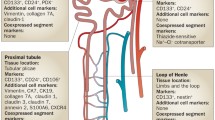
Abstract
Nephropathies arise from conditions that alter nephron development or trigger nephron damage during neonatal, juvenile, and adult stages of life. Much evidence suggests that a key role in maintaining kidney integrity, homeostasis, and regenerative capacity is played by a population of progenitor cells resident in the organ. Although the primary goals in the field of renal progenitor cells are understanding their ability to regenerate nephrons and to restore damaged kidney function, the discovery of these cells could also be used to elucidate the molecular and pathophysiological basis of kidney diseases. As a result, once the identification of a subset of progenitor cells capable of kidney regeneration has been obtained, the increasing knowledge about their characteristics and about the mechanisms of renal development had pointed out the possibility of understanding the molecular basis of kidney diseases, so that, nowadays, some renal disorders could also be related to renal progenitor dysfunction. In this review, we summarize the evidence on the existence of renal progenitors in fetal and adult kidneys and discuss their role in physiology as well as in the pathogenesis of renal disorders with a particular focus on childhood age.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Romagnani P (2010) From Proteus to Prometeus: learning from fish to modulate regeneration. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:726–728
Shahragim T (2009) Stem cell: what’s in the name? Nat Rep Stem Cells. doi:10.1038/stemcells.2009.90
Romagnani P, Lasagni L, Remuzzi G (2013) Renal progenitors: an evolutionary conserved strategy for kidney regeneration. Nat Rev Nephrol 9(3):137–146
Mc Campbell KK, Wingert RA (2012) Renal stem cells: fact or science fiction? Biochem J 444:153–168
Dressler GR (2006) The cellular basis of kidney development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:509–529
Schedl A (2007) Renal abnormalities and their developmental origin. Nat Rev Genet 8:791–802
Kobayashi A, Valerius MT, Mugford JW, Carroll TJ, Self M, Oliver G, McMahon AP (2008) Six2 defines and regulates a multipotent self-renewing nephron progenitor population throughout mammalian kidney development. Cell Stem Cell 3(2):169–181
Barker N, Rookmaaker MB, Kujala P, Ng A, Leushacke M, Snippert H, van de Wetering M, Tan S, Van Es JH, Huch M, Poulsom R, Verhaar MC, Peters PJ, Clevers H (2012) Lgr5(+ve) stem/progenitor cells contribute to nephron formation during kidney development. Cell Rep 2(3):540–552
Bhat PV, Manolescu DC (2008) Role of vitamin A in determining nephron mass and possible relationship to hypertension. J Nutr 138(8):1407–1410
Bertram JF, Douglas-Denton RN, Diouf B, Hughson MD, Hoy WE (2011) Human nephron number: implications for health and disease. Pediatr Nephrol 26:1529–1533
Lazzeri E, Crescioli C, Ronconi E, Mazzinghi B, Sagrinati C, Netti GS, Angelotti ML, Parente E, Ballerini L, Cosmi L, Maggi L, Gesualdo L, Rotondi M, Annunziato F, Maggi E, Lasagni L, Serio M, Romagnani S, Vannelli GB, Romagnani P (2007) Regenerative potential of embryonic renal multipotent progenitors in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 18(12):3128–3138
Sagrinati C, Netti GS, Mazzinghi B, Lazzeri E, Liotta F, Frosali F, Ronconi E, Meini C, Gacci M, Squecco R, Carini M, Gesualdo L, Francini F, Maggi E, Annunziato F, Lasagni L, Serio M, Romagnani S, Romagnani P (2006) Isolation and characterization of multipotent progenitor cells from the Bowman’s capsule of adult human kidneys. J Am Soc Nephrol 17(9):2443–2456
