Abstract
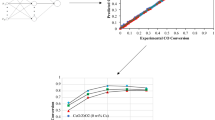
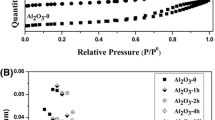
This paper presents an artificial neural network (ANN) for modeling the relationship between catalyst composition and catalytic performance in the NH3-SCR of NO process. The supported catalysts with different transition metals (Mn, Fe, Co and Cu) and (γ-Al2O3, ZSM5 and SAPO-34) supports were prepared and tested in NH3–NO-SCR reaction to generate required data for neural network development. The ANN was constructed using the experimental dataset, and all the data were integrated using support and metal atomic descriptors for the construction of general catalyst design model. The statistical analysis of the results indicated that the R 2 values for the training and test data were high, more than 0.9, and this indicates that ANN-based model developed in this work can predict catalyst performance correctly. More evaluation of the obtained model revealed that metal has more influence than support on catalyst activity at supported catalysts.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forzatti P (2001) Present status and perspectives in de-NO x SCR catalysis. J Appl Catal A 222(1):221–236
ACEA (2003) Final report on selective catalytic reduction. http://europa.eu.int/comm/enterprise/automotive/mveg_meetings/meeting94/scr_paper_final.pdf
Koebel M, Strutz EO (2003) Thermal and hydrolytic decomposition of urea for automotive selective catalytic reduction systems: thermochemical and practical aspects. Ind Eng Chem Res 42(10):2093–2100
Sjövall H, Olsson L, Fridell E, Blint RJ (2006) Selective catalytic reduction of NO x with NH3 over Cu-ZSM-5—the effect of changing the gas composition. J Appl Catal B 64(3):180–188
Chmielarz L, Kuśtrowski P, Zbroja M, Rafalska-Łasocha A, Dudek B, Dziembaj R (2003) SCR of NO by NH3 on alumina or titania-pillared montmorillonite various modified with Cu or Co: part I. General characterization and catalysts screening. J Appl Catal B 45(2):103–116
Liu Q, Liu Z, Su J (2010) Al2O3-coated cordierite honeycomb supported CuO catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3: surface properties and reaction mechanism. Catal Today 158(3–4):370–376
Panahi PN, Salari D, Niaei A, Mousavi S (2013) NO reduction over nanostructure M-Cu/ZSM-5 (M: Cr, Mn, Co and Fe) bimetallic catalysts and optimization of catalyst preparation by RSM. J Ind Eng Chem 19(6):1793–1799
Irfan MF, Goo JH, Kim SD (2008) Co3O4 based catalysts for NO oxidation and NO x reduction in fast SCR process. J Appl Catal B 78(3):267–274
Iwasaki M, Yamazaki K, Shinjoh H (2011) NO x reduction performance of fresh and aged Fe-zeolites prepared by CVD: effects of zeolite structure and Si/Al2 ratio. J Appl Catal B 102(1–2):302–309. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.12.016
Mousavi SM, Niaei A, Illán Gómez MJ, Salari D, Nakhostin Panahi P, Abaladejo-Fuentes V (2014) Characterization and activity of alkaline earth metals loaded CeO2–MO x (M = Mn, Fe) mixed oxides in catalytic reduction of NO. Mater Chem Phys 143(3):921–928. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.09.017
Mousavi SM, Salari D, Niaei A, Nakhostin Panahi P, Shafiei S (2014) A modelling study and optimization of catalytic reduction of NO over CeO2–MnO x (0.25)–Ba mixed oxide catalyst using design of experiments. Environ Technol 35(5):581–589. doi:10.1080/09593330.2013.837964
Clark JY, Warwick K (1998) Artificial keys for botanical identification using a multilayer perceptron neural network (MLP). Artif Intell Rev 12(1–3):95–115
Brace C (1998) Prediction of diesel engine exhaust emissions using artificial neural networks. In: IMechE Seminar S591, neural networks in systems design
Huang K, Chen F-Q, Lü D-W (2001) Artificial neural network-aided design of a multi-component catalyst for methane oxidative coupling. J Appl Catal A 219(1–2):61–68. doi:10.1016/S0926-860X(01)00659-7
Izadkhah B, Nabavi S, Niaei A, Salari D, Mahmuodi Badiki T, Çaylak N (2012) Design and optimization of Bi-metallic Ag-ZSM5 catalysts for catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds. J Ind Eng Chem 18(6):2083–2091
Gevrey M, Dimopoulos I, Lek S (2003) Review and comparison of methods to study the contribution of variables in artificial neural network models. Ecol Model 160(3):249–264
Oliveira MLM, Silva CM, Moreno-Tost R, Farias TL, Jiménez-López A, Rodríguez-Castellón E (2011) Modelling of NO x emission factors from heavy and light-duty vehicles equipped with advanced aftertreatment systems. Energy Convers Manag 52(8–9):2945–2951. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2011.02.025
