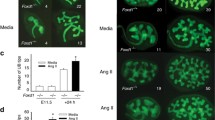
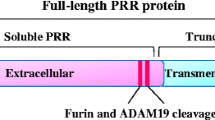
Abstract
The renin–angiotensin system (RAS) plays a critical role in kidney development. Mutations in the genes encoding components of the RAS cause a spectrum of congenital abnormalities of the kidney and renal collecting system, ranging from hypoplasia of the renal medulla and hydronephrosis in mice to renal tubular dysgenesis in humans. However, the mechanisms by which an intact RAS controls proper renal system development and how aberrations in the RAS result in abnormal kidney and renal collecting system development are poorly understood. The renal collecting system originates from the ureteric bud (UB). A number of transcription and growth factors regulate UB branching morphogenesis to ultimately form the ureter, pelvis, calyces, medullary, and cortical collecting ducts. Importantly, UB morphogenesis is a key developmental process that controls organogenesis of the entire metanephros. This review emphasizes emerging insights into the role for the RAS in UB morphogenesis and explores the mechanisms whereby RAS regulates this important process. A conceptual framework derived from recent work indicates that cooperation between the angiotensin II AT1 receptor and receptor tyrosine kinase signaling performs essential functions during renal collecting system development via control of UB branching morphogenesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yosypiv IV (2004) Hypothesis: a novel role for the renin-angiotensin system in ureteric bud branching. Organogenesis 1:26–32
Rossetti S, Harris PC (2007) Genotype-phenotype correlations in autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:1374–1380
Nagata M, Tanimoto K, Fukamizu A, Kon Y, Sugiyama F, Yagami K, Murakami K, Watanabe T (1996) Nephrogenesis and renovascular development in angiotensinogen-deficient mice. Lab Invest 75:745–753
Niimura F, Labosky PA, Kakuchi J, Okubo S, Yoshida H, Oikawa T, Ichiki T, Naftilan AJ, Fogo A, Inagami T (1995) Gene targeting in mice reveals a requirement for angiotensin in the development and maintenance of kidney morphology and growth factor regulation. J Clin Invest 96:2947–2954
Takahashi N, Lopez ML, Cowhig JE Jr, Taylor MA, Hatada T, Riggs E, Lee G, Gomez RA, Kim HS, Smithies O (2005) Ren1c homozygous null mice are hypotensive and polyuric, but heterozygotes are indistinguishable from wild-type. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:125–132
Esther CR Jr, Howard TE, Marino EM, Goddard JM, Capecchi MR, Bernstein KE (1996) Mice lacking angiotensin-converting enzyme have low blood pressure, renal pathology, and reduced male fertility. Lab Invest 7:953–965
Oliverio MI, Kim HS, Ito M, Le T, Audoly L, Best CF, Hiller S, Kluckman K, Maeda N, Smithies O, Coffman TM (1998) Reduced growth, abnormal kidney structure, and type 2 (AT2) angiotensin receptor-mediated blood pressure regulation in mice lacking both AT1A and AT1B receptors for angiotensin II. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:15496–15501
Tsuchida S, Matsusaka T, Chen X, Okubo S, Niimura F, Nishimura H, Fogo A, Utsunomiya H, Inagami T, Ichikawa I (1998) Murine double nullizygotes of the angiotensin type 1A and 1B receptor genes duplicate severe abnormal phenotypes of angiotensinogen nullizygotes. J Clin Invest 101:755–760
Miyazaki Y, Tsuchida S, Fogo A, Ichikawa I (1999) The renal lesions that develop in neonatal mice during angiotensin inhibition mimic obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int 55:1683–1695