Ronconi E, Sagrinati C, Angelotti ML, Lazzeri E, Mazzinghi B, Ballerini L, Parente E, Becherucci F, Gacci M, Carini M, Maggi E, Serio M, Vannelli GB, Lasagni L, Romagnani S, Romagnani P (2009) Regeneration of glomerular podocytes by human renal progenitors. J Am Soc Nephrol 20(2):322–332
Appel D, Kershaw DB, Smeets B, Yuan G, Fuss A, Frye B, Elger M, Kriz W, Floege J, Moeller MJ (2009) Recruitment of podocytes from glomerular parietal epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 20(2):333–343
Angelotti ML, Ronconi E, Ballerini L, Peired A, Mazzinghi B, Sagrinati C, Parente E, Gacci M, Carini M, Rotondi M, Fogo AB, Lazzeri E, Lasagni L, Romagnani P (2012) Characterization of renal progenitors committed toward tubular lineage and their regenerative potential in renal tubular injury. Stem Cells 30(8):1714–1725
Romagnani P (2009) Toward the identification of a “renopoietic system”? Stem Cells 27(9):2247–2253
Mazzinghi B, Ronconi E, Lazzeri E, Sagrinati C, Ballerini L, Angelotti ML, Parente E, Mancina R, Netti GS, Becherucci F, Gacci M, Carini M, Gesualdo L, Rotondi M, Maggi E, Lasagni L, Serio M, Romagnani S, Romagnani P (2008) Essential but differential role for CXCR4 and CXCR7 in the therapeutic homing of human renal progenitor cells. J Exp Med 205(2):479–490
Sanna-Cherchi S, Caridi G, Weng PL, Scolari F, Perfumo F, Gharavi AG, Ghiggeri GM (2007) Genetic approaches to human renal agenesis/hypoplasia and dysplasia. Pediatr Nephrol 22(10):1675–1684
Davies JA, Fisher CE (2002) Genes and proteins in renal development. Exp Nephrol 10:102–113
Zhang Z, Iglesias D, Eliopoulos N, El Kares R, Chu L, Romagnani P, Goodyer P (2011) A variant OSR1 allele which disturbs OSR1 mRNA expression in renal progenitor cells is associated with reduction of newborn kidney size and function. Hum Mol Genet 20(21):4167–4174
McCarroll MN, Lewis ZR, Culbertson MD, Martin BL, Kimelman D, Nechiporuk AV (2012) Graded levels of Pax2a and Pax8 regulate cell differentiation during sensory placode formation. Development 139(15):2740–2750
Kochhar A, Fischer SM, Kimberling WJ, Smith RJ (2007) Branchio-oto-renal syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 143A(14):1671–1678
Aboudehen K, Hilliard S, Saifudeen Z, El-Dahr SS (2012) Mechanisms of p53 activation and physiological relevance in the developing kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 302(8):F928–F940
Ahn SY, Kim Y, Kim ST, Swat W, Miner JH (2013) Scaffolding proteins DLG1 and CASK cooperate to maintain the nephron progenitor population during kidney development. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:1127–1138
Park JS, Valerius MT, McMahon AP (2007) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulates nephron induction during mouse kidney development. Development 134:2533–2539
Grouls S, Iglesias DM, Wentzensen N, Moeller MJ, Bouchard M, Kemler R, Goodyer P, Niggli F, Gröne HJ, Kriz W, Koesters R (2012) Lineage specification of parietal epithelial cells requires β-catenin/Wnt signaling. J Am Soc Nephrol 23(1):63–72
Wang Q, Lan Y, Cho ES, Maltby KM, Jiang R (2005) Odd-skipped related 1 (Odd 1) is an essential regulator of heart and urogenital. Dev Biol 288:582–594
Chai OH, Song CH, Park SK, Kim W, Cho ES (2013) Molecular regulation of kidney development. Anat Cell Biol 46(1):19–31
Black MJ, Sutherland MR, Gubhaju L, Kent AL, Dahlstrom JE, Moore L (2013) When birth comes early: effects on nephrogenesis. Nephrology 18(3):180–182
Schreuder MF (2012) Safety in glomerular numbers. Pediatr Nephrol 27(10):1881–1887
