Abstract
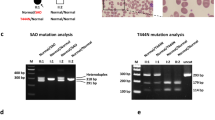
Mutations of the AE1 (SLC4A1, Anion-Exchanger 1) gene that codes for band 3, the renal and red cell anion exchanger, are responsible for many cases of familial distal renal tubular acidosis (dRTA). In Southeast Asia this disease is usually recessive, caused either by homozygosity of a single AE1 mutation or by compound heterozygosity of two different AE1 mutations. We describe two unrelated boys in Sarawak with dRTA associated with compound heterozygosity of AE1 mutations. Both had Southeast Asian ovalocytosis (SAO), a morphological abnormality of red cells caused by a deletion of band 3 residues 400–408. In addition, one boy had a DNA sequence abnormality of band 3 residue (G701D), which has been reported from elsewhere in Southeast Asia. The other boy had the novel sequence abnormality of band 3 (Q759H) and profound hemolytic anemia.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruce LJ, Cope DL, Jones GK, Schofield AE, Burley M, Povey S, Unwin RJ, Wrong O, Tanner MJA (1997) Familial renal tubular acidosis is associated with mutations in the red cell anion exchanger (band 3, AE1) gene. J Clin Invest 100:1693–1707
Wrong O, Bruce LJ, Unwin RJ, Toye AM, Tanner MJA (2002) Band 3 mutations, distal renal tubular acidosis, and Southeast Asian ovalocytosis. Kidney Int 62:10–19
Karet FE, Finberg KE, Nelson RD, Nayir A, Mocan H, Sanjad SA, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Santos F, Cremers CWRJ, Di Pietro A, Hoffbrand BI, Winiarski J, Bakkaloglu A, Ozen S, Dusunsel R, Goodyer P, Hulton SA, Wu DK, Skvorak AB, Morton CC, Cunningham MJ, Jha V, Lifton RP (1999) Mutations in the gene encoding B1 subunit of H+-ATPase cause renal tubular acidosis with sensorineural deafness. Nat Genet 21:84–90
Smith AN, Skaug J, Choate KA, Nayir A, Bakkaloglu A, Ozen S, Hulton SA, Sanjad SA, Al-Sabban EA, Lifton RP, Scherer SW, Karet FE (2000) Mutations in ATP6N1B, encoding a new kidney vacuolar proton pump 116-kD subunit, cause recessive distal renal tubular acidosis with preserved hearing. Nat Genet 26:71–75
Nurse GT, Coetzer TL, Palek J (1992) The elliptocytoses, ovalocytosis and related disorders. Baillieres Clin Haematol 5:187–207
Vasuvattakul S, Yenchitsomanus P, Vachuanichsanong P, Thuwajit P, Kaitwatcharachai C, Laosombat V, Malasit P, Wilairat P, Nimmannit S (1999) Autosomal recessive distal renal tubular acidosis associated with Southeast Asian ovalocytosis. Kidney Int 56:1674–1682
Bruce LJ, Wrong O, Toye AM, Young MT, Ogle G, Ismail Z, Sinha AK, McMaster P, Hwaihwanje I, Nash GB, Hart S, Lavu E, Palmer R, Othman A, Unwin RJ, Tanner MJA (2000) Band 3 mutations, renal tubular acidosis and Southeast Asian ovalocytosis in Malaysia and Papua New Guinea: loss of up to 95% band 3 transport in red cells. Biochem J 350:41–51
Tanphaichitr VS, Sumboonnanonda A, Ideguchi H, Shayakul C, Brugnara C, Takao M, Veerakul G, Alper SL (1998) Novel AE1 mutations in recessive distal renal tubular acidosis. Loss of function is rescued by glycophorin A. J Clin Invest 102:2173–2179
Schofield AE, Martin PG, Spillet D, Tanner MJA (1994) The structure of the human red blood cell anion exchanger (EPB3, AE1, band 3) gene. Blood 84:2000–2012
Miraglia del Giudice E, Vallier A, Maillet P, Perrotta S, Cutillo S, Iolascon A, Tanner MJA, Delaunay J, Alloisio N (1997) Novel band 3 variants (bands 3 Foggia, Napoli I and Napoli II) associated with hereditary spherocytosis and band 3 deficiency: status of the D38A polymorphism within the EPB3 locus. Brit J Haematol 96:70–76
Tanner MJA (1997) The structure and function of band 3 (AE1): recent developments. Mol Membr Biol 14:156–165
Popov M, Tam LY, Li J, Reithmeier RA (1997) Mapping the ends of transmembrane segments in a polytopic membrane protein. Scanning N-glycosylation mutagenesis of extracytosolic loops in the anion exchanger, band 3. J Biol Chem 272:18325–18332
McSherry E, Morris RC (1978) Attainment and maintenance of normal stature with alkali therapy in infants and children with classic renal tubular acidosis. J Clin Invest 61:509–527
Alper SL (2002) Genetic diseases of acid-base transporters. Annu Rev Physiol 64:899–923
Allen SJ, O’Donnell A, Alexander ND, Mgone CS, Peto TE, Clegg JB, Alpers MP, Weatherall DJ (1999) Prevention of cerebral malaria in children in Papua New Guinea by southeast Asian ovalocytosis band 3. Am J Trop Med Hyg 60:1056–1060
Yenchitsomanus P, Vasuvattakul S, Kirdpon S, Wasanawatana S, Susaengrat W, Sreethiphayawan S, Chuawatana D, Mingkum S, Sawasdee N, Thuwajit P, Wilairat P, Malasit P, Nimmannit S (2002) Autosomal recessive distal renal tubular acidosis caused by G701D mutation of anion exchanger 1 gene. Am J Kidney Dis 40:21–29
Anacleto FE, Benzon DE, Cutiongco EC, Nicoli TP, Linares AR, Wrong OM (2004) Anion-exchanger-one (AE1) mutations among Filipino children with distal renal tubular acidosis. Pediatric Nephrol, 19:C183
Sritippayawan S, Sumboonnanonda A, Vasuvattakul S, Keskanokwong T, Sawasdee N, Paemanee A, Thuwajit P, Wilairat P, Nimmannit S, Malasit P, Yenchitsomanus P (2004) Novel compound heterozygous SLC4A1 mutations in Thai patients with autosomal recessive distal renal tubular acidosis. Am J Kidney Dis 44:64–70
Yenchitsomanus PT, Sawadee N, Paemanee A, Keskanokwong T, Vasuvattakul S, Bejrachandra S, Kunachiwa W, Fucharoen J, Jittphakdee P, Yindee W, Promwong C (2003) Anion exchanger 1 mutations associated with distal renal tubular acidosis in the Thai population. J Hum Genet 48:451–456
Bellwood P (1997) Prehistory of the Indo-Malaysian Archipelago, revised edn. University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Association of Physicians of Great Britain and Ireland, the St Peter’s Trust, and the Wellcome Trust for financial assistance with this work, and to Professors Susan Povey and RJ Unwin for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choo, K.E., Nicoli, T.K., Bruce, L.J. et al. Recessive distal renal tubular acidosis in Sarawak caused by AE1 mutations. Pediatr Nephrol 21, 212–217 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-2061-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-2061-z