Gribouval O, Gonzales M, Neuhaus T (2005) Mutations in genes in the renin-angiotensin system are associated with autosomal recessive renal tubular dysgenesis. Nat Genet 37:964–968
North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies (2006) Annual report. NAPRTCS, Boston
Saxen L (1987) Organogenesis of the kidney. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ekblom P (1989) Developmentally regulated conversion of mesenchyme to epithelium. FASEB J 3:2141–2150
Grobstein C (1953) Inductive epithelio-mesenchymal interaction in cultured organ rudiments of the mouse metanephros. Science 118:52–55
Batourina E, Choi C, Paragas N, Bello N, Hensle T, Costantini FD, Schuchardt A, Bacallao RL, Mendelsohn CL (2002) Distal ureter morphogenesis depends on epithelial cell remodeling mediated by vitamin A and Ret. Nat Genet 32:109–115
Batourina E, Tsai S, Lambert S, Sprenkle P, Viana R, Dutta S, Hensle T, Wang F, Niederreither K, McMahon AP, Carroll TJ, Mendelsohn CL (2005) Apoptosis induced by vitamin A signaling is crucial for connecting the ureters to the bladder. Nat Genet 37:1082–1089
Sakurai H, Nigam S (1998) In vitro branching tubulogenesis: implications for developmental and cystic disorders, nephron number, renal repair, and nephron engineering. Kidney Int 54:14–26
Brenner BM, Garcia DL, Anderson S (1988) Glomeruli and blood pressure. Less of one, more the other? Am J Hypertens 1:335–347
Lisle SJ, Lewis RM, Petry CJ, Ozanne SE, Hales CN, Forhead AJ (2003) Effect of maternal iron restriction during pregnancy on renal morphology in the adult rat offspring. Br J Nutr 90:33–39
Costantini F (2006) Renal branching morphogenesis: concepts, questions, and recent advances. Differentiation 74:402–421
Pachnis V, Mankoo B, Costantini F (1993) Expression of the c-ret proto-oncogene during mouse embryogenesis. Development 119:1005–1017
Brophy PD, Ostrom L, Lang KM, Dressler GR (2001) Regulation of ureteric bud outgrowth by Pax2-dependent activation of the glial derived neurotrophic factor gene. Development 128:4747–4756
Clarke JC, Patel SR, Raymond RM Jr, Andrew S, Robinson BG, Dressler GR, Brophy PD (2006) Regulation of c-Ret in the developing kidney is responsive to Pax2 gene dosage. Hum Mol Genet 15:3420–3428
Hatini A, Huh SO, Herzlinger D, Soares VC, Lai E (1996) Essential role of stromal mesenchyme in kidney morphogenesis revealed by targeted disruption of Winged Helix transcription factor BF-2. Genes Dev 10:1467–1478
Mendelsohn C, Batourina E, Fung S, Gilbert T, Dodd J (1999) Stromal cells mediate retinoid-dependent functions essential for renal development. Development 126:1139–1148
Carroll TJ, Park JS, Hayashi S, Majumdar A, McMahon AP (2005) Wnt9b plays a central role in the regulation of mesenchymal to epithelial transitions underlying organogenesis of the mammalian urogenital system. Dev Cell 9:283–292
Majumdar A, Vainio S, Kispert A, McMahon J, McMahon AP (2003) Wnt11 and Ret/Gdnf pathways cooperate in regulating ureteric branching during metanephric kidney development. Development 130:3175–3185
Basson MA, Watson-Johnson J, Shakya R, Akbulut S, Hyink D, Costantini FD, Wilson PD, Mason IJ, Licht JD (2006) Branching morphogenesis of the ureteric epithelium during kidney development is coordinated by the opposing functions of GDNF and Sprouty1. Dev Biol 299:466–477
Bridgewater D, Cox B, Cain J, Lau A, Athaide V, Gill PS, Kuure S, Sainio K, Rosenblum ND (2008) Canonical WNT/beta-catenin signaling is required for ureteric branching. Dev Biol 317:83–94
Schmidt-Ott KM, Chen X, Paragas N, Levinson RS, Mendelsohn CL, Barasch J (2006) c-kit delineates a distinct domain of progenitors in the developing kidney. Dev Biol 299:238–249