Makrakis J, Zimanyi MA, Black MJ (2007) Retinoic acid enhances nephron endowment in rats exposed to maternal protein restriction. Pediatr Nephrol 22:1861–1867
Lelièvre-Pégorier M, Vilar J, Ferrier ML, Moreau E, Freund N, Gilbert T, Merlet-Bénichou C (1998) Mild vitamin A deficiency leads to inborn nephron deficit in the rat. Kidney Int 54(5):1455–1462
Batourina E, Gim S, Bello N, Shy M, Clagett-Dame M, Srinivas S, Costantini F, Mendelsohn C (2001) Vitamin A controls epithelial/mesenchymal interactions through Ret expression. Nat Genet 27(1):74–78
Wingert RA, Selleck R, Yu J, Song HD, Chen Z, Song A, Zhou Y, Thisse B, Thisse C, McMahon AP, Davidson AJ (2007) The cdx genes and retinoic acid control the positioning and segmentation of the zebrafish pronephros. PLoS Genet 3(10):1922–1938
Vaughan MR, Pippin JW, Griffin SV, Krofft R, Fleet M, Haseley L, Shankland SJ (2005) ATRA induces podocyte differentiation and alters nephrin and podocin expression in vitro and in vivo. Kidney Int 68(1):133–144
Zhang J, Pippin JW, Vaughan MR, Krofft RD, Taniguchi Y, Romagnani P, Nelson PJ, Liu ZH, Shankland SJ (2012) Retinoids augment the expression of podocyte proteins by glomerular parietal epithelial cells in experimental glomerular disease. Nephron Exp Nephrol 121(1–2):e23–e37
Walkley CR, Olsen GH, Dworkin S, Fabb SA, Swann J, McArthur GA, Westmoreland SV, Chambon P, Scadden DT, Purton LE (2007) A microenvironment-induced myeloproliferative syndrome caused by retinoic acid receptor gamma deficiency. Cell 129(6):1097–1110
Young NS, Maciejewski J (1997) The pathophysiology of acquired aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med 336(19):1365–1372
Smeets B, Angelotti ML, Rizzo P, Dijkman H, Lazzeri E, Mooren F, Ballerini L, Parente E, Sagrinati C, Mazzinghi B, Ronconi E, Becherucci F, Benigni A, Steenbergen E, Lasagni L, Remuzzi G, Wetzels J, Romagnani P (2009) Renal progenitor cells contribute to hyperplastic lesions of podocytopathies and crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 20(12):2593–2603
Smeets B, Uhlig S, Fuss A, Mooren F, Wetzels JF, Floege J, Moeller MJ (2009) Tracing the origin of glomerular extracapillary lesions from parietal epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 20(12):2604–2615
Ryu M, Migliorini A, Miosge N, Gross O, Shankland S, Brinkkoetter PT, Hagmann H, Romagnani P, Liapis H, Anders HJ (2012) Plasma leakage through glomerular basement membrane ruptures triggers the proliferation of parietal epithelial cells and crescent formation in non-inflammatory glomerular injury. J Pathol. doi:10.1002/path.4046
Sicking EM, Fuss A, Uhlig S, Jirak P, Dijkman H, Wetzels J, Engel DR, Urzynicok T, Heidenreich S, Kriz W, Kurts C, Ostendorf T, Floege J, Smeets B, Moeller MJ (2012) Subtotal ablation of parietal epithelial cells induces crescent formation. J Am Soc Nephrol 23(4):629–640
Smeets B, Kuppe C, Sicking EM, Fuss A, Jirak P, van Kuppevelt TH, Endlich K, Wetzels JF, Gröne HJ, Floege J, Moeller MJ (2011) Parietal epithelial cells participate in the formation of sclerotic lesions in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(7):1262–1274
Wharram BL, Goyal M, Wiggins JE, Sanden SK, Hussain S, Filipiak WE, Saunders TL, Dysko RC, Kohno K, Holzman LB, Wiggins RC (2005) Podocyte depletion causes glomerulosclerosis: diphtheria toxin-induced podocyte depletion in rats expressing human diphtheria toxin receptor transgene. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(10):2941–2952
Peti-Peterdi J, Sipos A (2010) A high-powered view of the filtration barrier. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1835–1841
