIDS. 2004;18:1595–8.
Acknowledgments
This article supported by grants from the National Natural Science Fund of China (No. 30801093).
Conflict of interest
All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript. No potential conflicts do exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. Liu and H. Zhang contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Zhang, H., Shen, D. et al. Identification of two new HLA-A*0201-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes from colorectal carcinoma-associated antigen PLAC1/CP1. J Gastroenterol 49, 419–426 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0811-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-013-0811-4