Gao X, Chen X, Taglienti M, Rumballe B, Little MH, Kreidberg JA (2005) Angioblast-mesenchyme induction of early kidney development is mediated by Wt1 and Vegfa. Development 132:5437–5449
Qiao J, Uzzo R, Obara-Ishihara T, Degenstein L, Fuchs E, Herzlinger D (1999) FGF-7 modulates ureteric bud growth and nephron number in the developing kidney. Development 126:547–554
Sakurai H, Barros EJ, Tsukamoto T, Barasch J, Nigam SK (1997) An in vitro tubulogenesis system using cell lines derived from the embryonic kidney shows dependence on multiple soluble growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6279–6284
Ohuchi H, Hori Y, Yamasaki M, Harada H, Sekine K, Kato S, Itoh N (2000) FGF10 acts as a major ligand for FGF receptor 2 IIIb in mouse multi-organ development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 277:643–649
Ritvos O, Tuuri T, Erämaa M, Sainio K, Hildén K, Saxén L, Gilbert SF (1995) Activin disrupts epithelial branching morphogenesis in developing glandular organs of the mouse. Mech Dev 50:229–245
Sakurai H, Tsukamoto T, Kjelsberg CA, Cantley LG, Nigam SK (1997) Department EGF receptor ligands are a large fraction of in vitro branching morphogens secreted by embryonic kidney. Am J Physiol 273:F463–F472
Qiao J, Bush KT, Steer DL, Stuart RO, Sakurai H, Wachsman W, Nigam SK (2001) Multiple fibroblast growth factors support growth of the ureteric bud but have different effects on branching morphogenesis. Mech Dev 109:123–135
Zhao H, Kegg H, Grady S, Truong HT, Robinson ML, Baum M, Bates CM (2004) Center role of fibroblast growth factor receptors 1 and 2 in the ureteric bud. Dev Biol 276:403–415
Zhang X, Ibrahimi OA, Olsen SK, Umemori H, Mohammadi M, Ornitz DM (2006) Department receptor specificity of the fibroblast growth factor family. The complete mammalian FGF family. J Biol Chem 281:15694–15700
Bernardini N, Bianchi F, Lupetti M, Dolfi A (1996) Immunohistochemical localization of the epidermal growth factor, transforming growth factor alpha, and their receptor in the human mesonephros and metanephros. Dev Dyn 206:231–238
Sakurai H, Tsukamoto T, Kjelsberg CA, Cantley LG, Nigam SK (1997) EGF receptor ligands are a large fraction of in vitro branching morphogens secreted by embryonic kidney. Am J Physiol 273:F463–F472
Threadgill DW, Dlugosz AA, Hansen LA, Tennenbaum T, Lichti U, Yee D, LaMantia C, Mourton T, Herrup K, Harris RC (1995) Targeted disruption of mouse EGF receptor: effect of genetic background on mutant phenotype. Science 269:230–234
Maeshima A, Vaughn DA, Choi Y, Nigam SK (2006) Activin A is an endogenous inhibitor of ureteric bud outgrowth from the Wolffian duct. Dev Biol 295:473–485
Cain JE, Hartwig S, Bertram JF, Rosenblum ND (2008) Bone morphogenetic protein signaling in the developing kidney: present and future. Differentiation 76:831–842
Bush KT, Sakurai H, Steer DL, Leonard MO, Sampogna RV, Meyer TN, Schwesinger C, Qiao J, Nigam SK (2004) TGF-beta superfamily members modulate growth, branching, shaping, and patterning of the ureteric bud. Dev Biol 266:285–298
Piscione TD, Yager TD, Gupta IR, Grinfeld B, Pei Y, Attisano L, Wrana JL, Rosenblum ND (1997) BMP-2 and OP-1 exert direct and opposite effects on renal branching morphogenesis. Am J Physiol 273:F961–F975
Miyazaki Y, Oshima K, Fogo A, Ichikawa I (2000) Bone morphogenetic protein 4 regulates the budding site and elongation of the mouse ureter. J Clin Invest 105:863–873
Cain JE, Nion T, Jeulin D, Bertram JF (2005) BMP-4 amplifies asymmetric ureteric branching in the developing mouse kidney in vitro. Kidney Int 67:420–431