Shankland SJ, Anders HJ, Romagnani P (2013) Glomerular parietal epithelial cells in kidney physiology, pathology, and repair. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. doi:10.1097/MNH.0b013e32835fefd4
Lasagni L, Ballerini L, Angelotti ML, Parente E, Sagrinati C, Mazzinghi B, Peired A, Ronconi E, Becherucci F, Bani D, Gacci M, Carini M, Lazzeri E, Romagnani P (2010) Notch activation differentially regulates renal progenitors proliferation and differentiation toward the podocyte lineage in glomerular disorders. Stem Cells 28(9):1674–1685
Lasagni L, Lazzeri E, Shankland SJ, Anders HJ, Romagnani P (2013) Podocyte mitosis—a catastrophe. Curr Mol Med 13(1):13–23
Darisipudi MN, Kulkarni OP, Sayyed SG, Ryu M, Migliorini A, Sagrinati C, Parente E, Vater A, Eulberg D, Klussmann S, Romagnani P, Anders HJ (2011) Dual blockade of the homeostatic Chemokine CXCL12 and the proinflammatory Chemokine CCL2 has additive protective effects on diabetic kidney disease. Am J Pathol 179(1):116–124
Ohtaka A, Ootaka T, Sato H, Soma J, Sato T, Saito T, Ito S (2002) Significance of early phenotypic change of glomerular podocytes detected by Pax2 in primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Am J Kidney Dis 39(3):475–485
Fatima H, Moeller MJ, Smeets B, Yang HC, D’Agati VD, Alpers CE, Fogo AB (2012) Parietal epithelial cell activation marker in early recurrence of FSGS in the transplant. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7(11):1852–1858
Hodgin JB, Borczuk AC, Nasr SH, Markowitz GS, Nair V, Martini S, Eichinger F, Vining C, Berthier CC, Kretzler M, D’Agati VD (2010) A molecular profile of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. Am J Pathol 177(4):1674–1686
Peired A, Angelotti ML, Ronconi E, la Marca G, Mazzinghi B, Sisti A, Lombardi D, Giocaliere E, Della Bona M, Villanelli F, Parente E, Ballerini L, Sagrinati C, Wanner N, Huber TB, Liapis H, Lazzeri E, Lasagni L, Romagnani P (2013) Proteinuria impairs podocyte regeneration by sequestering retinoic acid. J Am Soc Nephrol 24(11):1756–1768
Pode-Shakked N, Dekel B (2011) Wilms tumor–a renal stem cell malignancy? Pediatr Nephrol 26(9):1535–1543
Pode-Shakked N, Shukrun R, Mark-Danieli M, Tsvetkov P, Bahar S, Pri-Chen S, Goldstein RS, Rom-Gross E, Mor Y, Fridman E, Meir K, Simon A, Magister M, Kaminski N, Goldmacher VS, Harari-Steinberg O, Dekel B (2013) The isolation and characterization of renal cancer initiating cells from human Wilms tumour xenografts unveils new therapeutic targets. EMBO Mol Med 5(1):18–37
Lindgren D, Boström AK, Nilsson K, Hansson J, Sjölund J, Möller C, Jirström K, Nilsson E, Landberg G, Axelson H, Johansson ME (2011) Isolation and characterization of progenitor-like cells from human renal proximal tubules. Am J Pathol 178(2):828–837
Romagnani P (2011) Family portrait: renal progenitor of Bowman’s capsule and its tubular brothers. Am J Pathol 178(2):490–493
Romagnani P (2013) Of mice and men: the riddle of tubular regeneration. J Pathol 229:641–644
Smeets B, Boor P, Dijkman H, Sharma SV, Jirak P, Mooren F, Berger K, Bornemann J, Gelman IH, Floege J, van der Vlag J, Wetzels JF, Moeller MJ (2013) Proximal tubular cells contain a phenotypically distinct, scattered cell population involved in tubular regeneration. J Pathol 229(5):645–659
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becherucci, F., Lazzeri, E., Lasagni, L. et al. Renal progenitors and childhood: from development to disorders. Pediatr Nephrol 29, 711–719 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2686-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2686-2