de Oliveira MLM, Silva CM, Moreno-Tost R, Farias TL, Jiménez-López A, Rodríguez-Castellón E (2009) Simulation of SCR equipped vehicles using iron-zeolite catalysts. J Appl Catal A 366(1):13–21. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2009.06.020
Oliveira MLM, Silva CM, Moreno-Tost R, Farias TL, Jiménez-López A, Rodríguez-Castellón E (2009) A study of copper-exchanged mordenite natural and ZSM-5 zeolites as SCR–NO x catalysts for diesel road vehicles: simulation by neural networks approach. J Appl Catal B 88(3–4):420–429. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.10.015
Choudhary VR, Dumbre DK (2009) Magnesium oxide supported nano-gold: a highly active catalyst for solvent-free oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde by TBHP. Catal Commun 10(13):1738–1742. doi:10.1016/j.catcom.2009.05.020
Beale R, Jackson T (1990) Introduction to neural networks. Adam Hilger Ed., Bristol
Holeňa M, Baerns M (2003) Feedforward neural networks in catalysis: a tool for the approximation of the dependency of yield on catalyst composition, and for knowledge extraction. Catal Today 81(3):485–494
Sasaki M, Hamada H, Kintaichi Y, Ito T (1995) Application of a neural network to the analysis of catalytic reactions Analysis of NO decomposition over Cu/ZSM-5 zeolite. J Appl Catal A 132(2):261–270
Hormik K, Stinchcombe H, White H (1989) Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw 2:359–366
Molga E (2003) Neural network approach to support modelling of chemical reactors: problems, resolutions, criteria of application. Chem Eng Process 42(8):675–695
Günay ME, Yıldırım R (2008) Neural network aided design of Pt-Co-Ce/Al2O3 catalyst for selective CO oxidation in hydrogen-rich streams. Chem Eng J 140(1–3):324–331. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2007.09.047
Wang J, Yu T, Wang X, Qi G, Xue J, Shen M, Li W (2012) The influence of silicon on the catalytic properties of Cu/SAPO-34 for NO x reduction by ammonia-SCR. J Appl Catal B 127:137–147. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.08.016
Ertl G, Knozinger H, Schuth F, Weitkamp J (2014) Handbook of heterogeneous catalysis. Wiley Online Library, Hoboken
www.webelements.com (11.3.2014)
Kröcher O, Devadas M, Elsener M, Wokaun A, Söger N, Pfeifer M, Demel Y, Mussmann L (2006) Investigation of the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 on Fe-ZSM5 monolith catalysts. J Appl Catal B 66(3):208–216
Garson GD (1991) Interpreting neural-network connection weights. AI Expert 6:47–51
Sultana A, Nanba T, Haneda M, Hamada H (2009) SCR of NO x with NH3 over Cu/NaZSM-5 and Cu/HZSM-5 in the presence of decane. Catal Commun 10(14):1859–1863
Sultana A, Nanba T, Sasaki M, Haneda M, Suzuki K, Hamada H (2011) Selective catalytic reduction of NO x with NH3 over different copper exchanged zeolites in the presence of decane. Catal Today 164(1):495–499
Tang X, Hao J, Xu W, Li J (2007) Low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO x with NH3 over amorphous MnO x catalysts prepared by three methods. Catal Commun 8(3):329–334
Park TS, Jeong SK, Hong SH, Hong SC (2001) Selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with NH3 over natural manganese ore at low temperature. Ind Eng Chem Res 40(21):4491–4495
Niaei A, Badiki TM, Nabavi SR, Salari D, Izadkhah B, Çaylak N (2013) Neuro-genetic aided design of modified H-ZSM-5 catalyst for catalytic conversion of methanol to gasoline range hydrocarbons. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 44(2):247–256. doi:10.1016/j.jtice.2012.11.008
Fedeyko JM, Chen B, Chen H-Y (2010) Mechanistic study of the low temperature activity of transition metal exchanged zeolite SCR catalysts. Catal Today 151(3):231–236
Busca G, Lietti L, Ramis G, Berti F (1998) Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NO x by ammonia over oxide catalysts: a review. J Appl Catal B 18(1):1–36
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support from University of Tabriz and Iranian Nanotechnology Initiative.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakhostin Panahi, P., Niaei, A., Tseng, HH. et al. Modeling of catalyst composition–activity relationship of supported catalysts in NH3–NO-SCR process using artificial neural network. Neural Comput & Applic 26, 1515–1523 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1781-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1781-z