Hartwig S, Bridgewater D, Di Giovanni V, Cain J, Mishina Y, Rosenblum ND (2008) BMP receptor ALK3 controls collecting system development. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:117–124
Wolf G, Thaiss F, Schoeppe W, Stahl RA (1992) Angiotensin II-induced proliferation of cultured murine mesangial cells: inhibitory role of atrial natriuretic peptide. J Am Soc Nephrol 3:1270–1278
Goto M, Mukoyama M, Suga S, Matsumoto T, Nakagawa M, Ishibashi R, Kasahara M, Sugawara A, Tanaka I, Nakao K (1997) Growth-dependent induction of angiotensin II type 2 receptor in rat mesangial cells. Hypertension 30:358–362
Santos RA, Simoes e Silva AC, Maric C, Silva DM, Machado RP, de Buhr I, Heringer-Walther S, Pinheiro SV, Lopes MT, Bader M, Mendes EP, Lemos VS, Campagnole-Santos MJ, Schultheiss HP, Speth R, Walther T (2003) Angiotensin-(1–7) is an endogenous ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor Mas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8258–8263
Santos RA, Ferreira AJ (2007) Angiotensin-(1–7) and the renin-angiotensin system. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 16:122–128
Miyazaki Y, Tsuchida S, Nishimura H, Pope JC 4th, Harris RC, McKanna JM, Inagami T, Hogan BL, Fogo A, Ichikawa I (1998) Angiotensin induces the urinary peristaltic machinery during the perinatal period. J Clin Invest 102:1489–1497
Schaefer C (2003) Angiotensin II-receptor-antagonists: further evidence of fetotoxicity but not teratogenicity. Birth Defects Res Part A Clin Mol Teratol 67:591–594
Tabacova S, Little R, Tsong Y, Vega A, Kimmel CA (2003) Adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with maternal enalapril antihypertensive treatment. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 12:633–646
Nishimura H, Yerkes E, Hohenfellner K, Miyazaki Y, Ma J, Hunley TE, Yoshida H, Ichiki T, Threadgill D, Phillips JA 3rd, Hogan BM, Fogo A, Brock JW 3rd, Inagami T, Ichikawa I (1999) Role of the angiotensin type 2 receptor gene in congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract, CAKUT, of mice and men. Mol Cell 3:1–10
Oshima K, Miyazaki Y, Brock JW, Adams MC, Ichikawa I, Pope JC (2001) Angiotensin type II receptor expression and ureteral budding. J Urol 166:1848–1852
Zhang H, Wada J, Hida K, Tsuchiyama Y, Hiragushi K, Shikata K, Wang H, Lin S, Kanwar YS, Makino H (2001) Collectrin, a collecting duct-specific transmembrane glycoprotein, is a novel homolog of ACE2 and is developmentally regulated in embryonic kidneys. J Biol Chem 276:17132–17139
Lacoste M, Cai Y, Guicharnaud L, Mounier F, Dumez Y, Bouvier R, Dijoud F, Gonzales M, Chatten J, Delezoide AL, Daniel L, Joubert M, Laurent N, Aziza J, Sellami T, Amar HB, Jarnet C, Frances AM, Daïkha-Dahmane F, Coulomb A, Neuhaus TJ, Foliguet B, Chenal P, Marcorelles P, Gasc JM, Corvol P, Gubler MC (2006) Renal tubular dysgenesis, a not uncommon autosomal recessive disorder leading to oligohydramnios: role of the renin-angiotensin system. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2253–2263
Iosipiv IV, Schroeder M (2003) A role for angiotensin II AT1 receptors in ureteric bud cell branching. Am J Physiol 285:F199–F207
Lopez ML, Pentz ES, Robert B, Abrahamson DR, Gomez RA (2001) Embryonic origin and lineage of juxtaglomerular cells. Am J Physiol 281:F345–F356
Yosypiv IV, Schroeder M, El-Dahr SS (2006) AT1R-EGFR crosstalk regulates ureteric bud branching morphogenesis. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1005–1014
Zhang SL, Moini B, Ingelfinger JR (2004) Angiotensin II increases Pax-2 expression in fetal kidney cells via the AT2 receptor. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:1452–1465
Nilsson AB, Nitescu N, Chen Y, Guron GS, Marcussen N, Matejka GL, Friberg P (2000) IGF-I treatment attenuates renal abnormalities induced by neonatal ACE inhibition. Am J Physiol 279:R1050–R1060
Stirling D, Magness RR, Stone R, Waterman MR, Simpson ER (1990) Angiotensin II inhibits luteinizing hormone-stimulated cholesterol side chain cleavage expression and stimulates basic fibroblast growth factor expression in bovine luteal cells in primary culture. J Biol Chem 265:5–8
Yosypiv IV, Boh MK, Spera M, El-Dahr SS (2008) Downregulation of Spry-1, an inhibitor of GDNF/Ret, as a mechanism for angiotensin II-induced ureteric bud branching. Kidney Int doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2008.378
Tang MJ, Cai Y, Tsai SJ, Wang YK, Dressler GR (2002) Ureteric bud outgrowth in response to RET activation is mediated by phosphatidylinositol3-kinase. Dev Biol 243:128–136
Kim D, Dressler GR (2007) PTEN modulates GDNF/RET mediated chemotaxis and branching morphogenesis in the developing kidney. Dev Biol 307:290–299
Berry C, Touyz R, Dominiczak AF, Webb RC, Johns DG (2001) Angiotensin receptors: signaling,vascular pathophysiology, and interactions with ceramide. Am J Physiol 281:H2337–H2365
Watanabe G, Lee RJ, Albanese C, Rainey WE, Batle D, Pestell RG (1996) Angiotensin II activation of cyclin D1-dependent kinase activity. J Biol Chem 271:22570–22577
Prenzel N, Zwick E, Daub H, Leserer M, Abraham R, Wallasch C, Ullrich A (1999) EGF receptor transactivation by G-protein-coupled receptors requires metalloproteinase cleavage of proHB-EGF. Nature 402:884–888
Ushio-Fukai M, Hilenski L, Santanam N, Becker PL, Ma Y, Griendling KK, Alexander RW (2001) Cholesterol depletion inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation by angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells: role of cholesterol-rich microdomains and focal adhesions in angiotensin II signaling. J Biol Chem 276:48269–48275
Olivares-Reyes JA, Shah BH, Hernandez-Aranda J, Garcia-Gaballero A, Farshori MP, Gatcia-Sainz JA, Catt KJ (2005) Agonist-induced interactions between angiotensin AT1 and epidermal growth factor receptors. Mol Pharmacol 68:356–364
Stoll M, Steckelings UM, Paul M, Bottari SP, Metzger R, Unger T (1995) The angiotensin AT2-receptor mediates inhibition of cell proliferation in coronary endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 95:651–657
AbdAlla S, Lother H, Abdel-tawab AM, Quitterer U (2001) The angiotensin II AT2 receptor is an AT1 receptor antagonist. J Biol Chem 276:39721–39726
Garcia-Villalba P, Denkers ND, Wittwer CT, Wittwer CT, Hoff C, Nelson RD, Mauch TJ (2003) Real-time PCR quantification of AT1 and AT2 angiotensin receptor mRNA expression in the developing rat kidney. Nephron. Exp Nephrol 94:e154–e159
Yosypiv IV (2004) A new role for the renin–angiotensin system in ureteric bud branching. Organogenesis 1:26–32
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank colleagues who have contributed in various ways to our studies in this area, particularly Mercedes Schroeder, Mary Kate Boh, Melissa Spera, Renfang Song, and Samir El-Dahr. The original work was supported by NIH Grants P20 RR17659 and DK071699-01 (Ihor Yosypiv).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yosypiv, I.V. Renin–angiotensin system–growth factor cross-talk: a novel mechanism for ureteric bud morphogenesis. Pediatr Nephrol 24, 1113–1120 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-1021-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-1021-9